 | ÐлекÑÑоннÑй компоненÑ: IRF630N | СкаÑаÑÑ:  PDF PDF  ZIP ZIP |
Äîêóìåíòàöèÿ è îïèñàíèÿ www.docs.chipfind.ru
HEXFET
®
Power MOSFET
10/11/00
Parameter
Max.
Units
I
D
@ T
C
= 25°C
Continuous Drain Current, V
GS
@ 10V
9.3
I
D
@ T
C
= 100°C
Continuous Drain Current, V
GS
@ 10V
6.5
A
I
DM
Pulsed Drain Current
37
P
D
@T
C
= 25°C
Power Dissipation
82
W
Linear Derating Factor
0.5
W/°C
V
GS
Gate-to-Source Voltage
±20
V
E
AS
Single Pulse Avalanche Energy
94
mJ
I
AR
Avalanche Current
9.3
A
E
AR
Repetitive Avalanche Energy
8.2
mJ
dv/dt
Peak Diode Recovery dv/dt
8.1
V/ns
T
J
Operating Junction and
-55 to +175
T
STG
Storage Temperature Range
Soldering Temperature, for 10 seconds
300 (1.6mm from case )
°C
Mounting torque, 6-32 or M3 srew
10 lbf·in (1.1N·m)
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Description
V
DSS
= 200V
R
DS(on)
= 0.30
I
D
= 9.3A
S
D
G
l
Advanced Process Technology
l
Dynamic dv/dt Rating
l
175°C Operating Temperature
l
Fast Switching
l
Fully Avalanche Rated
l
Ease of Paralleling
l
Simple Drive Requirements
D
2
Pak
IRF630NS
TO-220AB
IRF630N
TO-262
IRF630NL
IRF630N
IRF630NS
IRF630NL
Fifth Generation HEXFET
®
Power MOSFETs from
International Rectifier utilize advanced processing
techniques to achieve extremely low on-resistance per
silicon area. This benefit, combined with the fast switching
speed and ruggedized device design that HEXFET Power
MOSFETs are well known for, provides the designer with an
extremely efficient and reliable device for use in a wide
variety of applications.
The TO-220 package is universally preferred for all
commercial-industrial applications at power dissipation levels
to approximately 50 watts. The low thermal resistance and
low package cost of the TO-220 contribute to its wide
acceptance throughout the industry.
The D
2
Pak is a surface mount power package capable of
accommodating die sizes up to HEX-4. It provides the
highest power capability and the lowest possible on-
resistance in any existing surface mount package. The
D
2
Pak is suitable for high current applications because of its
low internal connection resistance and can dissipate up to
2.0W in a typical surface mount application.
The through-hole version (IRF630NL) is available for low-
profile application.
www.irf.com
1
PD - 94005A
www.irf.com
2
IRF630N/S/L
S
D
G
Parameter
Min. Typ. Max. Units
Conditions
I
S
Continuous Source Current
MOSFET symbol
(Body Diode)
showing the
I
SM
Pulsed Source Current
integral reverse
(Body Diode)
p-n junction diode.
V
SD
Diode Forward Voltage
1.3
V
T
J
= 25°C, I
S
= 5.4A, V
GS
= 0V
t
rr
Reverse Recovery Time
117
176
ns
T
J
= 25°C, I
F
= 5.4A
Q
rr
Reverse Recovery Charge
542
813
nC
di/dt = 100A/µs
t
on
Forward Turn-On Time
Intrinsic turn-on time is negligible (turn-on is dominated by L
S
+L
D
)
Source-Drain Ratings and Characteristics
9.3
37
A
Parameter
Min. Typ. Max. Units
Conditions
V
(BR)DSS
Drain-to-Source Breakdown Voltage
200
V
V
GS
= 0V, I
D
= 250µA
V
(BR)DSS
/
T
J
Breakdown Voltage Temp. Coefficient
0.26
V/°C
Reference to 25°C, I
D
= 1mA
R
DS(on)
Static Drain-to-Source On-Resistance
0.30
V
GS
= 10V, I
D
= 5.4A
V
GS(th)
Gate Threshold Voltage
2.0
4.0
V
V
DS
= V
GS
, I
D
= 250µA
g
fs
Forward Transconductance
4.9
S
V
DS
= 50V, I
D
= 5.4A
25
µA
V
DS
= 200V, V
GS
= 0V
250
V
DS
= 160V, V
GS
= 0V, T
J
= 150°C
Gate-to-Source Forward Leakage
100
V
GS
= 20V
Gate-to-Source Reverse Leakage
-100
nA
V
GS
= -20V
Q
g
Total Gate Charge
35
I
D
= 5.4A
Q
gs
Gate-to-Source Charge
6.5
nC
V
DS
= 160V
Q
gd
Gate-to-Drain ("Miller") Charge
17
V
GS
= 10V
t
d(on)
Turn-On Delay Time
7.9
V
DD
= 100V
t
r
Rise Time
14
I
D
= 5.4A
t
d(off)
Turn-Off Delay Time
27
R
G
= 13
t
f
Fall Time
15
R
D
= 18
Between lead,
6mm (0.25in.)
from package
and center of die contact
C
iss
Input Capacitance
575
V
GS
= 0V
C
oss
Output Capacitance
89
V
DS
= 25V
C
rss
Reverse Transfer Capacitance
25
pF
= 1.0MHz
nH
Electrical Characteristics @ T
J
= 25°C (unless otherwise specified)
L
D
Internal Drain Inductance
L
S
Internal Source Inductance
S
D
G
I
GSS
ns
4.5
7.5
I
DSS
Drain-to-Source Leakage Current
Thermal Resistance
Parameter
Typ.
Max.
Units
R
JC
Junction-to-Case
1.83
R
CS
Case-to-Sink, Flat, Greased Surface
0.50
°C/W
R
JA
Junction-to-Ambient
62
R
JA
Junction-to-Ambient (PCB mount)
40
IRF630N/S/L
www.irf.com
3
0.01
0.1
1
10
100
0.1
1
10
100
20µs PULSE WIDTH
T = 25 C
J
°
TOP
BOTTOM
VGS
15V
10V
8.0V
7.0V
6.0V
5.5V
5.0V
4.5V
V , Drain-to-Source Voltage (V)
I , Drain-to-Source Current (A)
DS
D
4.5V
0.1
1
10
100
0.1
1
10
100
20µs PULSE WIDTH
T = 175 C
J
°
TOP
BOTTOM
VGS
15V
10V
8.0V
7.0V
6.0V
5.5V
5.0V
4.5V
V , Drain-to-Source Voltage (V)
I , Drain-to-Source Current (A)
DS
D
4.5V
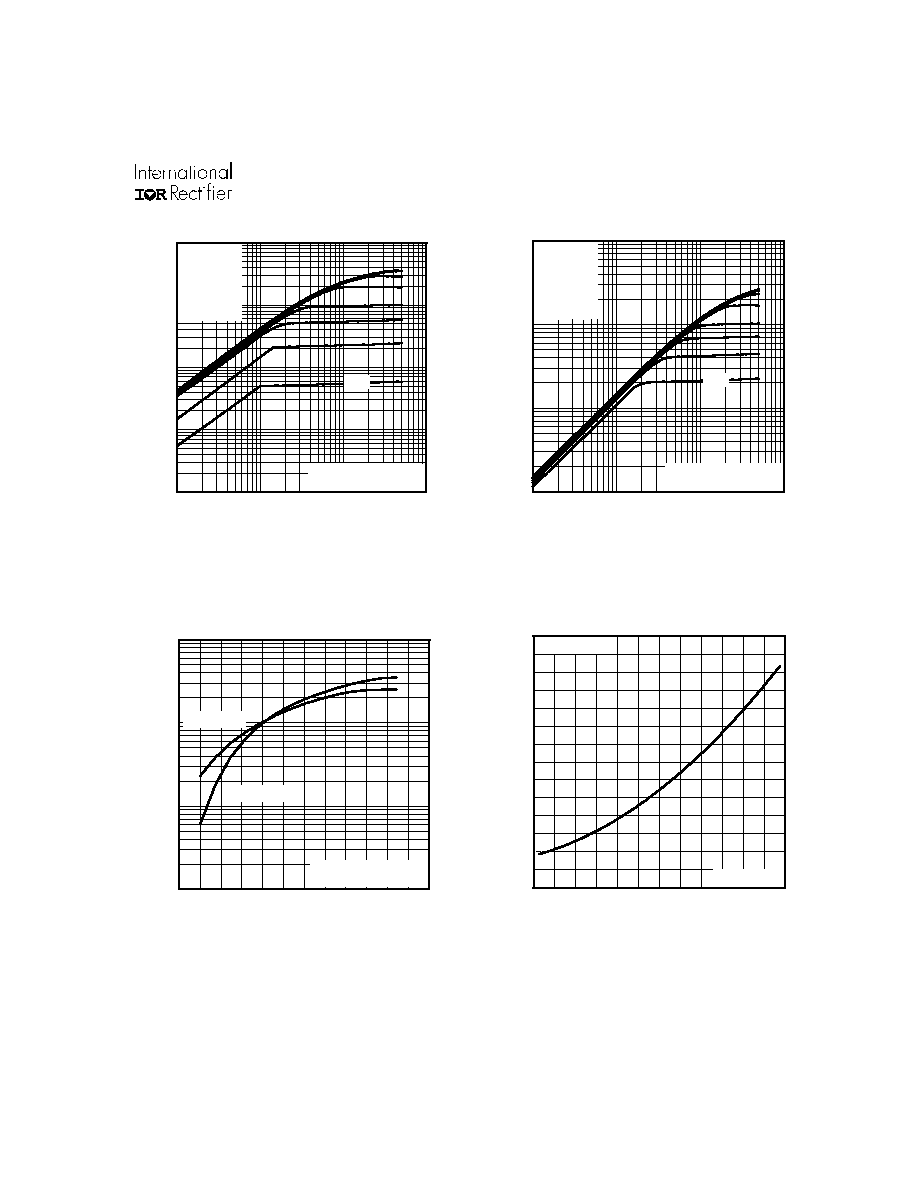
Fig 2. Typical Output Characteristics
Fig 1. Typical Output Characteristics
Fig 3. Typical Transfer Characteristics
0.1
1
10
100
4.0
5.0
6.0
7.0
8.0
9.0
10.0
V = 50V
20µs PULSE WIDTH
DS
V , Gate-to-Source Voltage (V)
I , Drain-to-Source Current (A)
GS
D
T = 25 C
J
°
T = 175 C
J
°
-60 -40 -20
0
20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180
0.0
0.5
1.0
1.5
2.0
2.5
3.0
3.5
T , Junction Temperature( C)
R , Drain-to-Source On Resistance
(Normalized)
J
DS(on)
°
V
=
I =
GS
D
10V
9.3A
Fig 4. Normalized On-Resistance
Vs. Temperature
www.irf.com
4
IRF630N/S/L
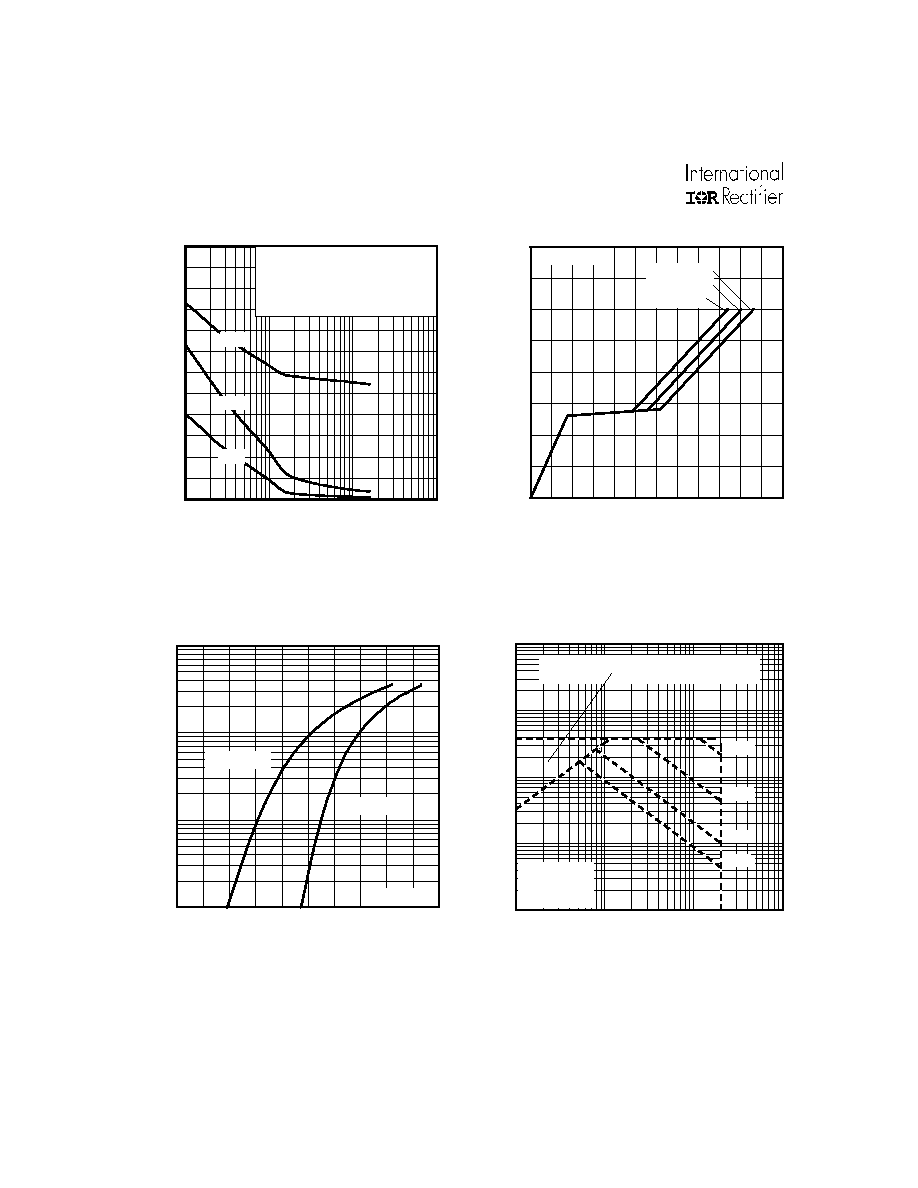
Fig 7. Typical Source-Drain Diode
Forward Voltage
Fig 5. Typical Capacitance Vs.
Drain-to-Source Voltage
Fig 6. Typical Gate Charge Vs.
Gate-to-Source Voltage
0.1
1
10
100
1000
1
10
100
1000
OPERATION IN THIS AREA LIMITED
BY R
DS(on)
Single Pulse
T
T
= 175 C
= 25 C
°
°
J
C
V , Drain-to-Source Voltage (V)
I , Drain Current (A)
I , Drain Current (A)
DS
D
10us
100us
1ms
10ms
Fig 7. Typical Source-Drain Diode
Forward Voltage
Fig 8. Maximum Safe Operating Area
Fig 6. Typical Gate Charge Vs.
Gate-to-Source Voltage
1
10
100
1000
VDS, Drain-to-Source Voltage (V)
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
C, Capacitance(pF)
Coss
Crss
Ciss
VGS = 0V, f = 1 MHZ
Ciss = Cgs + Cgd, Cds SHORTED
Crss = Cgd
Coss = Cds + Cgd
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
0
4
8
12
16
Q , Total Gate Charge (nC)
V , Gate-to-Source Voltage (V)
G
GS
I =
D
5.4A
V
= 40V
DS
V
= 100V
DS
V
= 160V
DS
0.1
1
10
100
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
1.2
V ,Source-to-Drain Voltage (V)
I , Reverse Drain Current (A)
SD
SD
V = 0 V
GS
T = 25 C
J
°
T = 175 C
J
°
IRF630N/S/L
www.irf.com
5
R
D
Fig 9. Maximum Drain Current Vs.
Case Temperature
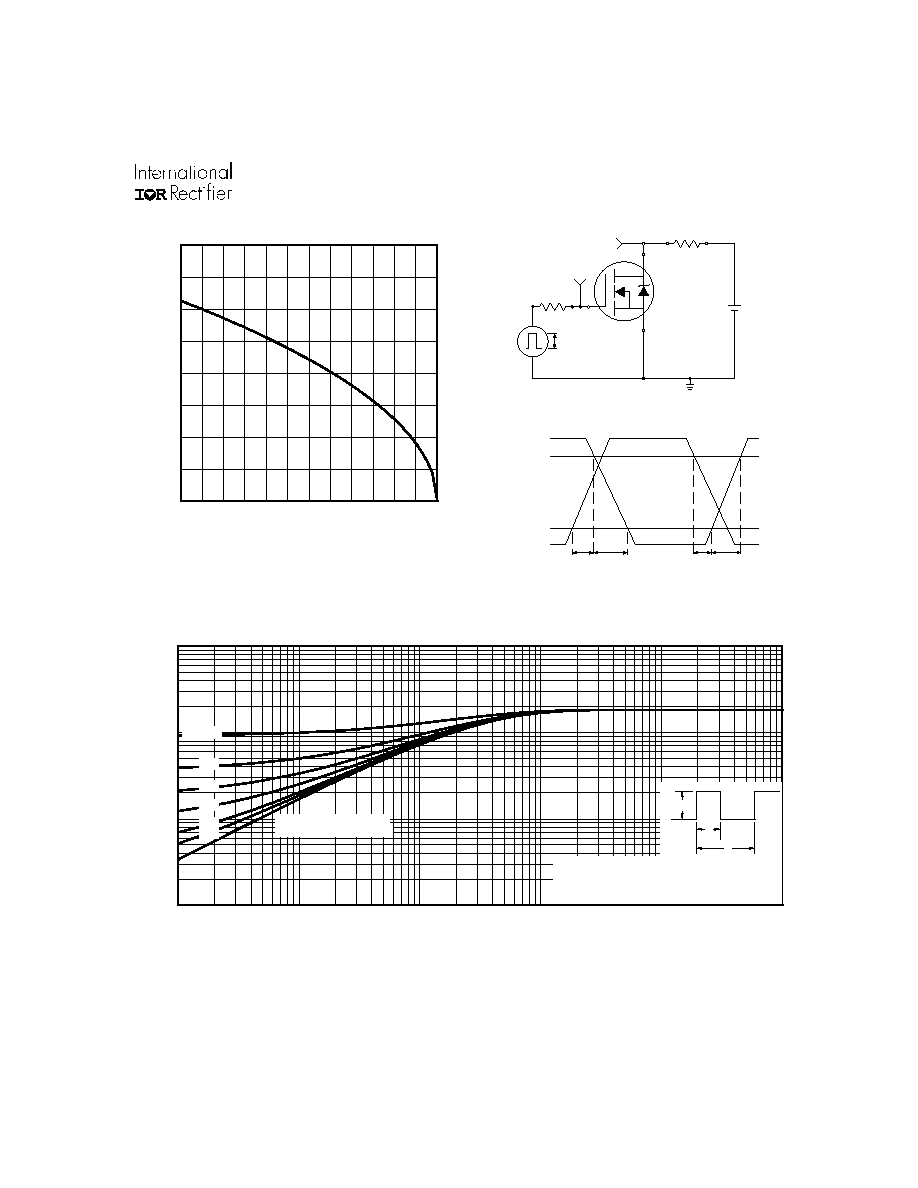
Fig 10a. Switching Time Test Circuit
V
DS
90%
10%
V
GS
t
d(on)
t
r
t
d(off)
t
f
Fig 10b. Switching Time Waveforms
Fig 11. Maximum Effective Transient Thermal Impedance, Junction-to-Case
V
DS
Pulse Width
1
µs
Duty Factor
0.1 %
V
GS
R
G
D.U.T.
10V
+
-
25
50
75
100
125
150
175
0
3
6
9
12
T , Case Temperature ( C)
I , Drain Current (A)
°
C
D
Fig 9. Maximum Drain Current Vs.
Case Temperature
Fig 10a. Switching Time Test Circuit
V
DS
90%
10%
V
GS
t
d(on)
t
r
t
d(off)
t
f
Fig 10b. Switching Time Waveforms
Fig 11. Maximum Effective Transient Thermal Impedance, Junction-to-Case
V
DS
Pulse Width
1
µs
Duty Factor
0.1 %
V
GS
R
G
10V
V
DD
25
50
75
100
125
150
175
0
3
6
9
12
T , Case Temperature ( C)
I , Drain Current (A)
°
C
D
0.01
0.1
1
10
0.00001
0.0001
0.001
0.01
0.1
1
Notes:
1. Duty factor D = t / t
2. Peak T = P
x Z
+ T
1
2
J
DM
thJC
C
P
t
t
DM
1
2
t , Rectangular Pulse Duration (sec)
Thermal Response
(Z )
1
thJC
0.01
0.02
0.05
0.10
0.20
D = 0.50
SINGLE PULSE
(THERMAL RESPONSE)




