 | ÐлекÑÑоннÑй компоненÑ: IRF1503 | СкаÑаÑÑ:  PDF PDF  ZIP ZIP |
Äîêóìåíòàöèÿ è îïèñàíèÿ www.docs.chipfind.ru
HEXFET
®
Power MOSFET
Specifically designed for Automotive applications, this
design of HEXFET
®
Power MOSFETs utilizes the lastest
processing techniques to achieve extremely low on-
resistance per silicon area. Additional features of this
HEXFET power MOSFET are a 175°C junction operating
temperature, fast switching speed and improved repetitive
avalanche rating. These combine to make this design an
extremely efficient and reliable device for use in Automotive
applications and a wide variety of other applications.
S
D
G
V
DSS
= 30V
R
DS(on)
= 3.3m
I
D
= 75A
Description
12/11/02
www.irf.com
1
Advanced Process Technology
Ultra Low On-Resistance
175°C Operating Temperature
Fast Switching
Repetitive Avalanche Allowed up to Tjmax
Features
Typical Applications
14V Automotive Electrical Systems
14V Electronic Power Steering
AUTOMOTIVE MOSFET
IRF1503
Parameter
Typ.
Max.
Units
R
JC
Junction-to-Case
0.45
R
CS
Case-to-Sink, Flat, Greased Surface
0.50
°C/W
R
JA
Junction-to-Ambient
62
Thermal Resistance
TO-220AB
Parameter
Max.
Units
I
D
@ T
C
= 25°C
Continuous Drain Current, V
GS
@ 10V (Silicon limited)
240
I
D
@ T
C
= 100°C
Continuous Drain Current, V
GS
@ 10V (See Fig.9)
170
A
I
D
@ T
C
= 25°C
Continuous Drain Current, V
GS
@ 10V (Package limited)
75
I
DM
Pulsed Drain Current
960
P
D
@T
C
= 25°C
Power Dissipation
330
W
Linear Derating Factor
2.2
W/°C
V
GS
Gate-to-Source Voltage
± 20
V
E
AS
Single Pulse Avalanche Energy
510
mJ
E
AS
(tested)
Single Pulse Avalanche Energy Tested Value
980
I
AR
Avalanche Current
See Fig.12a, 12b, 15, 16
A
E
AR
Repetitive Avalanche Energy
mJ
T
J
Operating Junction and
-55 to + 175
T
STG
Storage Temperature Range
Soldering Temperature, for 10 seconds
300 (1.6mm from case )
°C
Absolute Maximum Ratings
PD-94526A
IRF1503
2
www.irf.com
Parameter
Min. Typ. Max. Units
Conditions
V
(BR)DSS
Drain-to-Source Breakdown Voltage
30
V
V
GS
= 0V, I
D
= 250µA
V
(BR)DSS
/
T
J
Breakdown Voltage Temp. Coefficient
0.028
V/°C
Reference to 25°C, I
D
= 1mA
R
DS(on)
Static Drain-to-Source On-Resistance
2.6
3.3
m
V
GS
= 10V, I
D
= 140A
V
GS(th)
Gate Threshold Voltage
2.0
4.0
V
V
DS
= 10V, I
D
= 250µA
g
fs
Forward Transconductance
75
S
V
DS
= 25V, I
D
= 140A
20
µA
V
DS
= 30V, V
GS
= 0V
250
V
DS
= 30V, V
GS
= 0V, T
J
= 125°C
Gate-to-Source Forward Leakage
200
V
GS
= 20V
Gate-to-Source Reverse Leakage
-200
nA
V
GS
= -20V
Q
g
Total Gate Charge
130
200
I
D
= 140A
Q
gs
Gate-to-Source Charge
36
54
nC
V
DS
= 24V
Q
gd
Gate-to-Drain ("Miller") Charge
41
62
V
GS
= 10V
t
d(on)
Turn-On Delay Time
17
V
DD
= 15V
t
r
Rise Time
130
I
D
= 140A
t
d(off)
Turn-Off Delay Time
59
R
G
= 2.5
t
f
Fall Time
48
V
GS
= 10V
Between lead,
6mm (0.25in.)
from package
and center of die contact
C
iss
Input Capacitance
5730
V
GS
= 0V
C
oss
Output Capacitance
2250
pF
V
DS
= 25V
C
rss
Reverse Transfer Capacitance
290
= 1.0MHz, See Fig. 5
C
oss
Output Capacitance
7580
V
GS
= 0V, V
DS
= 1.0V, = 1.0MHz
C
oss
Output Capacitance
2290
V
GS
= 0V, V
DS
= 24V, = 1.0MHz
C
oss
eff.
Effective Output Capacitance
3420
V
GS
= 0V, V
DS
= 0V to 24V
nH
Electrical Characteristics @ T
J
= 25°C (unless otherwise specified)
L
D
Internal Drain Inductance
L
S
Internal Source Inductance
S
D
G
I
GSS
ns
5.0
13
I
DSS
Drain-to-Source Leakage Current
S
D
G
Parameter
Min. Typ. Max. Units
Conditions
I
S
Continuous Source Current
MOSFET symbol
(Body Diode)
showing the
I
SM
Pulsed Source Current
integral reverse
(Body Diode)
p-n junction diode.
V
SD
Diode Forward Voltage
1.3
V
T
J
= 25°C, I
S
= 140A, V
GS
= 0V
t
rr
Reverse Recovery Time
71
110
ns
T
J
= 25°C, I
F
= 140A, V
DD
= 15V
Q
rr
Reverse RecoveryCharge
110
170
nC
di/dt = 100A/µs
t
on
Forward Turn-On Time
Intrinsic turn-on time is negligible (turn-on is dominated by L
S
+L
D
)
Source-Drain Ratings and Characteristics
240
960
A
Repetitive rating; pulse width limited by
max. junction temperature. (See fig. 11).
Starting T
J
= 25°C, L = 0.049mH
R
G
= 25
, I
AS
= 140A. (See Figure 12).
Pulse width
400µs; duty cycle 2%.
Notes:
C
oss
eff. is a fixed capacitance that gives the same charging time
as C
oss
while V
DS
is rising from 0 to 80% V
DSS
.
Limited by T
Jmax
, see Fig.12a, 12b, 15, 16 for typical repetitive
avalanche performance.
This value determined from sample failure population. 100%
tested to this value in production.
IRF1503
www.irf.com
3
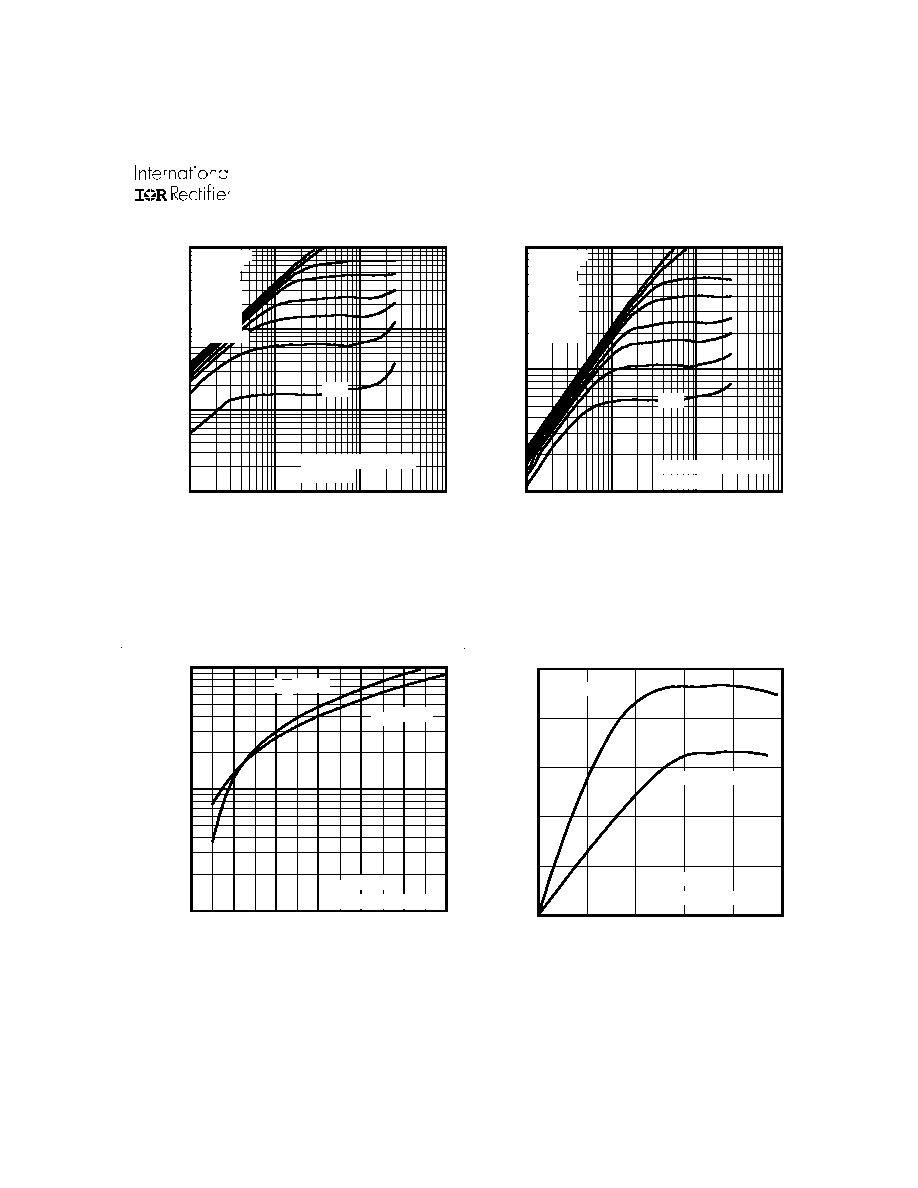
Fig 2. Typical Output Characteristics
Fig 1. Typical Output Characteristics
Fig 3. Typical Transfer Characteristics
0.1
1
10
100
VDS, Drain-to-Source Voltage (V)
1
10
100
1000
I D
,
D
r
a
i
n
-
t
o
-
S
o
u
r
c
e
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
A
)
4.5V
20µs PULSE WIDTH
Tj = 25°C
VGS
TOP 15V
10V
8.0V
7.0V
6.0V
5.5V
5.0V
BOTTOM 4.5V
0.1
1
10
100
VDS, Drain-to-Source Voltage (V)
10
100
1000
I D
,
D
r
a
i
n
-
t
o
-
S
o
u
r
c
e
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
A
)
4.5V
20µs PULSE WIDTH
Tj = 175°C
VGS
TOP 15V
10V
8.0V
7.0V
6.0V
5.5V
5.0V
BOTTOM 4.5V
4.0
5.0
6.0
7.0
8.0
9.0
10.0
VGS, Gate-to-Source Voltage (V)
10
100
1000
I D
,
D
r
a
i
n
-
t
o
-
S
o
u
r
c
e
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
)
TJ = 25°C
TJ = 175°C
VDS = 25V
20µs PULSE WIDTH
0
40
80
120
160
200
ID, Drain-to-Source Current (A)
0
40
80
120
160
200
G
f
s
,
F
o
r
w
a
r
d
T
r
a
n
s
c
o
n
d
u
c
t
a
n
c
e
(
S
)
TJ = 25°C
TJ = 175°C
VDS = 25V
20µs PULSE WIDTH
Fig 4. Typical Forward Transconductance
Vs. Drain Current
IRF1503
4
www.irf.com
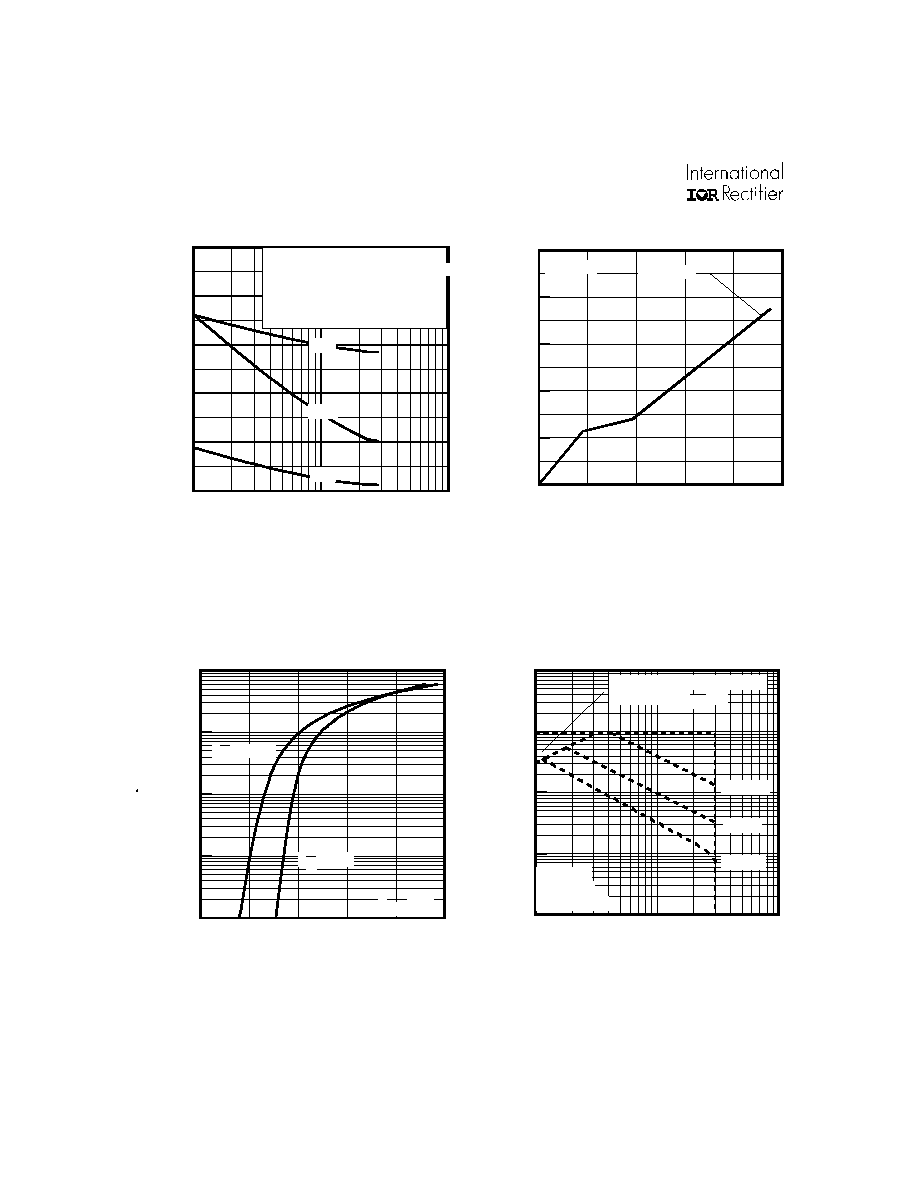
Fig 8. Maximum Safe Operating Area
Fig 6. Typical Gate Charge Vs.
Gate-to-Source Voltage
Fig 5. Typical Capacitance Vs.
Drain-to-Source Voltage
Fig 7. Typical Source-Drain Diode
Forward Voltage
0.0
0.4
0.8
1.2
1.6
2.0
VSD, Source-toDrain Voltage (V)
0.1
1.0
10.0
100.0
1000.0
I S
D
,
R
e
v
e
r
s
e
D
r
a
i
n
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
A
)
TJ = 25°C
TJ = 175°C
VGS = 0V
0
40
80
120
160
200
QG Total Gate Charge (nC)
0
4
8
12
16
20
V
G
S
,
G
a
t
e
-
t
o
-
S
o
u
r
c
e
V
o
l
t
a
g
e
(
V
)
VDS= 24V
ID= 140A
1
10
100
VDS , Drain-toSource Voltage (V)
1
10
100
1000
10000
I D
,
D
r
a
i
n
-
t
o
-
S
o
u
r
c
e
C
u
r
r
e
n
t
(
A
)
Tc = 25°C
Tj = 175°C
Single Pulse
1msec
10msec
OPERATION IN THIS AREA
LIMITED BY RDS(on)
100µsec
1
10
100
VDS, Drain-to-Source Voltage (V)
0
2000
4000
6000
8000
10000
C
,
C
a
p
a
c
i
t
a
n
c
e
(
p
F
)
Coss
Crss
Ciss
VGS = 0V, f = 1 MHZ
C iss = C gs + C gd , C ds
SHORTED
Crss = Cgd
Coss = Cds + Cgd
IRF1503
www.irf.com
5
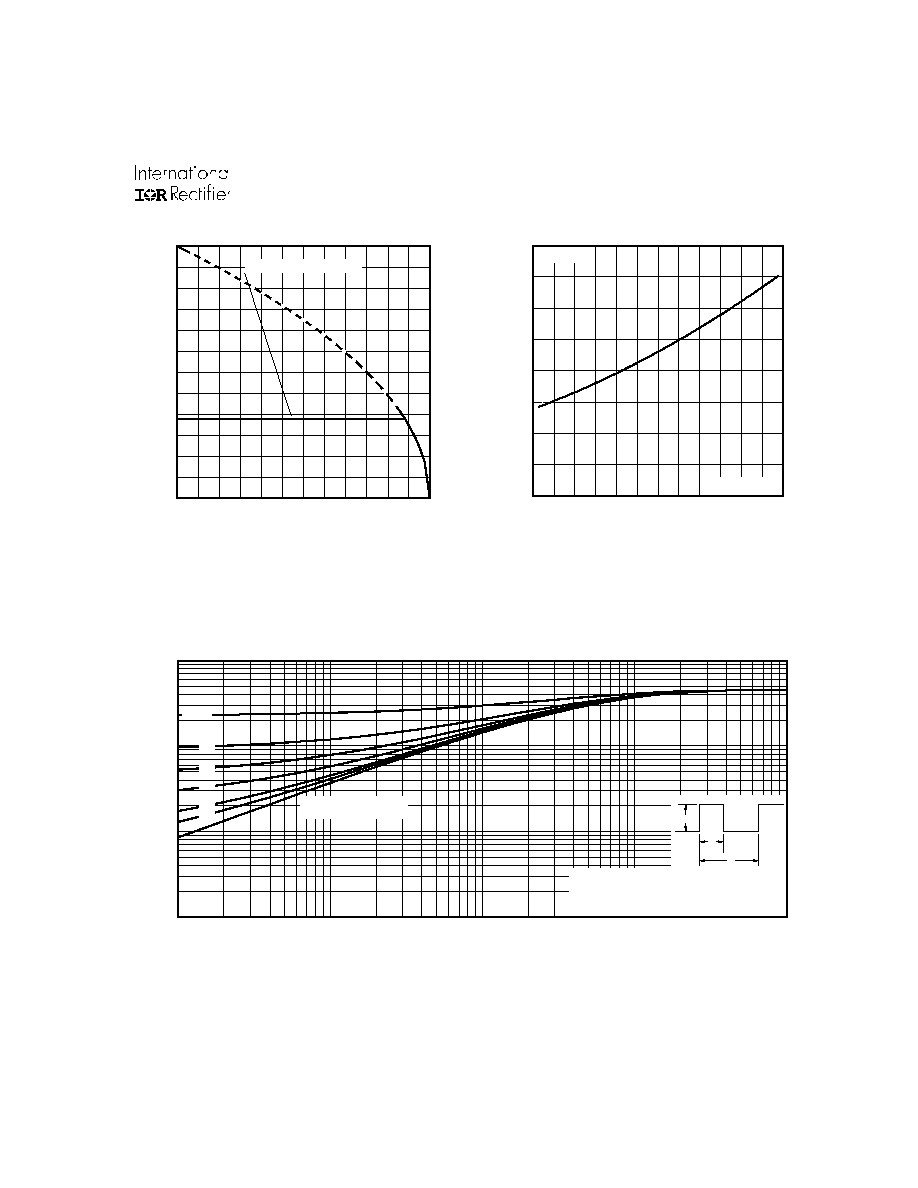
Fig 11. Maximum Effective Transient Thermal Impedance, Junction-to-Case
Fig 9. Maximum Drain Current Vs.
Case Temperature
0.001
0.01
0.1
1
0.00001
0.0001
0.001
0.01
0.1
Notes:
1. Duty factor D =
t / t
2. Peak T
= P
x Z
+ T
1
2
J
DM
thJC
C
P
t
t
DM
1
2
t , Rectangular Pulse Duration (sec)
T
her
m
a
l
Res
pons
e
(
Z
)
1
th
JC
0.01
0.02
0.05
0.10
0.20
D = 0.50
SINGLE PULSE
(THERMAL RESPONSE)
25
50
75
100
125
150
175
0
40
80
120
160
200
240
T , Case Temperature
( C)
I
,
D
r
ai
n C
u
r
r
ent
(
A
)
°
C
D
LIMITED BY PACKAGE
Fig 10. Normalized On-Resistance
Vs. Temperature
-60
-40
-20
0
20
40
60
80
100 120 140 160 180
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
T , Junction Temperature
( C)
R
, D
r
a
i
n
-
to
-
S
o
u
r
c
e
O
n
R
e
s
i
s
t
a
n
c
e
(
N
or
m
a
l
i
z
ed)
J
D
S
(
on)
°
V
=
I
=
GS
D
10V
240A




