
PD -2.531
∑ Fast Recovery time characteristic
∑ Eletrically isolated base plate
∑ Large creepage distance between terminal
∑ Simplified mechanical designs, rapid assembly
Features
Description
This SOT-227 modules with FRED rectifier are available in two basic
configurations. They are the antiparallel and the parallel configurations.
The antiparallel configuration (HFA120EA60) is used for simple series
rectifier and high voltage application. The parallel configuration
(HFA120FA60) is used for simple parallel rectifier and high current application.
The semiconductor in the SOT-227 package is isolated from the copper
base plate, allowing for common heatsinks and compact assemblies to be
built.
These modules are intended for general applications such as power
supplies, battery chargers, electronic welders, motor control, DC chopper,
and inverters.
Ultrafast, Soft Recovery Diode
HEXFRED
TM
HFA120FA60, HFA120EA60
S O T -22 7
V
R
= 600V
V
F
(typ.)* = 1.4V
I
F(AV)
= 60A
Q
rr
(typ.) = 270nC
I
RRM
(typ.)
= 7.0A
t
rr
(typ.)
= 65ns
di
(rec)M
/dt (typ.)* = 270A/µs
K2
A2
K1
A1
A1
A2
K1
K2
HFA120FA60
HFA120EA60
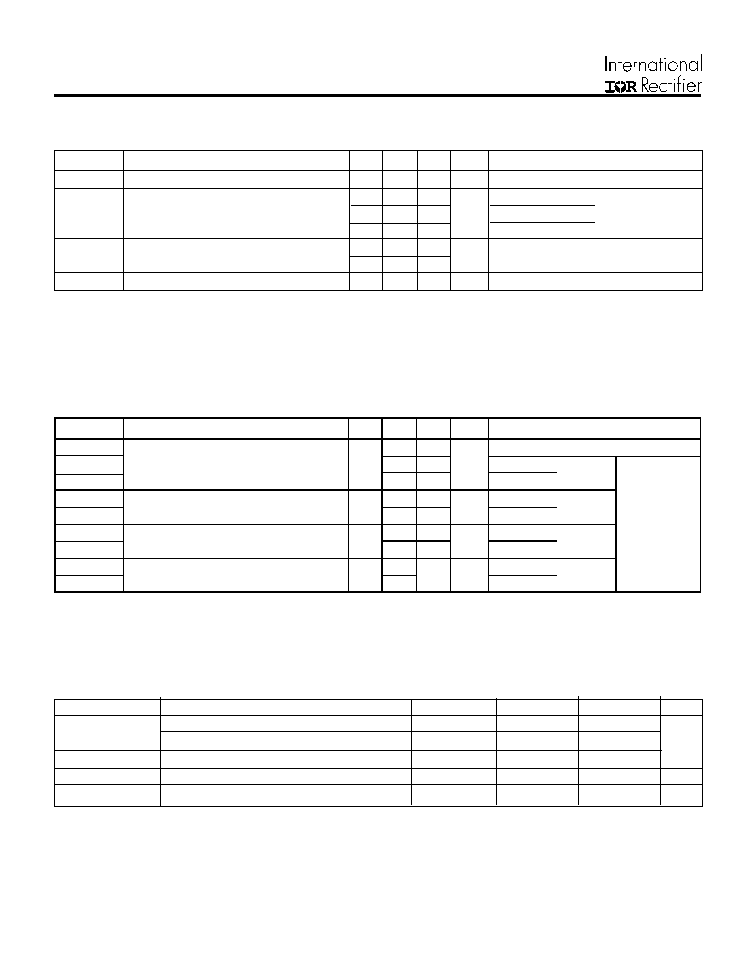
Parameter
Max.
Units
V
R
Cathode-to-Anode Voltage
600
V
I
F
@ T
C
= 25∞C
Continuous Forward Current
75
I
F
@ T
C
= 100∞C
Continuous Forward Current
40
I
FSM
Single Pulse Forward Current
TBD
I
FRM
Maximum Repetitive Forward Current
180
V
ISOL
RMS Isolation Voltage, Any Terminal to Case, t=1 min
2500
V
P
D
@ T
C
= 25∞C
Maximum Power Dissipation
180
P
D
@ T
C
= 100∞C
Maximum Power Dissipation
71
T
J
Operating Junction and
T
STG
Storage Temperature Range
*125 ∞C
Absolute Maximum Ratings (per Leg)
W
A
∞C
10/09/97
-55 to +150
HFA120FA60, HFA120EA60
Parameter
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Units
R
JC
Junction-to-Case, Single Leg Conducting
≠≠≠≠
≠≠≠≠
0.70
Junction-to-Case, Both Legs Conducting
≠≠≠≠
≠≠≠≠
0.35
R
CS
Case-to-Sink, Flat , Greased Surface
≠≠≠≠
0.05
≠≠≠≠
Wt
Weight
≠≠≠≠
30
≠≠≠≠
gm
Mounting Torque
≠≠≠≠
1.3
≠≠≠≠
(N∑m)
Parameter
Min. Typ. Max. Units Test Conditions
t
rr
Reverse Recovery Time
≠≠≠
34
≠≠≠
I
F
= 1.0A, di
f
/dt = 200A/µs, V
R
= 30V
t
rr1
≠≠≠
65
98
ns
T
J
= 25∞C
t
rr2
≠≠≠
130
200
T
J
= 125∞C
I
F
= 60A
I
RRM1
Peak Recovery Current
≠≠≠
7.0
13
T
J
= 25∞C
I
RRM2
≠≠≠
13
23
T
J
= 125∞C
V
R
= 200V
Q
rr1
Reverse Recovery Charge
≠≠≠
270
410
T
J
= 25∞C
Q
rr2
≠≠≠
490
740
T
J
= 125∞C
di
f
/dt = 200A/µs
di
(rec)M
/dt1
Peak Rate of Fall of Recovery Current
≠≠≠
350
≠≠≠
T
J
= 25∞C
di
(rec)M
/dt2
During t
b
≠≠≠
270
≠≠≠
T
J
= 125∞C
Parameter
Min. Typ. Max. Units
Test Conditions
V
BR
Cathode Anode Breakdown Voltage
600
≠≠≠
≠≠≠
V
I
R
= 100µA
≠≠≠
1.5
1.7
I
F
= 60A
≠≠≠
1.9
2.1
V
I
F
= 120A
≠≠≠
1.4
1.6
I
F
= 60A, T
J
= 125∞C
≠≠≠
2.5
20
V
R
= V
R
Rated
≠≠≠
130 2000
T
J
= 125∞C, V
R
= 0.8 x V
R
Rated
D
Rated
C
T
Junction Capacitance
≠≠≠
120
170
pF
V
R
= 200V
Electrical Characteristics (per Leg) @ T
J
= 25∞C (unless otherwise specified)
Dynamic Recovery Characteristics (per Leg) @ T
J
= 25∞C (unless otherwise specified)
A/µs
nC
A
See Fig. 3
See Fig. 2
See Fig. 1
See Fig. 5, 6 & 16
See Fig. 7& 8
See Fig. 9 & 10
See Fig. 11 & 12
V
FM
Max Forward Voltage
µA
Max Reverse Leakage Current
I
RM
∞C/W
K/W
Thermal - Mechanical Characteristics

HFA120FA60, HFA120EA60
Fig. 4 - Maximum Thermal Impedance Z
thjc
Characteristics, (per Leg)
Fig. 2 - Typical Reverse Current vs. Reverse
Voltage, (per Leg)
Fig. 3 - Typical Junction Capacitance vs.
Reverse Voltage, (per Leg)
Fig. 1 - Maximum Forward Voltage Drop
vs. Instantaneous Forward Current,
(per Leg)
Reverse Current - I
R
(µA)
Junction Capacitance -C
T
(pF)
Instantaneous Forward Current - I
F
(A)
1
10
100
1000
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
FM
T = 15 0∞C
T = 12 5∞C
T = 2 5∞C
J
J
J
Fo rward V olta ge D ro p - V (V)
0.1
1
10
100
1000
10000
0
200
400
600
R
T = 150∞C
T = 125 ∞C
T = 25∞C
J
J
J
Re ve rse Vo ltag e - V (V)
Reverse Voltage - V
R
( V )
10
100
1000
10000
1
10
100
1000
T = 25 ∞C
J
R eve rse Vo lta ge - V (V)
R
A
0.01
0.1
1
0.00001
0.0001
0.001
0.01
0.1
1
Notes:
1. Duty factor D =
t / t
2. Peak T
= P
x Z
+ T
1
2
J
DM
thJC
C
P
t
t
DM
1
2
t , Rectangular Pulse Duration (sec)
Thermal Response
(Z )
1
thJC
0.01
0.02
0.05
0.10
0.20
D = 0.50
SINGLE PULSE
(THERMAL RESPONSE)

HFA120FA60, HFA120EA60
Fig. 7 - Typical Stored Charge vs. di
f
/dt,
(per Leg)
Fig. 8 - Typical di
(rec)M
/dt vs. di
f
/dt,
(per Leg)
Fig. 5 - Typical Reverse Recovery vs. di
f
/dt,
(per Leg)
Fig. 6 - Typical Recovery Current vs. di
f
/dt,
(per Leg)
di (rec) M/dt-
(A
/µs)
Qrr-
(nC)
Irr-
(
A)
trr-
(ns)
40
80
120
160
200
100
1000
f
d i /dt - (A/µ s)
I = 1 20A
I = 60A
I = 30A
V = 200 V
T = 1 2 5∞C
T = 2 5 ∞C
R
J
J
F
F
F
1
10
100
100
1000
f
d i /dt - (A/µ s)
I = 120 A
I = 60A
I = 30A
V = 2 00 V
T = 125 ∞C
T = 25∞ C
R
J
J
F
F
F
0
1000
2000
3000
4000
100
1000
f
d i /dt - (A/µ s)
I = 12 0A
I = 60A
I = 30A
F
F
F
V = 20 0V
T = 1 2 5∞C
T = 2 5 ∞C
R
J
J
100
1000
10000
100
1000
f
d i /dt - (A/µ s)
I = 120A
I = 60A
I = 3 0A
V = 200 V
T = 1 25 ∞C
T = 2 5∞C
R
J
J
F
F
F

HFA120FA60, HFA120EA60
4. Q
rr
- Area under curve defined by t
rr
and I
RRM
t
rr
X I
RRM
Q
rr
=
2
5. di
(rec)M
/dt - Peak rate of change of
current during t
b
portion of t
rr
V
(A V A L )
R (R A T E D )
I
L (P K )
V
DE C AY
TIM E
Fig. 11 - Avalanche Test Circuit and Waveforms
Fig. 10 - Reverse Recovery Waveform and
Definitions
Fig. 9 - Reverse Recovery Parameter Test
Circuit
t
a
t
b
t
rr
Q
rr
I
F
I
R R M
I
R R M
0.5
di(re c) M/dt
0.75 I
R R M
5
4
3
2
0
1
di /dt
f
1. di
f
/dt - Rate of change of current
through zero crossing
2. I
RRM
- Peak reverse recovery current
3. trr - Reverse recovery time measured
from zero crossing point of negative
going I
F
to point where a line passing
through 0.75 I
RRM
and 0.50 I
RRM
extrapolated to zero current
R E VER SE R EC O VER Y C IR C U IT
IR F P 2 5 0
D . U . T .
L = 7 0 µ H
V = 20 0 V
R
0 .0 1
G
D
S
d if /d t
A D J U S T
C U R R E N T
M O N IT O R
H IG H -S PE ED
SW IT C H
D U T
R g = 2 5 o h m
+
FR EE -W H E EL
D I O D E
V d = 5 0 V
L = 1 0 0µ H




