 | –≠–ª–µ–∫—Ç—Ä–æ–Ω–Ω—ã–π –∫–æ–º–ø–æ–Ω–µ–Ω—Ç: HLMP-D101 | –°–∫–∞—á–∞—Ç—å:  PDF PDF  ZIP ZIP |
Agilent
T-1
3
/
4
(5 mm), T-1 (3 mm),
High Intensity, Double Heterojunction
AlGaAs Red LED Lamps
Data Sheet
HLMP-D101/D105, HLMP-K101/K105
Description
These solid state LED lamps utilize
newly developed double
heterojunction (DH) AlGaAs/GaAs
material technology. This LED
material has outstanding light
output efficiency over a wide range
Features
∑ Exceptional brightness
∑ Wide viewing angle
∑ Outstanding material efficiency
∑ Low forward voltage
∑ CMOS/MOS compatible
∑ TTL compatible
∑ Deep red color
Applications
∑ Bright ambient lighting conditions
∑ Moving message panels
∑ Portable equipment
∑ General use
of drive currents. The color is
deep red at the dominant
wavelength of 637 nanometres.
These lamps may be DC or pulse
driven to achieve desired light
output.
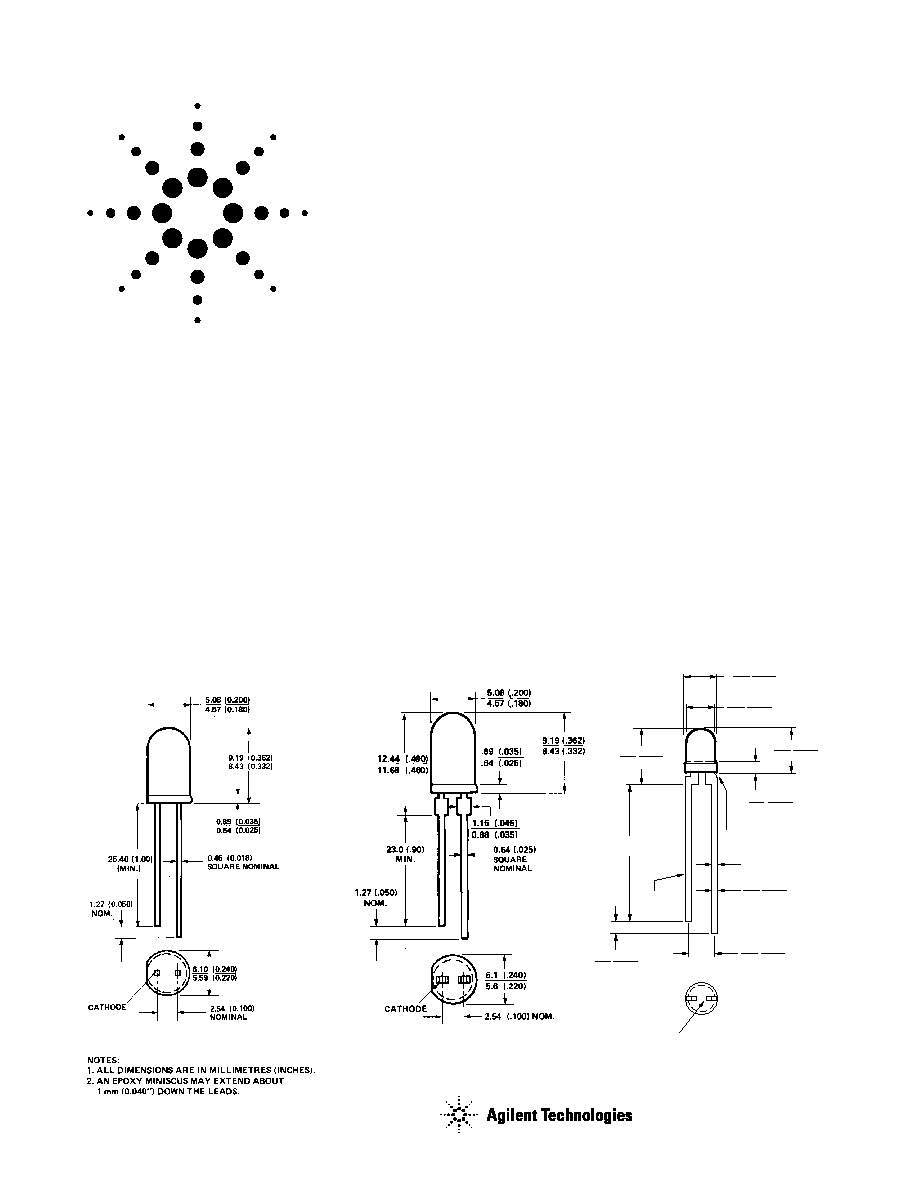
Package Dimensions
A
B
C
1.14 (0.045)
0.51 (0.020)
3.43 (0.135)
2.92 (0.115)
24.1
(0.95)
MIN.
4.70 (0.185)
4.19 (0.165)
3.17 (0.125)
2.67 (0.105)
2.79 (0.110)
2.29 (0.090)
1.52 (0.060)
1.02 (0.040)
6.35 (0.250)
5.58 (0.220)
0.55 (0.022)
0.40 (0.016)
CATHODE
0.65 (0.026) MAX.
SQ. TYP.
SHOULDER
CATHODE

2
Selection Guide
Luminous Intensity
Iv (mcd) at 20 mA
2
1/2
[1]
Package
Package Description
Device HLMP-
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Degree
Outline
T-1 3/4 Red Tinted Diffused
D101
35.2
70.0
≠
65
A
D101-J00xx
35.2
70.0
≠
65
A
D101-JK0xx
35.2
70.0
112.8
65
A
T-1 3/4 Red Untinted Non-diffused
D105
138.0
240.0
≠
24
B
D105-M00xx
138.0
240.0
≠
24
B
D105-NO0xx
200.0
290.0
580.0
24
B
T-1 Red Tinted Diffused
K101
22.0
45.0
≠
60
C
K101-100xx
22.0
45.0
≠
60
C
K101-IJ0xx
22.0
45.0
70.4
60
C
T-1 Red Untinted Non-diffused
K105
35.2
65.0
≠
45
C
K105-J00xx
35.2
65.0
≠
45
C
K105-KL0xx
56.4
110.0
180.4
45
C
Note:
1.
1/2
is the off axis angle from lamp centerline where the luminous intensity is
1
/
2
the on-axis value.
Part Numbering System
HLMP - x x xx - x x x xx
Mechanical Option
00: Bulk
01: Tape & Reel, Crimped Leads
02: Tape & Reel, Straight Leads
A1: Right Angle Housing, Uneven Leads, T1
A2: Right Angle Housing, Even Leads, T1
B1: Right Angle Housing, Uneven Leads, T-1 3/4
B2: Right Angle Housing, Even Leads, T-1 3/4
DD, UQ: Ammo Pack
Color Bin Options
0: Full Color Bin Distribution
Maximum Iv Bin Options
0: Open (no max. limit)
Others: Please refer to the Iv Bin Table
Minimum Iv Bin Options
Please refer to the Iv Bin Table
Lens Type
01: Tinted, Diffused
05: Untinted, Nondiffused
Color Options
1: AlGaAs Red
Package Options
D: T-1 3/4
K: T-1

3
Absolute Maximum Ratings at T
A
= 25
∞
C
Parameter
Value
Peak Forward Current
[1,2]
300 mA
Average Forward Current
[2]
20 mA
DC Current
[3]
30 mA
Power Dissipation
87 mW
Reverse Voltage (I
R
= 100
µ
A)
5 V
Transient Forward Current (10
µ
s Pulse)
[4]
500 mA
LED Junction Temperature
110
∞
C
Operating Temperature Range
-20 to +100
∞
C
Storage Temperature Range
-55 to +100
∞
C
Wave Soldering Temperature [1.59 mm (0.063 in.) from body]
250
∞
C for 3 seconds
Lead Solder Dipping Temperature [1.59 mm (0.063 in.) from body]
260
∞
C for 5 seconds
Notes:
1. Maximum I
PEAK
at f = 1 kHz, DF = 6.7%.
2. Refer to Figure 6 to establish pulsed operating conditions.
3. Derate linearly as shown in Figure 5.
4. The transient peak current is the maximum non-recurring peak current the device can withstand without damaging the LED die and wire bonds. It is
not recommended that the device be operated at peak currents beyond the Absolute Maximum Peak Forward Current.
Electrical/Optical Characteristics at T
A
= 25
∞
C
Symbol
Description
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
Test Condition
V
F
Forward Voltage
1.8
2.2
V
I
F
= 20 mA
V
R
Reverse Breakdown Voltage
5.0
15.0
V
I
R
= 100
µ
A
p
Peak Wavelength
645
nm
Measurement at Peak
d
Dominant Wavelength
637
nm
Note 1
1
/
2
Spectral Line Halfwidth
20
nm
S
Speed of Response
30
ns
Exponential Time
Constant, e
-t
/T
S
C
Capacitance
30
pF
V
F
= 0, f = 1 MHz
R
J-PIN
Thermal Resistance
260
[3]
∞
C/W
Junction to Cathode Lead
210
[4]
290
[5]
V
Luminous Efficacy
80
Im/W
Note 2
Notes:
1. The dominant wavelength,
d
, is derived from the CIE chromaticity diagram and represents the color of the device.
2. The radiant intensity, I
e
, in watts per steradian, may be found from the equation I
e
= l
V
/
V
, where I
V
is the luminous intensity in candelas and
V
is
luminous efficacy in lumens/watt.
3. HLMP-D101.
4. HLMP-D105.
5. HLMP-K101/-K105.

4
Figure 3. Relative luminous intensity vs. dc forward current.
Figure 4. Relative efficiency vs. peak forward current.
Figure 5. Maximum forward dc current vs. ambient temperature.
Derating based on T
J
MAX. = 110
∞
C.
Figure 6. Maximum tolerable peak current vs. peak duration (I
PEAK
MAX. determined from temperature derated I
DC
MAX.).
Figure 1. Relative intensity vs. wavelength.
Figure 2. Forward current vs. forward voltage.

5
Figure 7. Relative luminous intensity vs. angular displacement.
HLMP-D101.
Figure 8. Relative luminous intensity vs. angular displacement.
HLMP-K101.
Figure 9. Relative luminous intensity vs. angular displacement.
HLMP-D105.
Figure 10. Relative luminous intensity vs. angular displacement.
HLMP-K105.




