 | –≠–ª–µ–∫—Ç—Ä–æ–Ω–Ω—ã–π –∫–æ–º–ø–æ–Ω–µ–Ω—Ç: HLMP-3365 | –°–∫–∞—á–∞—Ç—å:  PDF PDF  ZIP ZIP |

1-101
H
T-1
3
/
4
(5 mm) Low Profile
LED Lamps
Technical Data
Features
∑ High Intensity
∑ Low Profile: 5.8 mm
(0.23 in.) Nominal
∑ T-1
3
/
4
Diameter Package
∑ Diffused and Non-diffused
Types
∑ General Purpose Leads
∑ IC Compatible/Low Current
Requirements
∑ Reliable and Rugged
Description
The HLMP-335X/-336X Series are
Gallium Arsenide Phosphide on
Gallium Phosphide High
Efficiency Red Light Emitting
Diodes.
The HLMP-345X/-346X Series are
Gallium Arsenide Phosphide on
Gallium Phosphide Yellow Light
Emitting Diodes.
The HLMP-355X/-356X Series are
Gallium Phosphide Green Light
Emitting Diodes.
The Low Profile T-1
3
/
4
package
provides space savings and is
excellent for backlighting
applications.
Package Dimensions
HLMP-335X Series
HLMP-336X Series
HLMP-345X Series
HLMP-346X Series
HLMP-355X Series
HLMP-356X Series
5.34 (0.210)
4.83 (0.190)
5964-9295E
1-102
Selection Guide
Part
Minimum
Number
Intensity @
HLMP-
Application
10 mA (mcd)
Lens
3350
Indicator ≠ General Purpose
2.1
Tinted Diffused Wide Angle
3351
Indicator ≠ High Brightness
5.4
HER
3365
General Purpose Point Source
8.6
Tinted Non-diffused Narrow Angle
3366
Indicator ≠ High Brightness
13.8
HER
3450
Indicator ≠ General Purpose
2.2
Tinted Diffused Wide Angle
3451
Indicator ≠ High Brightness
5.7
Yellow
3465
General Purpose Point Source
5.7
Tinted Non-diffused Narrow Angle
3466
Indicator ≠ High Brightness
9.2
Yellow
3553
Indicator ≠ General Purpose
1.6
Tinted Diffused Wide Angle
3554
Indicator ≠ High Brightness
6.7
Green
3567
General Purpose Point Source
4.2
Tinted Non-diffused Narrow Angle
3568
Indicator ≠ High Brightness
10.6
Green
1-103
Electrical Specifications at T
A
= 25
∞
C
Device
Test
Symbol
Description
HLMP-
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Units
Conditions
I
V
Axial Luminous Intensity
3350
2.1
3.5
mcd
I
F
= 10 mA
3351
5.4
7.0
(Figure 8)
3365
8.6
10.0
3366
13.8
18.0
2
1
/
2
Including Angle Between Half
3350
50
Deg.
Note 1 (Figure 11)
Luminous Intensity Points
3351
50
3365
45
3366
45
PEAK
Peak Wavelength
635
nm
Measurement at
Peak (Figure 1)
d
Dominant Wavelength
626
nm
Note 2
1/2
Spectral Line Halfwidth
40
nm
s
Speed of Response
90
ns
C
Capacitance
11
pF
V
F
= 0; f = 1 MHz
R
J-PIN
Thermal Resistance
260
∞
C/W
Junction to
Cathode Lead
V
F
Forward Voltage
1.9
2.4
V
I
F
= 10 mA
(Figure 7)
V
R
Reverse Breakdown Voltage
5.0
V
I
R
= 100
µ
A
V
Luminous Efficacy
145
lm/W
Note 3
High Efficiency Red HLMP-335X/-336X Series
Notes:
1.
1
/
2
is the off-axis angle at which the luminous intensity is half the axial luminous intensity.
2. Dominant wavelength,
d
, is derived from the CIE chromaticity diagram and represents the single wavelength which defines the color
of the device.
3. Radiant Intensity, I
e
, in watts/steradian may be found from the equation I
e
= I
v
/
v
, where I
v
is the luminous intensity in candelas and
v
is the luminous efficacy in lumens/watt.
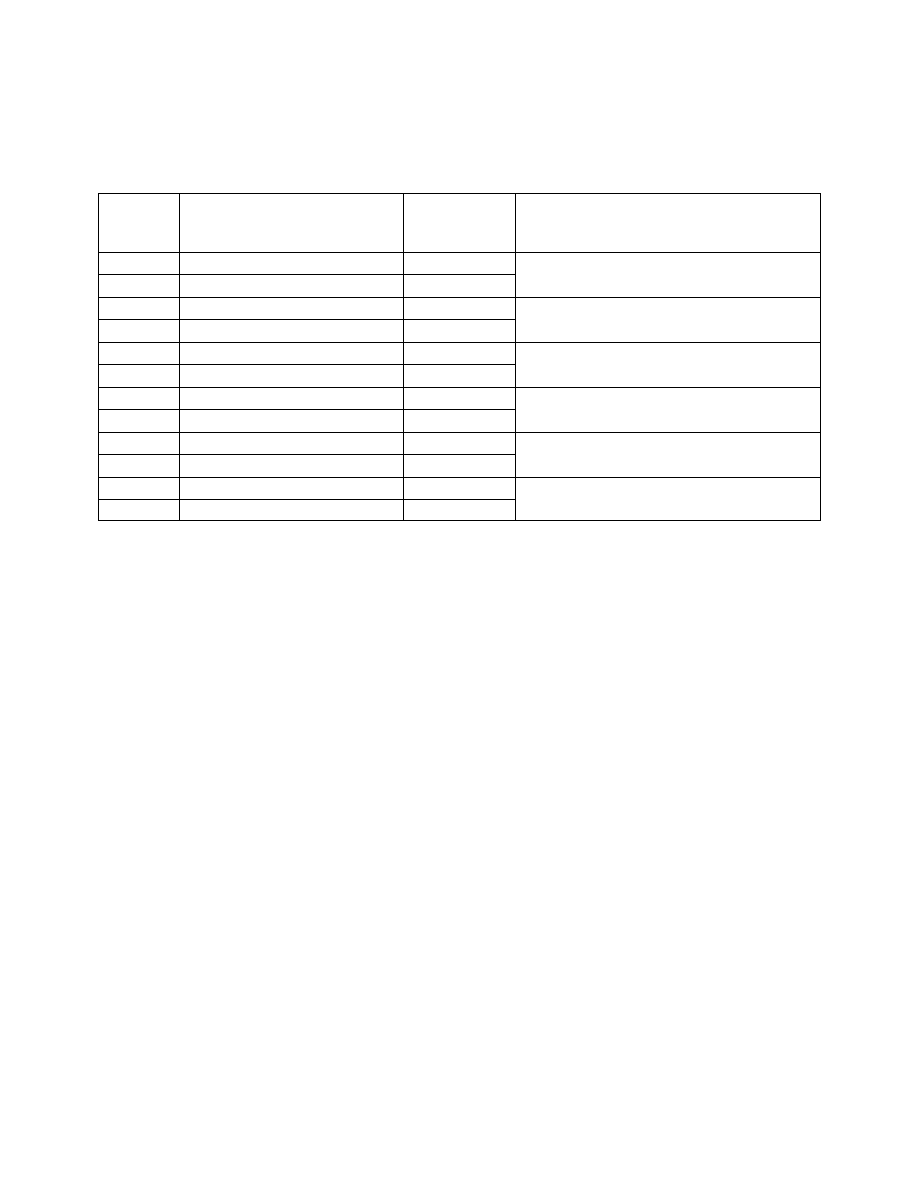
Figure 8. Relative Luminous Intensity
vs. Forward Current.
Figure 7. Forward Current vs.
Forward Voltage.
Figure 9. Relative Efficiency
(Luminous Intensity per Unit Current)
vs. Peak Current.

1-104
Figure 10. Maximum Tolerable Peak
Current vs. Pulse Duration. (I
DC
MAX
as per MAX Ratings).
Figure 11. Relative Luminous Intensity vs. Angular
Displacement.
Electrical Specifications at T
A
= 25
∞
C
Device
Test
Symbol
Description
HLMP-
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Units
Conditions
I
V
Axial Luminous Intensity
3450
2.2
4.0
mcd
I
F
= 10 mA
3451
5.7
10.0
(Figure 13)
3465
5.7
12.0
3466
9.2
18.0
2
1/2
Including Angle Between Half
3450
50
Deg.
Note 1 (Figure 16)
Luminous Intensity Points
3451
50
3465
45
3466
45
PEAK
Peak Wavelength
583
nm
Measurement at
Peak (Figure 1)
d
Dominant Wavelength
585
nm
Note 2
1/2
Spectral Line Halfwidth
36
nm
s
Speed of Response
90
ns
C
Capacitance
15
pF
V
F
= 0; f = 1 MHz
R
J-PIN
Thermal Resistance
260
∞
C/W
Junction to
Cathode Lead
V
F
Forward Voltage
2.0
2.4
V
I
F
= 10 mA
(Figure 12)
V
R
Reverse Breakdown Voltage
5.0
V
I
R
= 100
µ
A
V
Luminous Efficacy
500
lm/W
Note 3
Yellow HLMP-345X/-346X Series
Notes:
1.
1
/
2
is the off-axis angle at which the luminous intensity is half the axial luminous intensity.
2. Dominant wavelength,
d
, is derived from the CIE chromaticity diagram and represents the single wavelength which defines the color
of the device.
3. Radiant Intensity, I
e
, in watts/steradian may be found from the equation I
e
= I
v
/
v
, where I
v
is the luminous intensity in candelas and
v
is the luminous efficacy in lumens/watt.
1-105
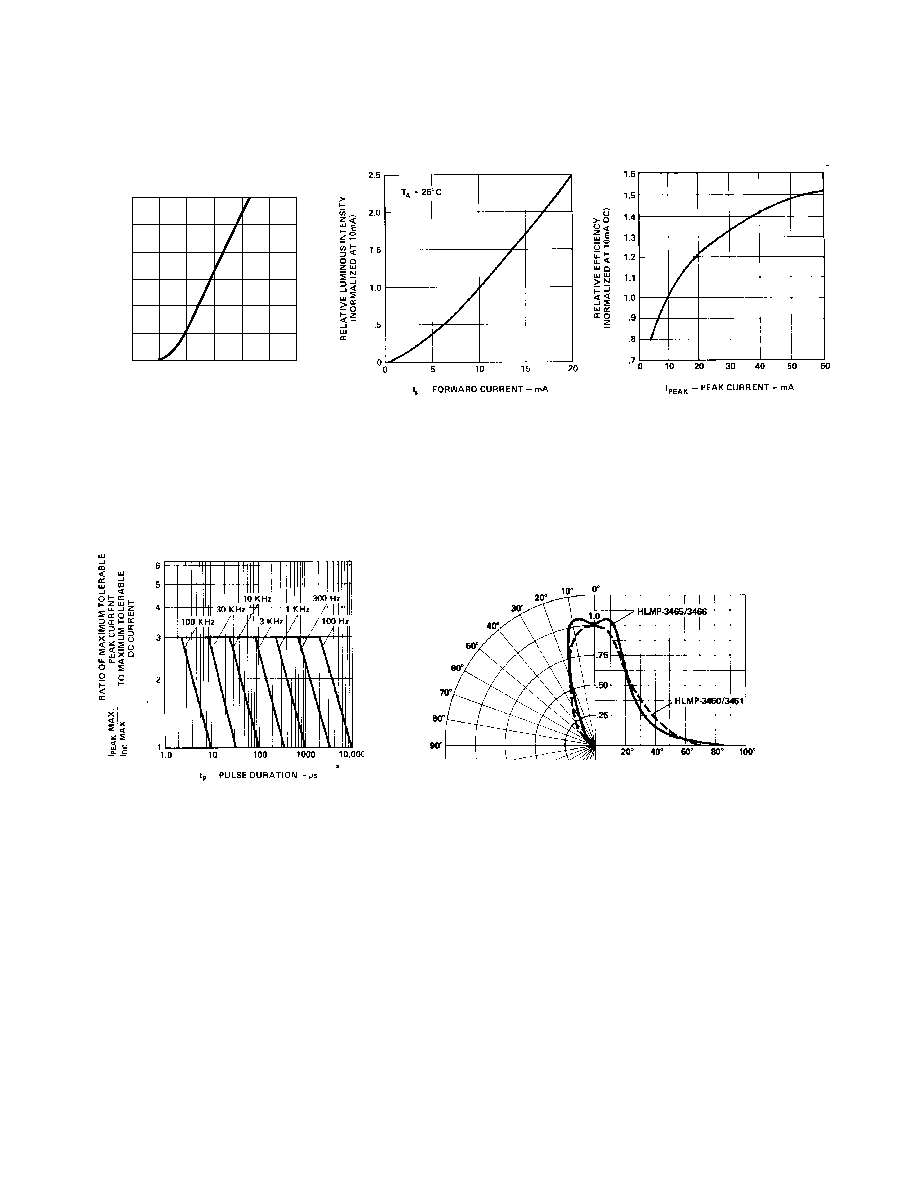
Figure 15. Maximum Tolerable Peak
Current vs. Pulse Duration. (I
DC
MAX
as per MAX Ratings).
Figure 16. Relative Luminous Intensity vs. Angular Displacement.
Figure 13. Relative Luminous
Intensity vs. Forward Current.
Figure 14. Relative Efficiency
(Luminous Intensity per Unit Current)
vs. Peak Current.
Figure 12. Forward Current vs.
Forward Voltage.
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
3.5
4.0
V ≠ FORWARD VOLTAGE ≠ V
F
I ≠ FORWARD CURRENT ≠ mA
F




