 | –≠–ª–µ–∫—Ç—Ä–æ–Ω–Ω—ã–π –∫–æ–º–ø–æ–Ω–µ–Ω—Ç: HT24LC64 | –°–∫–∞—á–∞—Ç—å:  PDF PDF  ZIP ZIP |
Document Outline
- ˛ˇ
- ˛ˇ
- ˛ˇ
- ˛ˇ
- ˛ˇ
- ˛ˇ
- ˛ˇ
- ˛ˇ
- ˛ˇ
- ˛ˇ
- ˛ˇ
- ˛ˇ
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Operating Temperature (Commercial) ........................................................................................................ 0
∞C to 70∞C
Storage Temperature ............................................................................................................................
-50∞C to 125∞C
Applied VCC Voltage with Respect to VSS .................................................................................V
SS
-0.3V to V
SS
+6.0V
Applied Voltage on any Pin with Respect to VSS
................................................................................................
V
SS
-0.3V to V
CC
+0.3V
Note: These are stress ratings only. Stresses exceeding the range specified under
≤Absolute Maximum Ratings≤ may
cause substantial damage to the device. Functional operation of this device at other conditions beyond those
listed in the specification is not implied and prolonged exposure to extreme conditions may affect device reliabil-
ity.
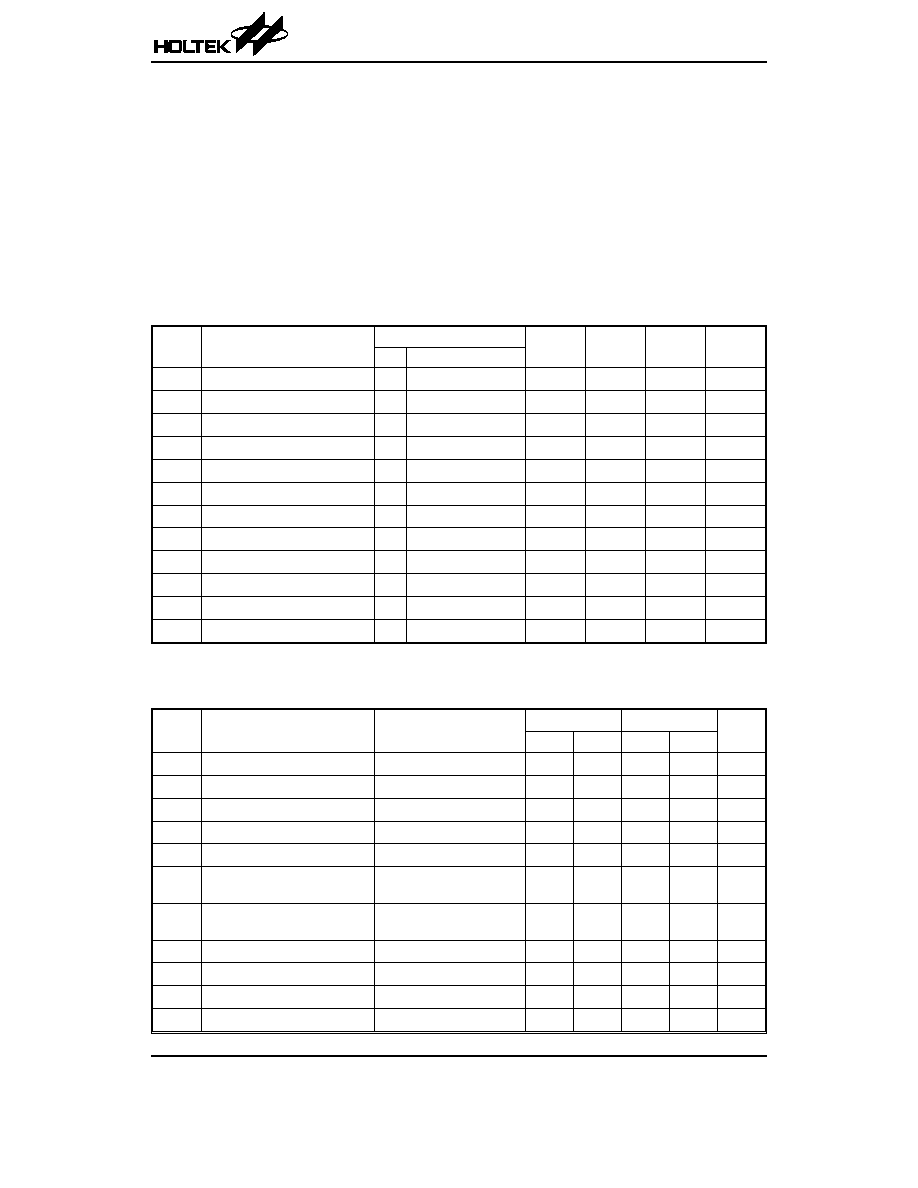
D.C. Characteristics
Ta=0
∞C to 70∞C
Symbol
Parameter
Test Conditions
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
V
CC
Conditions
V
CC
Operating Voltage
æ
æ
2.4
æ
5.5
V
I
CC1
Operating Current
5V
Read at 100kHz
æ
æ
2
mA
I
CC2
Operating Current
5V
Write at 100kHz
æ
æ
5
mA
V
IL
Input Low Voltage
æ
æ
-1
æ
0.3V
CC
V
V
IH
Input High Voltage
æ
æ
0.7V
CC
æ
V
CC
+0.5
V
V
OL
Output Low Voltage
2.4V I
OL
=2.1mA
æ
æ
0.4
V
I
LI
Input Leakage Current
5V
V
IN
=0 or V
CC
æ
æ
1
mA
I
LO
Output Leakage Current
5V
V
OUT
=0 or V
CC
æ
æ
1
mA
I
STB1
Standby Current
5V
V
IN
=0 or V
CC
æ
æ
5
mA
I
STB2
Standby Current
2.4V V
IN
=0 or V
CC
æ
æ
4
mA
C
IN
Input Capacitance (See Note)
æ f=1MHz 25∞C
æ
æ
6
pF
C
OUT
Output Capacitance (See Note)
æ f=1MHz 25∞C
æ
æ
8
pF
Note: These parameters are periodically sampled but not 100% tested.
A.C. Characteristics
Ta=0
∞C to 70∞C
Symbol
Parameter
Remark
Standard Mode*
V
CC
=5V
±10%
Unit
Min.
Max.
Min.
Max.
f
SK
Clock Frequency
æ
æ
100
æ
400
kHz
t
HIGH
Clock High Time
æ
4000
æ
600
æ
ns
t
LOW
Clock Low Time
æ
4700
æ
1200
æ
ns
t
R
SDA and SCL Rise Time
Note
æ
1000
æ
300
ns
t
F
SDA and SCL Fall Time
Note
æ
300
æ
300
ns
t
HD:STA
START Condition Hold Time
After this period, the first
clock pulse is generated.
4000
æ
600
æ
ns
t
SU:STA
START Condition Setup Time
Only relevant for repeated
START condition.
4000
æ
600
æ
ns
t
HD:DAT
Data Input Hold Time
æ
0
æ
0
æ
ns
t
SU:DAT
Data Input Setup Time
æ
200
æ
100
æ
ns
t
SU:STO
STOP Condition Setup Time
æ
4000
æ
600
æ
ns
t
AA
Output Valid from Clock
æ
æ
3500
æ
900
ns
HT24LC64
Rev. 1.00
2
January 5, 2005

Symbol
Parameter
Remark
Standard Mode*
V
CC
=5V
±10%
Unit
Min.
Max.
Min.
Max.
t
BUF
Bus Free Time
Time in which the bus must
be free before a new trans-
mission can start
4700
æ
1200
æ
ns
t
SP
Input Filter Time Constant
(SDA and SCL Pins)
Noise suppression time
æ
100
æ
50
ns
t
WR
Write Cycle Time
æ
æ
5
æ
5
ms
Note:
These parameters are periodically sampled but not 100% tested
* The standard mode means V
CC
=2.4V to 5.5V
For relative timing, refer to timing diagrams
HT24LC64
Rev. 1.00
3
January 5, 2005
Functional Description
∑
Serial clock (SCL)
The SCL input is used for positive edge clock data into
each EEPROM device and negative edge clock data
out of each device.
∑
Serial data (SDA)
The SDA pin is bidirectional for serial data transfer.
The pin is open drain driven and may be wired-OR
with any number of other open drain or open collector
devices.
∑
A0, A1, A2
The A2, A1 and A0 pins are device address inputs that
are hard wired or left not connected for hardware com-
patibility with HT24LC64. When the pins are hard-
wired, as many as eight 64K devices may be
addressed on a single bus system (device addressing
is discussed in detail under the Device Addressing
section). These inputs must be tied to V
CC
or V
SS
, to
establish the device select code.
∑
Write protect (WP)
The HT24LC64 has a write protect pin that provides
hardware data protection. The write protect pin allows
normal read/write operations when the connection is
grounded. When the write protect pin is connected to
V
CC
, the write protection feature is enabled and oper-
ates as shown in the following table.
WP Pin Status
Protect Array
At V
CC
Full Array (64K)
At V
SS
(floating)
Normal Read/Write Operations
Memory Organization
Internally organized with 8192 8-bit words, the 64K re-
quires a 13-bit data word address for random word ad-
dressing.
Device Operations
∑
Clock and data transition
Data transfer may be initiated only when the bus is not
busy. During data transfer, the data line must remain
stable whenever the clock line is high. Changes in
data line while the clock line is high will be interpreted
as a START or STOP condition.
∑
Start condition
A high-to-low transition of SDA with SCL high is a start
condition which must precede any other command
(refer to Start and Stop Definition Timing diagram).
∑
Stop condition
A low-to-high transition of SDA with SCL high is a stop
condition. After a read sequence, the stop command
will place the EEPROM in a standby power mode (re-
fer to Start and Stop Definition Timing Diagram).
∑
Acknowledge
All addresses and data words are serially transmitted
to and from the EEPROM in 8-bit words. The
EEPROM sends a zero to acknowledge that it has re-
ceived each word. This happens during the ninth clock
cycle.
Device Addressing
The 64K EEPROM devices require an 8-bit device ad-
dress word following a start condition to enable the chip
for a read or write operation. The device address word
consist of a mandatory one, zero sequence for the first
four most significant bits (refer to the diagram showing
the Device Address). This is common to all the
EEPROM device.
The 64K EEPROM uses the three device address bits
A2, A1, A0 to allow as many as eight devices on the
same bus. These bits must compare to their corre-
sponding hardwired input pins.
S C L
S D A
D a t a a l l o w e d
t o c h a n g e
A d d r e s s o r
a c k n o w l e d g e
v a l i d
S t o p
c o n d i t i o n
S t a r t
c o n d i t i o n
N o A C K
s t a t e

HT24LC64
Rev. 1.00
4
January 5, 2005
The 8th bit device address is the read/write operation
select bit. A read operation is initiated if this bit is high
and a write operation is initiated if this bit is low.
If the comparison of the device address succeed the
EEPROM will output a zero at ACK bit. If not, the chip will
return to a standby state.
Write Operations
∑
Byte write
A write operation requires an 8-bit data word address
following the device address word and acknowledg-
ment. Upon receipt of this address, the EEPROM will
again respond with a zero and then clock in the first
8-bit data word. After receiving the 8-bit data word, the
EEPROM will output a zero and the addressing de-
vice, such as a microcontroller, must terminate the
write sequence with a stop condition. At this time the
EEPROM enters an internally-timed write cycle to the
nonvolatile memory. All inputs are disabled during this
write cycle and EEPROM will not respond until the
write operation is completed (refer to Byte write tim-
ing).
∑
Page write
The 64K EEPROM is capable of a 32-byte page write.
A page write is initiated in the same way as a byte
write, but the microcontroller does not send a stop
condition after the first data word is clocked in. In-
stead, after the EEPROM acknowledges the receipt of
the first data word, the microcontroller can transmit up
to 31 more data words. The EEPROM will respond
with a zero after each data word received. The
microcontroller must terminate the page write se-
quence with a stop condition (refer to Page write tim-
ing).
The data word address lower 5 bits are internally in-
cremented following the receipt of each data word.
The higher data word address bits are not incre-
mented, retaining the memory page row location.
When the word address, internally generated,
reaches the page boundary, the following byte is
placed at the beginning of the same page. If more
than 32 data words are transmitted to the EEPROM,
the data word address will
≤roll over≤ and previous
data will be overwritten.
∑
Acknowledge polling
To maximize bus throughput, one technique is to allow
the master to poll for an acknowledge signal after the
start condition and the control byte for a write com-
mand have been sent. If the device is still busy imple-
menting its write cycle, then no ACK will be returned.
The master can send the next read/write command
when the ACK signal has finally been received.
R / W
1
0
A 2
A 1
A 0
D e v i c e A d d r e s s
1
0
Device Address
R
/
W
D e v i c e A d d r e s s
F i r s t W o r d A d d r e s s
A
C
K
S
t
a
r
t
S D A L i n e
W
r
i
t
e
S
t
o
p
A 2 A 1 A 0
A
C
K
S e c o n d W o r d A d d r e s s
D a t a
A
C
K
A
C
K
Byte Write Timing
R
/
W
D e v i c e A d d r e s s
F i r s t W o r d A d d r e s s ( n )
A
C
K
S
t
a
r
t
S D A L i n e
W
r
i
t
e
A 2 A 1 A 0
A
C
K
S e c o n d W o r d A d d r e s s ( n )
S
t
o
p
D a t a ( n + x )
A
C
K
A
C
K
A
C
K
D a t a ( n )
N o t e : * = D o n ' t c a r e b i t s
Page Write Timing
S e n d W r i t e C o m m a n d
S e n d S t o p C o n d i t i o n
t o I n i t i a t e W r i t e C y c l e
S e n d S t a r t
S e n d C o n t r o l B y t e
w i t h R / W = 0
( A C K = 0 ) ?
N e x t O p e r a t i o n
N o
Y e s
Acknowledge Polling Flow

HT24LC64
Rev. 1.00
5
January 5, 2005
∑
Write protect
The HT24LC64 has a write-protect function and pro-
gramming will then be inhibited when the WP pin is
connected to VCC. Under this mode, the HT24LC64 is
used as a serial ROM.
∑
Read operations
The HT24LC64 supports three read operations,
namely, current address read, random address read
and sequential read. During read operation execution,
the read/write select bit should be set to
≤1≤.
∑
Current address read
The internal data word address counter maintains the
last address accessed during the last read or write op-
eration, incremented by one. This address remains
valid between operations as long as the chip power is
maintained. The address will roll over during read
from the last byte of the last memory page to the first
byte of the first page. The address will roll over during
write from the last byte of the current page to the first
byte of the same page. Once the device address with
the read/write select bit set to one is clocked in and ac-
knowledged by the EEPROM, the current address
data word is serially clocked out. The microcontroller
does not respond with an input zero but generates a
following stop condition (refer to Current read timing).
∑
Random read
A random read requires a dummy byte write sequence
to load in the data word address which is then clocked
in and acknowledged by the EEPROM. The
microcontroller must then generate another start con-
dition. The microcontroller now initiates a current ad-
dress read by sending a device address with the
read/write select bit high. The EEPROM acknowl-
edges the device address and serially clocks out the
data word. The microcontroller should respond with a
≤no ACK≤ signal (high) followed by a stop condition
(refer to Random read timing).
∑
Sequential read
Sequential reads are initiated by either a current ad-
dress read or a random address read. After the
microcontroller receives a data word, it responds with
an acknowledgment. As long as the EEPROM re-
ceives an acknowledgment, it will continue to incre-
ment the data word address and serially clock out
sequential data words. When the memory address
limit is reached, the data word address will roll over
and the sequential read continues. The sequential
read operation is terminated when the microcontroller
does not respond with a zero but generates a following
stop condition.
R
/
W
D e v i c e A d d r e s s
1 s t , 2 n d W o r d
A d d r e s s ( n )
A
C
K
S
t
a
r
t
S D A L i n e
W
r
i
t
e
A 2 A 1 A 0
A
C
K
S
t
o
p
A 2 A 1 A 0
A
C
K
S
t
a
r
t
D e v i c e A d d r e s s
R
e
a
d
D a t a ( n )
N
o
A
C
K
D u m m y W r i t e
N o t e : * = D o n ' t c a r e b i t s
Random Read Timing
A 2 A 1 A 0
D e v i c e a d d r e s s
D a t a
S
t
o
p
S
t
a
r
t
S D A L i n e
N
o
A
C
K
R
/
W
A
C
K
R
e
a
d
Current Address Read Timing
R
/
W
A
C
K
S D A L i n e
R
e
a
d
A
C
K
S
t
o
p
D a t a ( n + x )
N
o
A
C
K
A
C
K
A
C
K
D a t a ( n + 2 )
D a t a ( n + 1 )
D a t a ( n )
D e v i c e
A d d r e s s
Sequential Read Timing

Timing Diagrams
Note: The write cycle time t
WR
is the time from a valid stop condition of a write sequence to the end of the valid start con-
dition of sequential command.
HT24LC64
Rev. 1.00
6
January 5, 2005
t
F
t
L O W
t
R
t
H I G H
t
S U : S T A
t
H D : S T A
t
S P
t
H D : D A T
t
S U : D A T
t
S U : S T O
t
B U F
V a l i d
V a l i d
S C L
S D A
S D A
O U T
t
A A
S C L
S D A
8 t h b i t
W o r d n
t
W R
A C K
S t o p
c o n d i t i o n
S t o p
c o n d i t i o n




