 | –≠–ª–µ–∫—Ç—Ä–æ–Ω–Ω—ã–π –∫–æ–º–ø–æ–Ω–µ–Ω—Ç: OPA627 | –°–∫–∞—á–∞—Ç—å:  PDF PDF  ZIP ZIP |
FEATURES
q
VERY LOW NOISE: 4.5nV/
Hz at 10kHz
q
FAST SETTLING TIME:
OPA627--550ns to 0.01%
OPA637--450ns to 0.01%
q
LOW V
OS
: 100
µ
V max
q
LOW DRIFT: 0.8
µ
V/
∞
C max
q
LOW I
B
: 5pA max
q
OPA627: Unity-Gain Stable
q
OPA637: Stable in Gain
5
OPA627
OPA637
DESCRIPTION
The OPA627 and OPA637
Difet
operational amplifi-
ers provide a new level of performance in a precision
FET op amp. When compared to the popular OPA111
op amp, the OPA627/637 has lower noise, lower offset
voltage, and much higher speed. It is useful in a broad
range of precision and high speed analog circuitry.
The OPA627/637 is fabricated on a high-speed, dielec-
trically-isolated complementary NPN/PNP process. It
operates over a wide range of power supply voltage--
±
4.5V to
±
18V. Laser-trimmed
Difet
input circuitry
provides high accuracy and low-noise performance
comparable with the best bipolar-input op amps.
High frequency complementary transistors allow in-
creased circuit bandwidth, attaining dynamic perform-
ance not possible with previous precision FET op
amps. The OPA627 is unity-gain stable. The OPA637
is stable in gains equal to or greater than five.
Difet
fabrication achieves extremely low input bias
currents without compromising input voltage noise
performance. Low input bias current is maintained
over a wide input common-mode voltage range with
unique cascode circuitry.
The OPA627/637 is available in plastic DIP, SOIC
and metal TO-99 packages. Industrial and military
temperature range models are available.
Difet
Æ
, Burr-Brown Corp.
Æ
Precision High-Speed
Difet
Æ
OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIERS
APPLICATIONS
q
PRECISION INSTRUMENTATION
q
FAST DATA ACQUISITION
q
DAC OUTPUT AMPLIFIER
q
OPTOELECTRONICS
q
SONAR, ULTRASOUND
q
HIGH-IMPEDANCE SENSOR AMPS
q
HIGH-PERFORMANCE AUDIO CIRCUITRY
q
ACTIVE FILTERS
Trim
5
Trim
1
+In
3
≠In
2
Output
6
7
+V
S
≠V
S
4
©1989 Burr-Brown Corporation
PDS-998H
Printed in U.S.A. March, 1998
International Airport Industrial Park ∑ Mailing Address: PO Box 11400, Tucson, AZ 85734 ∑ Street Address: 6730 S. Tucson Blvd., Tucson, AZ 85706 ∑ Tel: (520) 746-1111 ∑ Twx: 910-952-1111
Internet: http://www.burr-brown.com/ ∑ FAXLine: (800) 548-6133 (US/Canada Only) ∑ Cable: BBRCORP ∑ Telex: 066-6491 ∑ FAX: (520) 889-1510 ∑ Immediate Product Info: (800) 548-6132
OPA627
OPA627

2
Æ
OPA627, 637
SPECIFICATIONS
ELECTRICAL
At T
A
= +25
∞
C, and V
S
=
±
15V, unless otherwise noted.
OPA627BM, BP, SM
OPA627AM, AP, AU
OPA637BM, BP, SM
OPA637AM, AP, AU
PARAMETER
CONDITIONS
MIN
TYP
MAX
MIN
TYP
MAX
UNITS
OFFSET VOLTAGE
(1)
Input Offset Voltage
40
100
130
250
µ
V
AP, BP, AU Grades
100
250
280
500
µ
V
Average Drift
0.4
0.8
1.2
2
µ
V/
∞
C
AP, BP, AU Grades
0.8
2
2.5
µ
V/
∞
C
Power Supply Rejection
V
S
=
±
4.5 to
±
18V
106
120
100
116
dB
INPUT BIAS CURRENT
(2)
Input Bias Current
V
CM
= 0V
1
5
2
10
pA
Over Specified Temperature
V
CM
= 0V
1
2
nA
SM Grade
V
CM
= 0V
50
nA
Over Common-Mode Voltage
V
CM
=
±
10V
1
2
pA
Input Offset Current
V
CM
= 0V
0.5
5
1
10
pA
Over Specified Temperature
V
CM
= 0V
1
2
nA
SM Grade
50
nA
NOISE
Input Voltage Noise
Noise Density: f = 10Hz
15
40
20
nV/
Hz
f = 100Hz
8
20
10
nV/
Hz
f = 1kHz
5.2
8
5.6
nV/
Hz
f = 10kHz
4.5
6
4.8
nV/
Hz
Voltage Noise, BW = 0.1Hz to 10Hz
0.6
1.6
0.8
µ
Vp-p
Input Bias Current Noise
Noise Density, f = 100Hz
1.6
2.5
2.5
fA/
Hz
Current Noise, BW = 0.1Hz to 10Hz
30
60
48
fAp-p
INPUT IMPEDANCE
Differential
10
13
|| 8
*
|| pF
Common-Mode
10
13
|| 7
*
|| pF
INPUT VOLTAGE RANGE
Common-Mode Input Range
±
11
±
11.5
*
*
V
Over Specified Temperature
±
10.5
±
11
*
*
V
Common-Mode Rejection
V
CM
=
±
10.5V
106
116
100
110
dB
OPEN-LOOP GAIN
Open-Loop Voltage Gain
V
O
=
±
10V, R
L
= 1k
112
120
106
116
dB
Over Specified Temperature
V
O
=
±
10V, R
L
= 1k
106
117
100
110
dB
SM Grade
V
O
=
±
10V, R
L
= 1k
100
114
dB
FREQUENCY RESPONSE
Slew Rate: OPA627
G = ≠1, 10V Step
40
55
*
*
V/
µ
s
OPA637
G = ≠4, 10V Step
100
135
*
*
V/
µ
s
Settling Time: OPA627 0.01%
G = ≠1, 10V Step
550
*
ns
0.1%
G = ≠1, 10V Step
450
*
ns
OPA637 0.01%
G = ≠4, 10V Step
450
*
ns
0.1%
G = ≠4, 10V Step
300
*
ns
Gain-Bandwidth Product: OPA627
G = 1
16
*
MHz
OPA637
G = 10
80
*
MHz
Total Harmonic Distortion + Noise
G = +1, f = 1kHz
0.00003
*
%
POWER SUPPLY
Specified Operating Voltage
±
15
*
V
Operating Voltage Range
±
4.5
±
18
*
*
V
Current
±
7
±
7.5
*
*
mA
OUTPUT
Voltage Output
R
L
= 1k
±
11.5
±
12.3
*
*
Over Specified Temperature
±
11
±
11.5
*
*
V
Current Output
V
O
=
±
10V
±
45
*
mA
Short-Circuit Current
±
35
+70/≠55
±
100
*
*
*
mA
Output Impedance, Open-Loop
1MHz
55
*
TEMPERATURE RANGE
Specification: AP, BP, AM, BM, AU
≠25
+85
*
*
∞
C
SM
≠55
+125
∞
C
Storage: AM, BM, SM
≠60
+150
*
*
∞
C
AP, BP, AU
≠40
+125
*
*
∞
C
J-A
: AM, BM, SM
200
*
∞
C/W
AP, BP
100
*
∞
C/W
AU
160
∞
C/W
* Specifications same as "B" grade.
NOTES: (1) Offset voltage measured fully warmed-up. (2) High-speed test at T
J
= +25
∞
C. See Typical Performance Curves for warmed-up performance.
The information provided herein is believed to be reliable; however, BURR-BROWN assumes no responsibility for inaccuracies or omissions. BURR-BROWN assumes
no responsibility for the use of this information, and all use of such information shall be entirely at the user's own risk. Prices and specifications are subject to change
without notice. No patent rights or licenses to any of the circuits described herein are implied or granted to any third party. BURR-BROWN does not authorize or warrant
any BURR-BROWN product for use in life support devices and/or systems.
3
Æ
OPA627, 637
PIN CONFIGURATIONS
DIP/SOIC
Top View
Offset Trim
≠In
+In
≠V
No Internal Connection
+V
Output
Offset Trim
S
S
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
Top View
TO-99
Offset Trim
≠In
Output
Offset Trim
+In
≠V
S
+V
S
No Internal Connection
Case connected to ≠V
S
.
8
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
(1)
Supply Voltage ..................................................................................
±
18V
Input Voltage Range .............................................. +V
S
+ 2V to ≠V
S
≠ 2V
Differential Input Range ....................................................... Total V
S
+ 4V
Power Dissipation ........................................................................ 1000mW
Operating Temperature
M Package .................................................................. ≠55
∞
C to +125
∞
C
P, U Package ............................................................. ≠40
∞
C to +125
∞
C
Storage Temperature
M Package .................................................................. ≠65
∞
C to +150
∞
C
P, U Package ............................................................. ≠40
∞
C to +125
∞
C
Junction Temperature
M Package .................................................................................. +175
∞
C
P, U Package ............................................................................. +150
∞
C
Lead Temperature (soldering, 10s) ............................................... +300
∞
C
SOlC (soldering, 3s) ................................................................... +260
∞
C
NOTE: (1) Stresses above these ratings may cause permanent damage.
ELECTROSTATIC
DISCHARGE SENSITIVITY
This integrated circuit can be damaged by ESD. Burr-Brown
recommends that all integrated circuits be handled with
appropriate precautions. Failure to observe proper handling
and installation procedures can cause damage.
ESD damage can range from subtle performance degrada-
tion to complete device failure. Precision integrated circuits
may be more susceptible to damage because very small
parametric changes could cause the device not to meet its
published specifications.
PACKAGE/ORDERING INFORMATION
PACKAGE DRAWING
TEMPERATURE
PRODUCT
PACKAGE
NUMBER
(1)
RANGE
OPA627AP
Plastic DIP
006
≠25
∞
C to +85
∞
C
OPA627BP
Plastic DIP
006
≠25
∞
C to +85
∞
C
OPA627AU
SOIC
182
≠25
∞
C to +85
∞
C
OPA627AM
TO-99 Metal
001
≠25
∞
C to +85
∞
C
OPA627BM
TO-99 Metal
001
≠25
∞
C to +85
∞
C
OPA627SM
TO-99 Metal
001
≠55
∞
C to +125
∞
C
OPA637AP
Plastic DIP
006
≠25
∞
C to +85
∞
C
OPA637BP
Plastic DIP
006
≠25
∞
C to +85
∞
C
OPA637AU
SOIC
182
≠25
∞
C to +85
∞
C
OPA637AM
TO-99 Metal
001
≠25
∞
C to +85
∞
C
OPA637BM
TO-99 Metal
001
≠25
∞
C to +85
∞
C
OPA637SM
TO-99 Metal
001
≠55
∞
C to +125
∞
C
NOTE: (1) For detailed drawing and dimension table, please see end of data
sheet, or Appendix C of Burr-Brown IC Data Book.
4
Æ
OPA627, 637
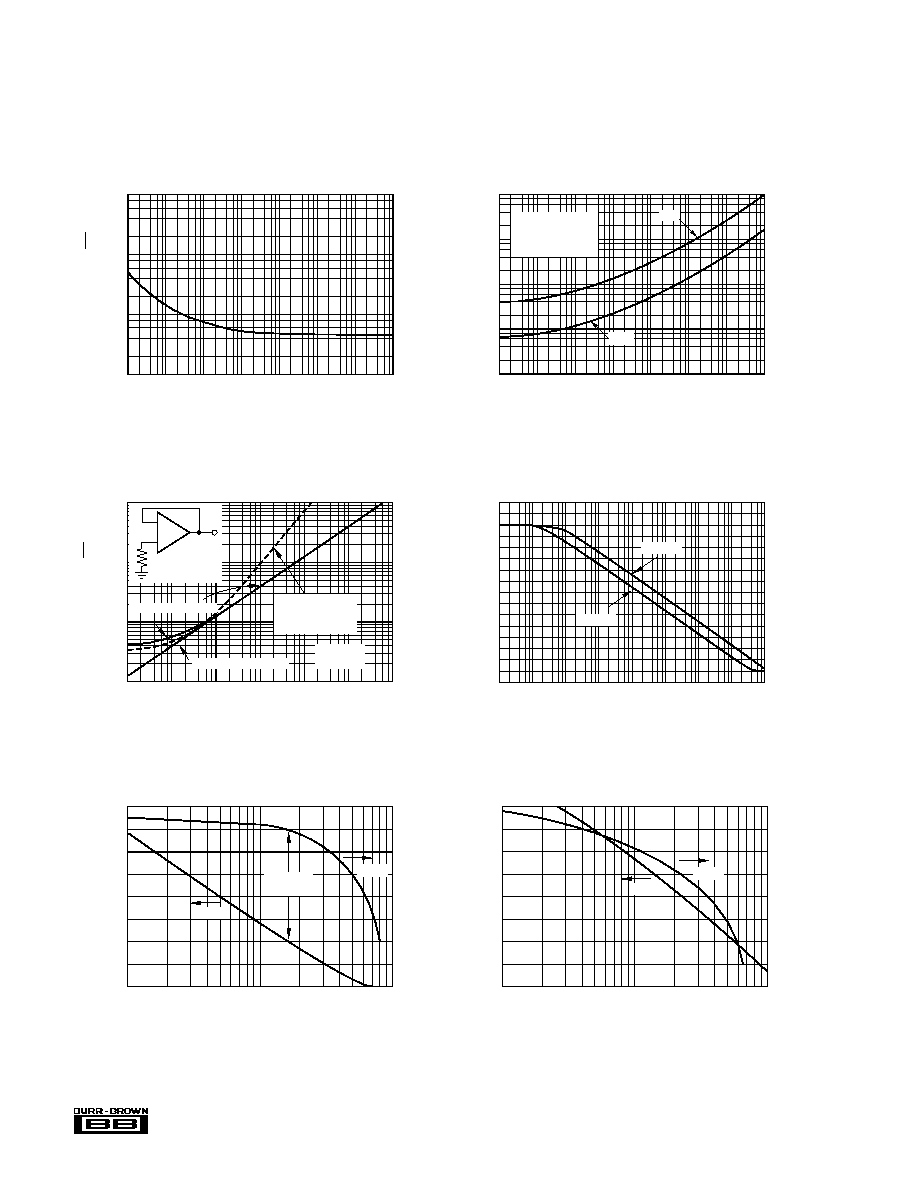
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CURVES
At T
A
= +25
∞
C, and V
S
=
±
15V, unless otherwise noted.
INPUT VOLTAGE NOISE SPECTRAL DENSITY
1k
100
10
1
1
Frequency (Hz)
Voltage Noise (nV/ Hz)
10
100
1k
10k
100k
1M
10M
VOLTAGE NOISE vs SOURCE RESISTANCE
Source Resistance ( )
1k
100
10
1
100
OPA627 + Resistor
Resistor Noise Only
Spot Noise
at 10kHz
Voltage Noise (nV/ Hz)
1k
10k
100k
1M
10M 100M
Comparison with
OPA27 Bipolar Op
Amp + Resistor
≠
+
R
S
OPA627 GAIN/PHASE vs FREQUENCY
Phase (Degrees)
Gain (dB)
30
20
10
0
≠10
≠90
≠120
≠150
≠180
≠210
1
Phase
Gain
Frequency (MHz)
10
100
75∞ Phase
Margin
OPA637 GAIN/PHASE vs FREQUENCY
Phase (Degrees)
Gain (dB)
30
20
10
0
≠10
≠90
≠120
≠150
≠180
≠210
1 10 100
Phase
Gain
Frequency (MHz)
TOTAL INPUT VOLTAGE NOISE vs BANDWIDTH
100
10
1
0.1
0.01
1
10
100
1k
10k
100k
1M
10M
Bandwidth (Hz)
Input Voltage Noise (µV)
Noise Bandwidth:
0.1Hz to indicated
frequency.
RMS
p-p
OPEN-LOOP GAIN vs FREQUENCY
Frequency (Hz)
Voltage Gain (dB)
1 10 100 1k 10k 100k 1M 10M 100M
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
≠20
OPA637
OPA627

5
Æ
OPA627, 637
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CURVES
(CONT)
At T
A
= +25
∞
C, and V
S
=
±
15V, unless otherwise noted.
OPEN-LOOP GAIN vs TEMPERATURE
Voltage Gain (dB)
Temperature (∞C)
125
120
115
110
105
≠75 ≠50 ≠25 0 25 50 75 100 125
OPEN-LOOP OUTPUT IMPEDANCE vs FREQUENCY
Frequency (Hz)
Output Resistance (
)
100
80
60
40
20
0
2 20 200 2k 20k 200k 2M 20M
COMMON-MODE REJECTION vs FREQUENCY
Frequency (Hz)
Common-Mode Rejection Ratio (dB)
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
1 10 100 1k 10k 100k 1M 10M
OPA627
OPA637
COMMON-MODE REJECTION vs
INPUT COMMON MODE VOLTAGE
130
120
110
100
90
80
Common-Mode Rejection (dB)
Common-Mode Voltage (V)
≠15
≠10
≠5
0
5
10
15
POWER-SUPPLY REJECTION vs FREQUENCY
Frequency (Hz)
Power-Supply Rejection (dB)
140
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
1
≠V
S
PSRR 627
and 637
+V
S
PSRR 627
637
10
100
1k
10k
100k
1M
10M
POWER-SUPPLY REJECTION AND COMMON-MODE
REJECTION vs TEMPERATURE
Temperature (∞C)
CMR and PSR (dB)
125
120
115
110
105
≠75
PSR
CMR
≠50
≠25
0
25
50
75
100
125

6
Æ
OPA627, 637
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CURVES
(CONT)
At T
A
= +25
∞
C, and V
S
=
±
15V, unless otherwise noted.
SUPPLY CURRENT vs TEMPERATURE
Temperature (∞C)
Supply Current (mA)
8
7.5
7
6.5
6
≠75 ≠50 ≠25 0 25 50 75 100 125
OUTPUT CURRENT LIMIT vs TEMPERATURE
Output Current (mA)
100
80
60
40
20
0
≠75 ≠50 ≠25 0 25 50 75 100 125
Temperature (∞C)
≠I
L
at V
O
= ≠10V
≠I
L
at V
O
= 0V
+I
L
at V
O
= +10V
+I
L
at V
O
= 0V
OPA627 GAIN-BANDWIDTH AND SLEW RATE
vs TEMPERATURE
Temperature (∞C)
Gain-Bandwidth (MHz)
24
20
16
12
8
≠75
Slew Rate
GBW
60
55
50
Slew Rate (V/µs)
≠50
≠25
0
25
50
75
100
125
OPA637 GAIN-BANDWIDTH AND SLEW RATE
vs TEMPERATURE
Temperature (∞C)
Gain-Bandwidth (MHz)
120
100
80
60
40
≠75
Slew Rate (V/µs)
160
140
120
100
80
Slew Rate
GBW
≠50
≠25
0
25
50
75
100
125
OPA627 TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION + NOISE
vs FREQUENCY
Frequency (Hz)
THD+N (%)
20 100 1k 10k 20k
0.1
0.01
0.001
0.0001
0.00001
G = +10
G = +1
Measurement BW: 80kHz
≠
+
≠
+
100pF
100pF
G = +1
G = +10
V
I
V
I
549
5k
600
600
V = ±10V
O
V = ±10V
O
OPA637 TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION + NOISE
vs FREQUENCY
Frequency (Hz)
THD+N (%)
20 100 1k 10k 20k
1
0.1
0.01
0.001
0.0001
G = +10
G = +50
≠
+
100pF
G = +10
V
I
549
5k
600
V = ±10V
O
≠
+
100pF
G = +50
V
I
102
5k
600
V = ±10V
O
Measurement BW: 80kHz

7
Æ
OPA627, 637
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CURVES
(CONT)
At T
A
= +25
∞
C, and V
S
=
±
15V, unless otherwise noted.
INPUT BIAS AND OFFSET CURRENT
vs JUNCTION TEMPERATURE
Junction Temperature (∞C)
Input Current (pA)
10k
1k
100
10
1
0.1
≠50 ≠25 0 25 50 75 100 125 150
I
B
I
OS
INPUT BIAS CURRENT
vs POWER SUPPLY VOLTAGE
Supply Voltage (±V
S
)
Input Bias Current (pA)
20
15
10
5
0
±4 ±6 ±8 ±10 ±12 ±14 ±16 ±18
NOTE: Measured fully
warmed-up.
TO-99 with 0807HS Heat Sink
TO-99
Plastic
DIP, SOIC
INPUT BIAS CURRENT vs COMMON-MODE VOLTAGE
Common-Mode Voltage (V)
Input Bias Current Multiplier
1.2
1.1
1
0.9
0.8
≠15 ≠10 ≠5 0 5 10 15
Beyond Linear
Common-Mode Range
Beyond Linear
Common-Mode Range
INPUT OFFSET VOLTAGE WARM-UP vs TIME
Time From Power Turn-On (Min)
Offset Voltage Change (µV)
50
25
0
≠25
≠50
0 1 2 3 4 5 6
MAX OUTPUT VOLTAGE vs FREQUENCY
Frequency (Hz)
Output Voltage (Vp-p)
30
20
10
0
100k 1M 10M 100M
OPA627
OPA637
SETTLING TIME vs CLOSED-LOOP GAIN
100
10
1
0.1
≠1
≠10
≠100
≠1000
Closed-Loop Gain (V/V)
Settling Time (µs)
Error Band: ±0.01%
OPA637
OPA627

8
Æ
OPA627, 637
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CURVES
(CONT)
At T
A
= +25
∞
C, and V
S
=
±
15V, unless otherwise noted.
FIGURE 1. Circuits with Noise Gain Less than Five Require
the OPA627 for Proper Stability.
SETTLING TIME vs ERROR BAND
1500
1000
500
0
0.001
0.01
0.1
1
10
Error Band (%)
Settling Time (ns)
OPA637
G = ≠4
OPA627
G = ≠1
≠
+
C
F
R
I
R
F
2k
+5V
≠5V
OPA627 OPA637
R
I
2k
500
R
F
2k
2k
C
F
6pF 4pF
SETTLING TIME vs LOAD CAPACITANCE
0
150
200
300
400
500
Load Capacitance (pF)
3
2
1
0
Settling Time (µs)
Error Band:
±0.01%
OPA637
G = ≠4
OPA627
G = ≠1
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
The OPA627 is unity-gain stable. The OPA637 may be used
to achieve higher speed and bandwidth in circuits with noise
gain greater than five. Noise gain refers to the closed-loop
gain of a circuit as if the non-inverting op amp input were
being driven. For example, the OPA637 may be used in a
non-inverting amplifier with gain greater than five, or an
inverting amplifier of gain greater than four.
When choosing between the OPA627 or OPA637, it is
important to consider the high frequency noise gain of your
circuit configuration. Circuits with a feedback capacitor
(Figure 1) place the op amp in unity noise-gain at high
frequency. These applications must use the OPA627 for
proper stability. An exception is the circuit in Figure 2,
where a small feedback capacitance is used to compensate
for the input capacitance at the op amp's inverting input. In
this case, the closed-loop noise gain remains constant with
frequency, so if the closed-loop gain is equal to five or
greater, the OPA637 may be used.
≠
+
≠
+
≠
+
≠
+
≠
+
≠
+
Buffer
Bandwidth
Limiting
Integrator
Filter
R
I
R
F
< 4R
Inverting Amp
G < |≠4|
R
I
R
F
< 4R
I
Non-Inverting Amp
G < 5
OPA627
OPA627
OPA627
OPA627
OPA627
OPA627

9
Æ
OPA627, 637
≠
+
C
2
C
1
R
2
R
1
OPA637
C
1
= C
IN
+ C
STRAY
C
2
=
R
1
C
1
R
2
OFFSET VOLTAGE ADJUSTMENT
The OPA627/637 is laser-trimmed for low offset voltage
and drift, so many circuits will not require external adjust-
ment. Figure 3 shows the optional connection of an external
potentiometer to adjust offset voltage. This adjustment should
not be used to compensate for offsets created elsewhere in a
system (such as in later amplification stages or in an A/D
converter) because this could introduce excessive tempera-
ture drift. Generally, the offset drift will change by approxi-
mately 4
µ
V/
∞
C for 1mV of change in the offset voltage due
to an offset adjustment (as shown on Figure 3).
FIGURE 2. Circuits with Noise Gain Equal to or Greater than
Five May Use the OPA637.
amp contributes little additional noise. Below 1k
, op amp
noise dominates over the resistor noise, but compares
favorably with precision bipolar op amps.
CIRCUIT LAYOUT
As with any high speed, wide bandwidth circuit, careful
layout will ensure best performance. Make short, direct
interconnections and avoid stray wiring capacitance--espe-
cially at the input pins and feedback circuitry.
The case (TO-99 metal package only) is internally connected
to the negative power supply as it is with most common op
amps. Pin 8 of the plastic DIP, SOIC, and TO-99 packages
has no internal connection.
Power supply connections should be bypassed with good
high frequency capacitors positioned close to the op amp
pins. In most cases 0.1
µ
F ceramic capacitors are adequate.
The OPA627/637 is capable of high output current (in
excess of 45mA). Applications with low impedance loads or
capacitive loads with fast transient signals demand large
currents from the power supplies. Larger bypass capacitors
such as 1
µ
F solid tantalum capacitors may improve dynamic
performance in these applications.
NOISE PERFORMANCE
Some bipolar op amps may provide lower voltage noise
performance, but both voltage noise and bias current noise
contribute to the total noise of a system. The OPA627/637
is unique in providing very low voltage noise and very low
current noise. This provides optimum noise performance
over a wide range of sources, including reactive source
impedances. This can be seen in the performance curve
showing the noise of a source resistor combined with the
noise of an OPA627. Above a 2k
source resistance, the op
FIGURE 4. Connection of Input Guard for Lowest I
B
.
Board Layout for Input Guarding:
Guard top and bottom of board.
Alternate--use Teflon
Æ
standoff for sen-
sitive input pins.
Teflon
Æ
E.I. du Pont de Nemours & Co.
≠
+
2
3
In
Non-inverting
6
OPA627
Out
≠
+
2
3
In
Inverting
6
OPA627
Out
≠
+
2
3
In
Buffer
6
OPA627
Out
3
2
4
5
6
7
8
No Internal Connection
1
TO-99 Bottom View
To Guard Drive
≠
+
2
3
7
1
5
6
+V
S
≠V
S
OPA627/637
100k
10k
to 1M
Potentiometer
(100k
preferred)
±10mV Typical
Trim Range
4
FIGURE 3. Optional Offset Voltage Trim Circuit.

10
Æ
OPA627, 637
takes approximately 500ns. When the output is driven into
the positive limit, recovery takes approximately 6
µ
s. Output
recovery of the OPA627 can be improved using the output
clamp circuit shown in Figure 5. Diodes at the inverting
input prevent degradation of input bias current.
INPUT BIAS CURRENT
Difet
fabrication of the OPA627/637 provides very low
input bias current. Since the gate current of a FET doubles
approximately every 10
∞
C, to achieve lowest input bias
current, the die temperature should be kept as low as pos-
sible. The high speed and therefore higher quiescent current
of the OPA627/637 can lead to higher chip temperature. A
simple press-on heat sink such as the Burr-Brown model
807HS (TO-99 metal package) can reduce chip temperature
by approximately 15
∞
C, lowering the I
B
to one-third its
warmed-up value. The 807HS heat sink can also reduce low-
frequency voltage noise caused by air currents and thermo-
electric effects. See the data sheet on the 807HS for details.
Temperature rise in the plastic DIP and SOIC packages can
be minimized by soldering the device to the circuit board.
Wide copper traces will also help dissipate heat.
The OPA627/637 may also be operated at reduced power
supply voltage to minimize power dissipation and tempera-
ture rise. Using
±
5V power supplies reduces power dissipa-
tion to one-third of that at
±
15V. This reduces the I
B
of TO-
99 metal package devices to approximately one-fourth the
value at
±
15V.
Leakage currents between printed circuit board traces can
easily exceed the input bias current of the OPA627/637. A
circuit board "guard" pattern (Figure 4) reduces leakage
effects. By surrounding critical high impedance input cir-
cuitry with a low impedance circuit connection at the same
potential, leakage current will flow harmlessly to the low-
impedance node. The case (TO-99 metal package only) is
internally connected to ≠V
S
.
Input bias current may also be degraded by improper han-
dling or cleaning. Contamination from handling parts and
circuit boards may be removed with cleaning solvents and
deionized water. Each rinsing operation should be followed
by a 30-minute bake at 85
∞
C.
Many FET-input op amps exhibit large changes in input
bias current with changes in input voltage. Input stage
cascode circuitry makes the input bias current of the
OPA627/637 virtually constant with wide common-mode
voltage changes. This is ideal for accurate high input-
impedance buffer applications.
PHASE-REVERSAL PROTECTION
The OPA627/637 has internal phase-reversal protection.
Many FET-input op amps exhibit a phase reversal when the
input is driven beyond its linear common-mode range. This
is most often encountered in non-inverting circuits when the
input is driven below ≠12V, causing the output to reverse
into the positive rail. The input circuitry of the OPA627/637
does not induce phase reversal with excessive common-
mode voltage, so the output limits into the appropriate rail.
OUTPUT OVERLOAD
When the inputs to the OPA627/637 are overdriven, the
output voltage of the OPA627/637 smoothly limits at ap-
proximately 2.5V from the positive and negative power
supplies. If driven to the negative swing limit, recovery
+V
S
5k
(2)
HP 5082-2811
1k
5k
≠V
S
V
O
Diode Bridge
BB: PWS740-3
ZD : 10V IN961
1
Clamps output
at V
O
= ±11.5V
R
I
V
I
≠
+
R
F
ZD
1
OPA627
FIGURE 5. Clamp Circuit for Improved Overload Recovery.
CAPACITIVE LOADS
As with any high-speed op amp, best dynamic performance
can be achieved by minimizing the capacitive load. Since a
load capacitance presents a decreasing impedance at higher
frequency, a load capacitance which is easily driven by a
slow op amp can cause a high-speed op amp to perform
poorly. See the typical curves showing settling times as a
function of capacitive load. The lower bandwidth of the
OPA627 makes it the better choice for driving large capaci-
tive loads. Figure 6 shows a circuit for driving very large
load capacitance. This circuit's two-pole response can also
be used to sharply limit system bandwidth. This is often
useful in reducing the noise of systems which do not require
the full bandwidth of the OPA627.
FIGURE 6. Driving Large Capacitive Loads.
R
1
≠
+
R
F
1k
OPA627
C
F
G = +1
BW 1MHz
200pF
For Approximate Butterworth Response:
C
F
=
2 R
O
C
L
R
F
R
F
>> R
O
G = 1+
R
F
R
1
Optional Gain
Gain > 1
f
≠3dB
=
1
2
R
F
R
O
C
F
C
L
C
L
5nF
R
O
20

11
Æ
OPA627, 637
INPUT PROTECTION
The inputs of the OPA627/637 are protected for voltages
between +V
S
+ 2V and ≠V
S
≠ 2V. If the input voltage can
exceed these limits, the amplifier should be protected. The
diode clamps shown in Figure 7a will prevent the input
voltage from exceeding one forward diode voltage drop
beyond the power supplies--well within the safe limits. If
the input source can deliver current in excess of the maxi-
mum forward current of the protection diodes, use a series
resistor, R
S
, to limit the current. Be aware that adding
resistance to the input will
increase noise. The 4nV/
Hz
theoretical thermal noise of a 1k
resistor will add to the
4.5nV/
Hz noise of the OPA627/637 (by the square-root of
the sum of the squares), producing a total noise of 6nV/
Hz.
Resistors below 100
add negligible noise.
Leakage current in the protection diodes can increase the
total input bias current of the circuit. The specified maxi-
mum leakage current for commonly used diodes such as the
1N4148 is approximately 25nA--more than a thousand
times larger than the input bias current of the OPA627/637.
Leakage current of these diodes is typically much lower and
may be adequate in many applications. Light falling on the
junction of the protection diodes can dramatically increase
leakage current, so common glass-packaged diodes should
be shielded from ambient light. Very low leakage can be
achieved by using a diode-connected FET as shown. The
2N4117A is specified at 1pA and its metal case shields the
junction from light.
Sometimes input protection is required on I/V converters of
inverting amplifiers (Figure 7b). Although in normal opera-
tion, the voltage at the summing junction will be near zero
(equal to the offset voltage of the amplifier), large input
transients may cause this node to exceed 2V beyond the
power supplies. In this case, the summing junction should
be protected with diode clamps connected to ground. Even
with the low voltage present at the summing junction,
common signal diodes may have excessive leakage current.
Since the reverse voltage on these diodes is clamped, a
diode-connected signal transistor can be used as an inexpen-
sive low leakage diode (Figure 7b).
FIGURE 7. Input Protection Circuits.
≠
+
≠V
S
+V
S
Optional R
S
V
O
D: IN4148 -- 25nA Leakage
2N4117A -- 1pA Leakage
(a)
=
≠
+
I
IN
V
O
D
D
D
(b)
D
D: 2N3904
=
NC
Siliconix
OPA627
OPA627
FPO
When used as a unity-gain buffer, large common-mode input voltage steps
produce transient variations in input-stage currents. This causes the rising
edge to be slower and falling edges to be faster than nominal slew rates
observed in higher-gain circuits.
(A)
(B)
SMALL SIGNAL RESPONSE
LARGE SIGNAL RESPONSE
FIGURE 8. OPA627 Dynamic Performance, G = +1.
≠
+
OPA627
G = 1

12
Æ
OPA627, 637
When driven with a very fast input step (left), common-mode
transients cause a slight variation in input stage currents which
will reduce output slew rate. If the input step slew rate is reduced
(right), output slew rate will increase slightly.
FIGURE 9. OPA627 Dynamic Performance, G = ≠1.
NOTE: (1) Optimum value will
depend on circuit board lay-
out and stray capacitance at
the inverting input.
LARGE SIGNAL RESPONSE
+10
0
≠10
V
OUT
(V)
+10
0
≠10
(C)
(D)
OPA637
LARGE SIGNAL RESPONSE
OPA637
SMALL SIGNAL RESPONSE
FPO
FIGURE 10. OPA637 Dynamic Response, G = 5.
≠10
0
+10
≠100
0
+100
(F)
(E)
V
OUT
(V)
≠
+
OPA627
G = ≠1
2k
2k
6pF
(1)
V
OUT
≠
+
OPA637
G = 5
2k
500
4pF
(1)
V
OUT
NOTE: (1) Optimum value will depend on circuit
board layout and capacitance at inverting input.
V
OUT
(V)
V
OUT
(mV)

13
Æ
OPA627, 637
OPA627
OPA637
R
I
, R
1
2k
500
C
F
6pF
4pF
Error Band
±
0.5mV
±
0.2mV
(0.01%)
NOTE: C
F
is selected for best settling time performance
depending on test fixture layout. Once optimum value is
determined, a fixed capacitor may be used.
FIGURE 12. High Speed Instrumentation Amplifier, Gain = 100.
≠In
+In
+
≠
OPA637
Differential Voltage Gain = 1 + 2R
F
/R
G
2
3
≠
+
≠
+
INA105
Differential
Amplifier
1
6
5
Output
Gain = 100
CMRR 116dB
Bandwidth 1MHz
OPA637
25k
25k
25k
25k
Input Common-Mode
Range = ±5V
3pF
R
F
5k
R
F
5k
R
G
101
≠
+
±5V
Out
+15V
2k
C
F
2k
Error Out
R
I
R
I
51
≠15V
HP-
5082-
2835
High Quality
Pulse Generator
/
FIGURE 11. Settling Time and Slew Rate Test Circuit.
FIGURE 14. Composite Amplifier for Wide Bandwidth.
This composite amplifier uses the OPA603 current-feedback op amp to
provide extended bandwidth and slew rate at high closed-loop gain. The
feedback loop is closed around the composite amp, preserving the
precision input characteristics of the OPA627/637. Use separate power
supply bypass capacitors for each op amp.
GAIN
A
1
R
1
R
2
R
3
R
4
≠3dB
SLEW RATE
(V/V)
OP AMP
(
)
(k
)
(
)
(k
)
(MHz)
(V/
µ
s)
100
OPA627
50.5
(1)
4.99
20
1
15
700
1000
OPA637
49.9
4.99
12
1
11
500
NOTE: (1) Closest 1/2% value.
*Minimize capacitance at this node.
FIGURE 13. High Speed Instrumentation Amplifier, Gain = 1000.
+
≠
OPA603
≠
+
A
1
R
3
R
1
R
4
R
2
V
I
V
O
*
R
L
150
for ±10V Out
≠In
+In
+
≠
OPA637
Differential Voltage Gain = (1 + 2R
F
/R
G
) ∑ 10
2
3
≠
+
≠
+
INA106
Differential
Amplifier
1
6
5
Output
Gain = 1000
CMRR 116dB
Bandwidth 400kHz
OPA637
10k
10k
100k
100k
Input Common-Mode
Range = ±10V
3pF
R
F
5k
R
F
5k
R
G
101












