
2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21166F-page 1
M
24AA52/24LCS52
Features
� Single supply with operation down to 1.8V
� Low power CMOS technology
- 1 mA active current typical
- 1 �A standby current typical (I-temp)
� Organized as 1 block of 256 bytes (256 x 8)
� Software write protection for lower 128 bytes
� Hardware write protection for entire array
� 2-wire serial interface bus, I
2
CTM compatible
� Schmitt trigger inputs for noise suppression
� Output slope control to eliminate ground bounce
� 100 kHz (24AA52) and 400 kHz (24LCS52)
compatibility
� Self-timed write cycle (including auto-erase)
� Page-write buffer for up to 16 bytes
� 3.5 ms typical write cycle time for page-write
� ESD protection > 4,000V
� 1,000,000 erase/write cycles
� Data retention > 200 years
� 8-lead PDIP, SOIC, TSSOP and MSOP package
� Available for extended temperature ranges:
- Industrial (I): -40�C to +85�C
Device Selection Table
Package Types
Description
The Microchip Technology Inc. 24AA52/24LCS52
(24XX52*) is a 2 Kbit Electrically Erasable PROM
capable of operation across a broad voltage range
(1.8V to 5.5V). This device has a software write protect
feature for the lower half of the array, as well as an
external pin that can be used to write protect the entire
array. The software write protect feature is enabled by
sending the device a special command. Once this fea-
ture has been enabled, it cannot be reversed. In addi-
tion to the software protect feature, there is a WP pin
that can be used to write protect the entire array,
regardless of whether the software write protect regis-
ter has been written or not. This allows the system
designer to protect none, half or all of the array,
depending on the application. The device is organized
as one block of 256 x 8-bit memory with a 2-wire serial
interface. Low voltage design permits operation down
to 1.8V, with standby and active currents of only 1 �A
and 1 mA respectively. The 24XX52 also has a page-
write capability for up to 16 bytes of data. The 24XX52
is available in the standard 8-pin PDIP, surface mount
SOIC, TSSOP and MSOP packages.
Block Diagram
Part
Number
V
CC
Range
Max Clock
Frequency
Temp
Ranges
24AA52
1.8-5.5
400 kHz
(1)
I
24LCS52
2.5-5.5
400 kHz
I
Note 1: 100 kHz for V
CC
<2.5V
2
4
XX5
2
A0
A1
A2
V
SS
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
V
CC
WP
SCL
SDA
PDIP/SOIC/TSSOP/MSOP
I/O
Control
Logic
Memory
Control
Logic
XDEC
HV Generator
Standard
Array
Software write
Write Protect
Circuitry
YDEC
V
CC
V
SS
SENSE AMP
R/W CONTROL
SDA SCL
A0 A1 A2
WP
protected area
(00h-7Fh)
2K I
2
C
TM
Serial EEPROM with Software Write Protect
*24XX52 is used in this document as a generic part number for the 24AA52/24LCS52 devices.

24AA52/24LCS52
DS21166F-page 2
2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
1.0
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Absolute Maximum Ratings
V
CC
.............................................................................................................................................................................6.5V
All inputs and outputs w.r.t. V
SS
......................................................................................................... -0.3V to V
CC
+1.0V
Storage temperature ...............................................................................................................................-65�C to +150�C
Ambient temp. with power applied ..........................................................................................................-40�C to +125�C
ESD protection on all pins
......................................................................................................................................................
4 kV
NOTICE: Stresses above those listed under "Absolute Maximum Ratings" may cause permanent damage to the
device. These are stress ratings only and functional operation of the device at these or any other conditions above
those indicated in the operation sections of the specifications is not implied. Exposure to Absolute Maximum Rating
conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
TABLE 1-1:
DC SPECIFICATIONS
DC CHARACTERISTICS
V
CC
= +1.8V to +5.5V
Industrial (I): T
AMB
= -40�C to +85�C
Param.
No.
Symbol
Characteristic
Min
Typ
Max
Units
Conditions
D1
V
IH
A0, A1, A2, SCL, SDA
and WP pins
--
--
--
--
--
D2
--
High level input voltage
0.7 V
CC
--
--
V
--
D3
V
IL
Low level input voltage
--
--
0.3 V
CC
V
0.2 V
CC
for V
CC
< 2.5V
D4
V
HYS
Hysteresis of Schmitt
trigger inputs
0.05 V
CC
--
--
V
(Note)
D5
V
OL
Low level output voltage
--
--
0.40
V
I
OL
= 3.0 mA, V
CC
= 2.5V
D6
I
LI
Input leakage current
--
--
�10
mA
V
IN
= 0.1V to V
CC
D7
I
LO
Output leakage current
--
--
�10
�A
V
OUT
= 0.1V to V
CC
D8
C
IN
,
C
OUT
Pin capacitance
(all inputs/outputs)
--
--
10
pF
V
CC
= 5.0V (Note)
T
AMB
= 25�C, F
CLK
= 1 MHz
D9
I
CC
write Operating current
--
1.0
3.0
mA
V
CC
= 5.5V, SCL = 400 kHz
D10
I
CC
read
--
0.20
1.0
mA
--
D11
I
CCS
Standby current
--
--
0.36
--
1.0
--
�A
Industrial
SDA = SCL = V
CC
A0, A1, A2, WP = V
SS
Note:
This parameter is periodically sampled and not 100% tested.

2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21166F-page 3
24AA52/24LCS52
TABLE 1-2:
AC SPECIFICATIONS
AC CHARACTERISTICS
V
CC
= +1.8V to +5.5V
Industrial (I): T
AMB
= -40�C to +85�C
Param.
No.
Symbol
Characteristic
Min
Typ
Max
Units
Conditions
1
F
CLK
Clock frequency
--
--
--
--
400
100
kHz
2.5V
V
CC
5.5V
1.8V
V
CC
<
2.5V (24AA52)
2
T
HIGH
Clock high time
600
4000
--
--
--
--
ns
2.5V
V
CC
5.5V
1.8V
V
CC
<
2.5V (24AA52)
3
T
LOW
Clock low time
1300
4700
--
--
--
--
ns
2.5V
V
CC
5.5V
1.8V
V
CC
<
2.5V (24AA52)
4
T
R
SDA and SCL rise time
(Note 1)
--
--
--
--
300
1000
ns
2.5V
V
CC
5.5V
1.8V
V
CC
<
2.5V (24AA52)
5
T
F
SDA and SCL fall time
--
--
--
300
ns
(Note 1)
6
T
HD
:
STA
START condition hold
time
600
4000
--
--
--
--
ns
2.5V
V
CC
5.5V
1.8V
V
CC
<
2.5V (24AA52)
7
T
SU
:
STA
START condition setup
time
600
4700
--
--
--
--
ns
2.5V
V
CC
5.5V
1.8V
V
CC
<
2.5V (24AA52)
8
T
HD
:
DAT
Data input hold time
0
--
--
--
ns
(Note 2)
9
T
SU
:
DAT
Data input setup time
100
250
--
--
--
--
ns
2.5V
V
CC
5.5V
1.8V
V
CC
<
2.5V (24AA52)
10
T
SU
:
STO
STOP condition setup
time
600
4000
--
--
--
--
ns
2.5V
V
CC
5.5V
1.8V
V
CC
<
2.5V (24AA52)
11
T
AA
Output valid from clock
(Note 2)
--
--
--
--
900
3500
ns
2.5V
V
CC
5.5V
1.8V
V
CC
<
2.5V (24AA52)
12
T
BUF
Bus free time: Time the
bus must be free before
a new transmission can
start
1300
4700
--
--
--
--
ns
2.5V
V
CC
5.5V
1.8V
V
CC
<
2.5V (24AA52)
13
T
OF
Output fall time from V
IH
minimum to V
IL
maximum
20+0.1C
B
--
--
--
250
250
ns
2.5V
V
CC
5.5V
1.8V
V
CC
<
2.5V (24AA52)
14
T
SP
Input filter spike
suppression
(SDA and SCL pins)
--
--
50
ns
(Note 1 and Note 3)
15
T
WC
Write cycle time
(byte or page)
--
--
5
ms
--
16
--
Endurance
1M
--
--
cycles 25�C, V
CC
= 5.0V, Block
Mode (Note 4)
Note 1: Not 100% tested. C
B
= total capacitance of one bus line in pF.
2: As a transmitter, the device must provide an internal minimum delay time to bridge the undefined region
(minimum 300 ns) of the falling edge of SCL to avoid unintended generation of START or STOP conditions.
3: The combined T
SP
and V
HYS
specifications are due to new Schmitt trigger inputs, which provide improved
noise spike suppression. This eliminates the need for a T
I
specification for standard operation.
4: This parameter is not tested but ensured by characterization. For endurance estimates in a specific appli-
cation, please consult the Total Endurance Model which can be obtained on Microchip's website:
www.microchip.com.

24AA52/24LCS52
DS21166F-page 4
2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
FIGURE 1-1:
BUS TIMING DATA
FIGURE 1-2:
BUS TIMING START/STOP
7
5
2
4
8
9
10
12
11
14
6
SCL
SDA
IN
SDA
OUT
3
7
6
D4
10
START
STOP
SCL
SDA
2002 Microchip Technology Inc.
DS21166F-page 5
24AA52/24LCS52
2.0
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The 24XX52 supports a bi-directional 2-wire bus and
data transmission protocol. A device that sends data
onto the bus is defined as a transmitter and a device
receiving data as a receiver. The bus has to be con-
trolled by a master device, which generates the serial
clock (SCL), controls the bus access and generates the
START and STOP conditions, while the 24XX52 works
as slave. Both master and slave can operate as trans-
mitter or receiver, but the master device determines
which mode is activated.
3.0
BUS CHARACTERISTICS
The following bus protocol has been defined:
� Data transfer may be initiated only when the bus
is not busy.
� During data transfer, the data line must remain
stable whenever the clock line is HIGH. Changes
in the data line while the clock line is HIGH will be
interpreted as a START or STOP condition.
Accordingly, the following bus conditions have been
defined (Figure 3-1).
3.1
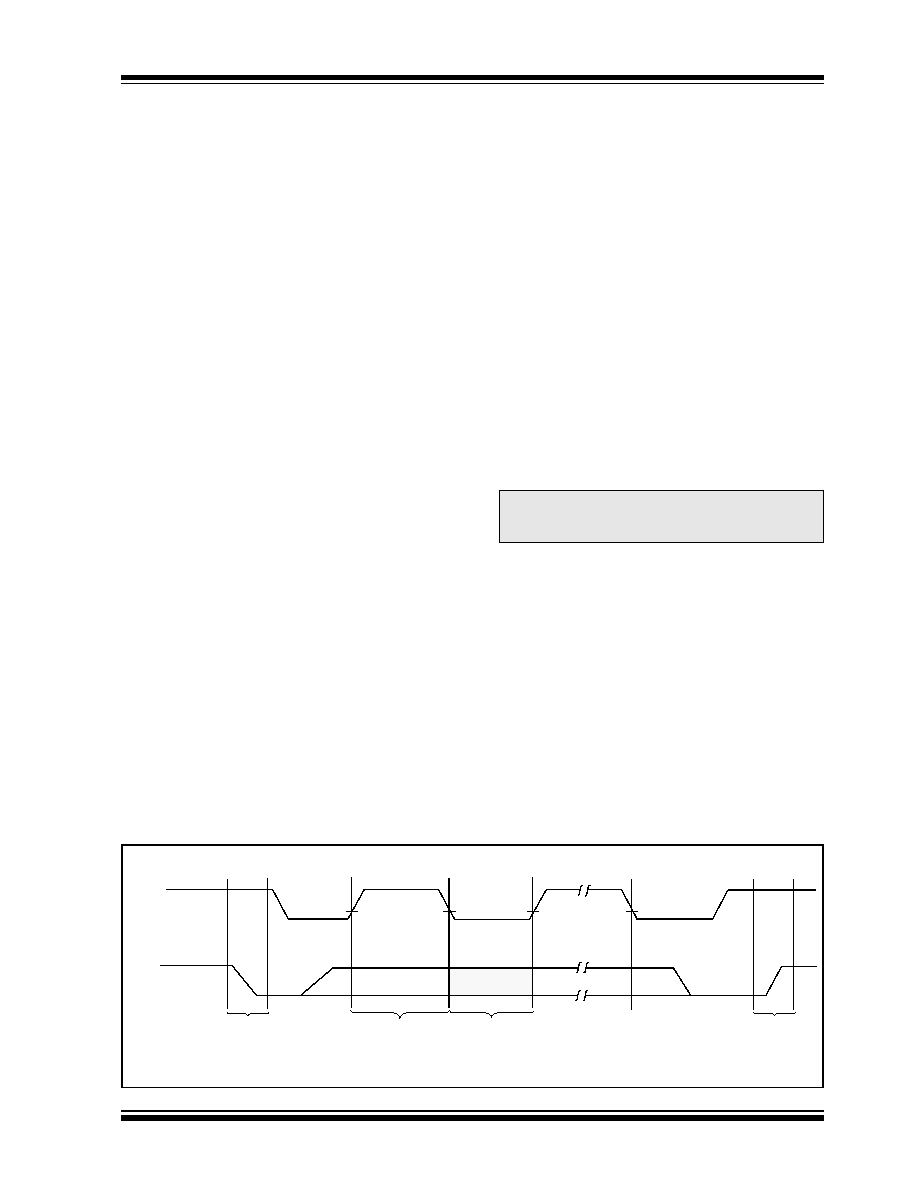
Bus Not Busy (A)
Both data and clock lines remain HIGH.
3.2
Start Data Transfer (B)
A HIGH to LOW transition of the SDA line while the
clock (SCL) is HIGH determines a START condition. All
commands must be preceded by a START condition.
3.3
Stop Data Transfer (C)
A LOW to HIGH transition of the SDA line while the
clock (SCL) is HIGH determines a STOP condition. All
operations must be ended with a STOP condition.
3.4
Data Valid (D)
The state of the data line represents valid data when,
after a START condition, the data line is stable for the
duration of the HIGH period of the clock signal.
The data on the line must be changed during the LOW
period of the clock signal. There is one clock pulse per
bit of data.
Each data transfer is initiated with a START condition
and terminated with a STOP condition. The number of
data bytes transferred between the START and STOP
conditions is determined by the master device and is,
theoretically, unlimited; although only the last sixteen
will be stored when doing a write operation. When an
overwrite does occur, it will replace data in a first-in,
first-out (FIFO) fashion.
3.5
Acknowledge
Each receiving device, when addressed, is obliged to
generate an acknowledge after the reception of each
byte. The master device must generate an extra clock
pulse, which is associated with this acknowledge bit.
The device that acknowledges has to pull down the
SDA line during the acknowledge clock pulse in such a
way that the SDA line is stable LOW during the HIGH
period of the acknowledge related clock pulse. Of
course, setup and hold times must be taken into
account. During reads, a master must signal an end of
data to the slave by not generating an acknowledge bit
on the last byte that has been clocked out of the slave.
In this case, the slave (24XX52) will leave the data line
HIGH to enable the master to generate the STOP con-
dition.
FIGURE 3-1:
DATA TRANSFER SEQUENCE ON THE SERIAL BUS
Note:
The 24XX52 does not generate any
acknowledge bits if an internal
programming cycle is in progress.
SCL
SDA
(A)
(B)
(D)
(D)
(A)
(C)
START
CONDITION
ADDRESS OR
ACKNOWLEDGE
VALID
DATA
ALLOWED
TO CHANGE
STOP
CONDITION




