One-PLL General Purpose
Flash-Programmable Clock Generator
CY22050
Cypress Semiconductor Corporation
∑
3901 North First Street
∑
San Jose
∑
CA 95134
∑
408-943-2600
Document #: 38-07006 Rev. *B
Revised December 14, 2002
Features
Benefits
∑ Integrated phase-locked loop (PLL)
Internal PLL to generate six outputs up to 200 MHz. Able to generate
custom frequencies from an external reference crystal or a driven source.
∑ Commercial and Industrial operation
Performance guaranteed for applications that require an extended temper-
ature range.
∑ Flash-programmable
Reprogrammable technology allows easy customization, quick turnaround
on design changes and product performance enhancements, and better
inventory control. Parts can be reprogrammed up to 100 times, reducing
inventory of custom parts and providing an easy method for upgrading
existing designs.
∑ Field-programmable
In-house programming of samples and prototype quantities is available
using the CY3672 FTG Development Kit. Production quantities are
available through Cypress's value-added distribution partners or by using
third party programmers from BP Microsystems, HiLo Systems, and
others.
∑ Low-skew, low-jitter, high-accuracy outputs
High performance suited for commercial, industrial, networking, telecomm
and other general-purpose applications.
∑ 3.3V operation with 2.5V output option
Application compatibility in standard and low-power systems.
∑ 16-lead TSSOP
Industry standard packaging saves on board space.
Part Number
Outputs
Input Frequency Range
Output Frequency Range
Specifications
CY22050FC
6
8 MHz ≠ 30 MHz (external crystal)
1 MHz ≠ 133 MHz (driven clock)
80 kHz ≠ 200 MHz (3.3V)
80 KHz ≠ 166.6 MHz (2.5V)
Field-programmable
commercial temperature
CY22050FI
6
8 MHz ≠ 30 MHz (external crystal)
1 MHz ≠ 133 MHz (driven clock)
80 kHz ≠166.6 MHz (3.3V)
80 KHz ≠ 150 MHz (2.5V)
Field-programmable
industrial temperature
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
VSS
VSSL
OE
LCLK1
XIN
XOUT
VDD
PWRDWN
AVSS
LCLK3
LCLK2
CLK6
CLK5
AVDD
VDDL
LCLK4
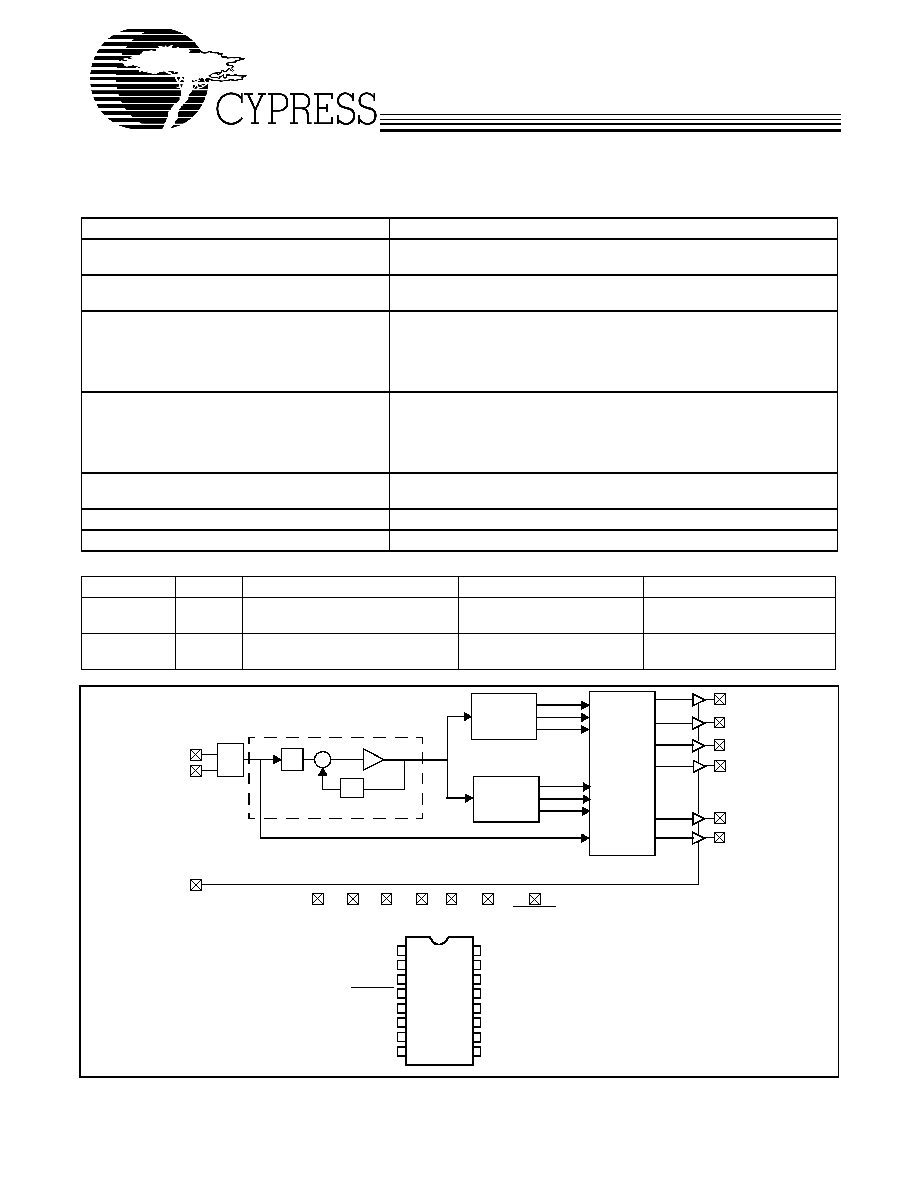
Pin Configuration
XIN
XOUT
Divider
PLL
OSC.
LCLK3
Q
P
VCO
VDDL
AVSS
AVDD
VSS
LCLK2
LCLK4
CLK5
CLK6
VSSL
VDD
Bank 1
Divider
Bank 2
Output
Select
OE
PWRDWN
LCLK1
Logic Block Diagram
Matrix

CY22050
Document #: 38-07006 Rev. *B
Page 2 of 8
Functional Description
The CY22050 is the next-generation programmable FTG
(frequency timing generator) for use in networking, telecom-
munication, datacom, and other general purpose applications.
The CY22050 offers up to six configurable outputs in a 16-pin
TSSOP, running off a 3.3V power supply. The on-chip
reference oscillator is designed to run off an 8 ≠ 30-MHz
crystal, or a 1 ≠ 133-MHz external clock signal.
The CY22050 has a single PLL driving 6 programmable output
clocks. The output clocks are derived from the PLL or the
reference frequency (REF). Output post dividers are available
for either. Four of the outputs can be set as 3.3V or 2.5V, for
use in a wide variety of portable and low-power applications.
Field Programming the CY22050F
The CY22050 is programmed at the package level, i.e. in a
programmer socket. The CY22050 is flash-technology based,
so the parts can be reprogrammed up to 100 times. This allows
for fast and easy design changes and product updates, and
eliminates any issues with old and out-of-date inventory.
Samples and small prototype quantities can be programmed
on the CY3672 programmer. Cypress's value-added distri-
bution partners and third-party programming systems from BP
Microsystems, HiLo Systems, and others are available for
large-production quantities.
CyClocksRT
Software
CyClocksRT is an easy-to-use software application that allows
the user to custom-configure the CY22050. Users can specify
the REF, PLL frequency, output frequencies and/or
post-dividers, and different functional options. CyClocksRT
outputs an industry standard JEDEC file used for
programming the CY22050.
CyClocksRT can be downloaded free of charge from the
Cypress website at http://www.cypress.com.
CY3672 FTG Development Kit
The Cypress CY3672 FTG Development Kit comes complete
with everything needed to design with the CY22050 and
program samples and small prototype quantities. The kit
comes with the latest version of CyClocksRT and a small
portable programmer that connects to a PC serial port for
on-the-fly programming of custom frequencies.
The JEDEC file output of CyClocksRT can be downloaded to
the portable programmer for small-volume programming, or
for use with a production programming system for larger
volumes.
Applications
Controlling Jitter
Jitter is defined in many ways, including: phase noise,
long-term jitter, cycle-to-cycle jitter, period jitter, absolute jitter,
and deterministic jitter. These jitter terms are usually given in
terms of rms, peak-to-peak, or in the case of phase noise
dBC/Hz with respect to the fundamental frequency. Actual jitter
is dependent on XIN jitter and edge rate, number of active
outputs, output frequencies, V
DDL
(2.5V or 3.3V), temperature,
and output load.
Power supply noise and clock output loading are two major
system sources of clock jitter. Power supply noise can be
mitigated by proper power supply decoupling (0.1
µ
F ceramic
cap) of the clock and ensuring a low-impedance ground to the
CY22050 Pin Summary
Name
Pin Number
Description
XIN
1
Reference Input. Driven by a crystal (8 MHz ≠ 30 MHz) or external clock (1 MHz ≠ 133
MHz). Programmable input load capacitors allow for maximum flexibility in selecting a
crystal, based on manufacturer, process, performance, or quality.
VDD
2
3.3V voltage supply
AVDD
3
3.3V analog voltage supply
PWRDWN
[1]
4
Power Down. When pin 4 is driven low, the CY22050 will go into shut-down mode.
AVSS
5
Analog ground
VSSL
6
LCLK ground
LCLK1
7
Configurable clock output 1 at V
DDL
level (3.3V or 2.5V)
LCLK2
8
Configurable clock output 2 at V
DDL
level (3.3V or 2.5V)
LCLK3
9
Configurable clock output 3 at V
DDL
level (3.3V or 2.5V)
OE
[1]
10
Output Enable. When pin 10 is driven LOW, all outputs are three-stated.
VDDL
11
LCLK voltage supply (2.5V or 3.3V)
LCLK4
12
Configurable clock output 4 at V
DDL
level (3.3V or 2.5V)
VSS
13
Ground
CLK5
14
Configurable clock output 5 (3.3V)
CLK6
15
Configurable clock output 6 (3.3V)
XOUT
[2]
16
Reference output
Notes:
1.
The CY22050 has no internal pull-up or pull-down resistors. PWRDWN and OE pins need to be driven as appropriate or tied to power or ground.
2.
Float XOUT if XIN is driven by an external clock source.

CY22050
Document #: 38-07006 Rev. *B
Page 3 of 8
chip. Reducing capacitive clock output loading to a minimum
lowers current spikes on the clock edges and thus reduces
jitter.
Reducing the total number of active outputs will also reduce
jitter in a linear fashion. However, it is better to use two outputs
to drive two loads than one output to drive two loads.
The rate and magnitude that the PLL corrects the VCO
frequency is directly related to jitter performance. If the rate is
too slow, then long term jitter and phase noise will be poor.
Therefore, to improve long-term jitter and phase noise,
reducing Q to a minimum is advisable. This technique will
increase the speed of the phase frequency detector, which in
turn drives the input voltage of the VCO. In a similar manner,
increasing P until the VCO is near its maximum rated speed
will also decrease long term jitter and phase noise. For
example: input reference of 12 MHz; desired output frequency
of 33.3 MHz. One might arrive at the following solution: Set
Q = 3, P = 25, Post Div = 3. However, the best jitter results will
be Q = 2, P = 50, Post Div = 9.
For additional information, refer to the application note, "Jitter
in PLL-based Systems: Causes, Effects, and Solutions,"
available at http://www.cypress.com/clock/appnotes.html, or
contact your local Cypress Field Applications Engineer.
CY22050 Frequency Calculation
The CY22050 is an extremely flexible clock generator with up
to six individual outputs, generated from an integrated PLL.
There are four variables used to determine the final output
frequency. They are: the input REF, the P and Q dividers, and
the post divider. The three basic formulas for determining the
final output frequency of a CY22150-based design are:
∑ CLK = ((REF * P)/Q)/Post Divider
∑ CLK = REF/Post Divider
∑ CLK = REF
The basic PLL block diagram is shown in Figure 1. Each of the
six clock outputs has a total of seven output options available
to it. There are six post divider options: /2 (two of these), /3, /4,
/DIV1N, and DIV2N. DIV1N and DIV2N are separately calcu-
lated and can be independent of each other. The post divider
options can be applied to the calculated PLL frequency or to
the REF directly.
In addition to the six post divider options, the seventh option
bypasses the PLL and passes the REF directly to the cross-
point switch matrix.
Clock Output Settings: Crosspoint Switch
Matrix
Each of the six clock outputs can come from any of seven
unique frequency sources. The crosspoint switch matrix
defines which source is attached to each individual clock
output. Although it may seem that there are an unlimited
number of divider options, there are several rules that should
be taken into account when selecting divider options.
Clock Output Divider
Definition and Notes
None
Clock output source is the reference input frequency
/DIV1N
Clock output uses a generated /DIV1N option from Divider Bank 1. Allowable values for DIV1N
are 4 to 127. If Divider Bank 1 is not being used, set DIV1N to 8.
/2
Clock output uses a fixed /2 option from Divider Bank 1. If this option is used, DIV1N must be
divisible by 4.
/3
Clock output uses a fixed /3 option from Divider Bank 1. If this option is used, set DIV1N to 6.
/DIV2N
Clock output uses a generated /DIV2N option from Divider Bank 2. Allowable values for DIV2N
are 4 to 127. If Divider Bank 2 is not being used, set DIV2N to 8.
/2
Clock output uses a fixed /2 option from Divider Bank 2. If this option is used, DIV2N must be
divisible by 4.
/4
Clock output 2 uses a fixed /4 option from Divider Bank 2. If this option is used, DIV2N must be
divisible by 8.
Q
VCO
P
/2
/
3
/
2
LCLK1
LCLK2
LCLK3
LCLK4
CLK5
CLK6
Crosspoint
Switch
REF
PFD
Divider Bank 1
/
4
Divider Bank 2
/DIV1N
/DIV2N
Matrix
Figure 1. Basic PLL Block Diagram

CY22050
Document #: 38-07006 Rev. *B
Page 4 of 8
Reference Crystal Input
The input crystal oscillator of the CY22050 is an important
feature because of the flexibility it allows the user in selecting
a crystal as a reference clock source. The oscillator inverter
has programmable gain, allowing for maximum compatibility
with a reference crystal, based on manufacturer, process,
performance, and quality.
The value of the input load capacitors is determined by eight
bits in a programmable register. Total load capacitance is
determined by the formula:
CapLoad = (C
L
≠ C
BRD
≠ C
CHIP
)/0.09375 pF
In CyClocksRT, enter the crystal capacitance (C
L
). The value
of CapLoad will be determined automatically and programmed
into the CY22050.
If you require greater control over the CapLoad value, consider
using the CY22150F for serial configuration and control of the
input load capacitors. For an external clock source, the
defaults is 0.
Input load capacitors are placed on the CY22050 die to reduce
external component cost. These capacitors are true
parallel-plate capacitors, designed to reduce the frequency
shift that occurs when non-linear load capacitance is affected
by load, bias, supply, and temperature changes.
Test Circuit
Figure 2. Duty Cycle Definition: DC = t2/t1
Figure 3. Rise and Fall Time Definitions
Figure 4. Peak-to-Peak Jitter
0.1
µ
F
V
DD
0.1
µ
F
AV
DD
CLK out
C
LOAD
GND
OUTPUTS
V
DDL
0.1
µ
F
t1
t2
CLK
50%
50%
t3
CLK
80%
20%
t4
CLK
t6
CY22050
Document #: 38-07006 Rev. *B
Page 5 of 8
Absolute Maximum Conditions
Recommended Operating Conditions
DC Electrical Characteristics
Notes:
3.
Rated for 10 years.
4.
Not 100% tested, guaranteed by design.
5.
I
VDD
currents specified for two CLK outputs running at 125 MHz, two LCLK outputs running at 80 MHz, and two LCLK outputs running at 66.6 MHz.
6.
Use CyClocksRT to calculate actual I
VDD
and I
VDDL
for specific output frequency configurations.
Parameter
Description
Min.
Max.
Unit
V
DD
Supply Voltage
≠0.5
7.0
V
V
DDL
I/O Supply Voltage
≠0.5
7.0
V
T
S
Storage Temperature
[3]
≠65
125
∞C
T
J
Junction Temperature
125
∞C
Package Power Dissipation - Commercial Temp
450
mW
Package Power Dissipation - Industrial Temp
380
mW
Digital Inputs
AV
SS
≠ 0.3
AV
DD
+ 0.3
V
Digital Outputs referred to V
DD
V
SS
≠ 0.3
V
DD
+ 0.3
V
Digital Outputs referred to V
DDL
V
SS
≠ 0.3
V
DDL
+0.3
V
ESD
Static Discharge Voltage per MIL-STD-833, Method 3015
2000
V
Parameter
Description
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
V
DD
Operating Voltage
3.135
3.3
3.465
V
VDDL
HI
Operating Voltage
3.135
3.3
3.465
V
VDDL
LO
Operating Voltage
2.375
2.5
2.625
V
T
AC
Ambient Commercial Temp
0
70
∞C
T
AI
Ambient Industrial Temp
≠40
85
∞C
C
LOAD
Max. Load Capacitance V
DD
/V
DDL
= 3.3V
15
pF
C
LOAD
Max. Load Capacitance V
DDL
= 2.5V
15
pF
f
REFD
Driven REF
1
133
MHz
f
REFC
Crystal REF
8
30
MHz
t
PU
Power-up time for all VDD's to reach minimum
specified voltage (power ramps must be
monotonic)
0.05
500
ms
Parameter
[4]
Name
Description
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
I
OH3.3
Output High Current
V
OH
= V
DD
≠ 0.5V, V
DD
/V
DDL
= 3.3V
12
24
mA
I
OL3.3
Output Low Current
V
OL
= 0.5V, V
DD
/V
DDL
= 3.3V
12
24
mA
I
OH2.5
Output High Current
V
OH
= V
DDL
≠ 0.5V, V
DDL
= 2.5V
8
16
mA
I
OL2.5
Output Low Current
V
OL
= 0.5V, V
DDL
= 2.5V
8
16
mA
V
IH
Input High Voltage
CMOS levels, 70% of V
DD
0.7
1.0
V
DD
V
IL
Input Low Voltage
CMOS levels, 30% of V
DD
0
0.3
V
DD
I
VDD
[5,6]
Supply Current
AV
DD
/V
DD
Current
45
mA
I
VDDL3.3
[5,6]
Supply Current
V
DDL
Current (V
DDL
= 3.465V)
25
mA
I
VDDL2.5
[5,6]
Supply Current
V
DDL
Current (V
DDL
= 2.625V)
17
mA
I
DDS
Power-Down Current
V
DD
= V
DDL
= AV
DD
= 3.465V
50
uA
I
OHZ
I
OLZ
Output Leakage
V
DD
= V
DDL
= AV
DD
= 3.465V
10
uA

CY22050
Document #: 38-07006 Rev. *B
Page 6 of 8
AC Electrical Characteristics
Parameter
[7]
Name
Description
Min
Typ
Max
Unit
t1
Output frequency,
commercial temp
Clock output limit, 3.3V
.08 (80 kHz)
200
MHz
Clock output limit, 2.5V
.08 (80 kHz)
166.6
MHz
Output frequency,
industrial temp
Clock output limit, 3.3V
.08 (80 kHz)
166.6
MHz
Clock output limit, 2.5V
.08 (80 kHz)
150
MHz
t2
Output duty cycle
Duty cycle is defined in Figure 2; t1/t2
f
OUT
> 166 MHz, 50% of V
DD
40
50
60
%
Duty cycle is defined in Figure 2; t1/t2
f
OUT
< 166 MHz, 50% of V
DD
45
50
55
%
t3
LO
Rising edge slew
rate (V
DDL
= 2.5V)
Output clock rise time, 20% ≠ 80% of V
DDL
.
Defined in Figure 3
0.6
1.2
V/ns
t4
LO
Falling edge slew
rate (V
DDL
= 2.5V)
Output clock fall time, 80% ≠ 20% of V
DDL
.
Defined in Figure 3
0.6
1.2
V/ns
t3
HI
Rising edge slew
rate (V
DDL
= 3.3V)
Output clock rise time, 20% ≠ 80% of
V
DD
/V
DDL
. Defined in Figure 3
0.8
1.4
V/ns
t4
HI
Falling edge slew
rate (V
DDL
= 3.3V)
Output clock fall time, 80% ≠ 20% of
V
DD
/V
DDL
. Defined in Figure 3
0.8
1.4
V/ns
t5
[8]
Skew
Output-output skew between related outputs
250
ps
t6
[9]
Clock jitter
Peak-to-peak period jitter (see Figure 4)
250
ps
t10
PLL lock time
0.30
3
ms
Ordering Information
Ordering Code
Package Name
Package Type
Temperature Operating
Range
Operating Voltage
CY22050FC
Z16
16-lead TSSOP
Commercial (0 to 70∞C)
3.3V
CY22050FI
Z16
16-lead TSSOP
Industrial (≠40 to 85∞C)
3.3V
CY22050ZC-xxx
[10]
Z16
16-lead TSSOP
Commercial (0 to 70∞C)
3.3V
CY22050ZI-xxx
[10]
Z16
16-lead TSSOP
Industrial (≠40 to 85∞C)
3.3V
CY3672
FTG Development Kit
CY3672ADP000
CY22050F Socket
16-lead TSSOP Package Characteristics
Parameter
Name
Value
Unit
JA
theta JA
115
∞C/W
Complexity
Transistor Count
74,600
Transistors
Notes:
7.
Not 100% tested, guaranteed by design.
8.
Skew value guaranteed when outputs are generated from the same divider bank. See Logic Block Diagram for more information.
9.
Jitter measurement will vary. Actual jitter is dependent on XIN jitter and edge rate, number of active outputs, output frequencies, VDDL (2.5V or 3.3V),
temperature, and output load. For more information, refer to the application note, "Jitter in PLL-based Systems: Causes, Effects, and Solutions," available at
http://www.cypress.com/clock/appnotes.html, or contact your local Cypress Field Applications Engineer.
10. The CY22050ZC-xxx and CY22050ZI-xxx are factory-programmed configurations. Factory programming is available for high-volume design opportunities of
100Ku/year or more in production. For more details, contact your local Cypress field application engineer or Cypress sales representative.

CY22050
Document #: 38-07006 Rev. *B
Page 7 of 8
© Cypress Semiconductor Corporation, 2002. The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. Cypress Semiconductor Corporation assumes no responsibility for the use
of any circuitry other than circuitry embodied in a Cypress Semiconductor product. Nor does it convey or imply any license under patent or other rights. Cypress Semiconductor does not authorize
its products for use as critical components in life-support systems where a malfunction or failure may reasonably be expected to result in significant injury to the user. The inclusion of Cypress
Semiconductor products in life-support systems application implies that the manufacturer assumes all risk of such use and in doing so indemnifies Cypress Semiconductor against all charges.
CyClocksRT
is a trademark of Cypress Semiconductor Corporation. BP Microsystems is a trademark of BP Microsystems. Hilo
Systems is a trademark of Hi-Lo Systems. All product and company names mentioned in this document are the trademarks of
their respective holders.
16-lead Thin Shrunk Small Outline Package (4.40 MM Body) Z16
51-85091
CY22050
Document #: 38-07006 Rev. *B
Page 8 of 8
Document Title: CY22050 One-PLL General Purpose Flash - Programmable Clock Generator
Document Number: 38-07006
REV.
ECN NO.
Issue
Date
Orig. of
Change
Description of Change
**
108185
08/08/01
CKN
New Data Sheet
*A
110054
03/04/02
CKN
Changed from Preliminary to Final
*B
121862
12/14/02
RBI
Power up requirements added to Operating Conditions Information







