This document contains detailed information on power considerations, AC/DC electrical
characteristics, and AC timing specifications for revision A,B, and C of the MPC850 Family.
This document contains the following topics:
Topic
Page
Part I, "Overview"
1
Part II, "Features"
3
Part III, "Electrical and Thermal Characteristics"
7
Part IV, "Thermal Characteristics"
9
Part V, "Power Considerations"
10
Part VI, "Bus Signal Timing"
12
Part VII, "IEEE 1149.1 Electrical Specifications"
42
Part VIII, "CPM Electrical Characteristics"
43
Part IX, "Mechanical Data and Ordering Information"
66
Part X, "Document Revision History"
72
Part I Overview
The MPC850 is a versatile, one-chip integrated microprocessor and peripheral
combination that can be used in a variety of controller applications, excelling
particularly in communications and networking products. The MPC850, which
includes support for Ethernet, is specifically designed for cost-sensitive,
remote-access, and telecommunications applications. It is provides functions
similar to the MPC860, with system enhancements such as universal serial bus
(USB) support and a larger (8-Kbyte) dual-port RAM.
In addition to a high-performance embedded MPC8xx core, the MPC850
integrates system functions, such as a versatile memory controller and a
communications processor module (CPM) that incorporates a specialized,
independent RISC communications processor (referred to as the CP). This
separate processor off-loads peripheral tasks from the embedded MPC8xx core.
Hardware Specification
MPC850ABEC/D
Rev. 1, 10/2002
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Family
Communications Controller
Hardware Specifications
2
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
The CPM of the MPC850 supports up to seven serial channels, as follows:
∑
One or two serial communications controllers (SCCs). The SCCs support Ethernet,
ATM (MPC850SR and MPC850DSL), HDLC and a number of other protocols,
along with a transparent mode of operation.
∑
One USB channel
∑
Two serial management controllers (SMCs)
∑
One I
2
C port
∑
One serial peripheral interface (SPI).
Table 1-1 shows the functionality supported by the members of the MPC850 family.
Additional documentation may be provided for parts listed in Table 1-1.
Table 1-1. MPC850 Functionality Matrix
Part
Number of
SCCs
Supported
Ethernet
Support
ATM Support
USB Support
Multi-channel
HDLC Support
Number of
PCMCIA Slots
Supported
MPC850 1
Yes
-
Yes
-
1
MPC850DE
2
Yes
-
Yes
-
1
MPC850SR
2
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
1
MPC850DSL
2
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
1

MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
3
Part II Features
Figure 2-1 is a block diagram of the MPC850, showing its major components and the
relationships among those components:
Figure 2-1. MPC850 Microprocessor Block Diagram
The following list summarizes the main features of the MPC850:
∑
Embedded single-issue, 32-bit MPC8xx core (implementing the PowerPC
architecture) with thirty-two 32-bit general-purpose registers (GPRs)
-- Performs branch folding and branch prediction with conditional prefetch, but
without conditional execution
System Interface Unit
Memory Controller
Bus Interface Unit
System Functions
Real-Time Clock
PCMCIA Interface
Bus
Embedded
2-Kbyte
I-Cache
MMU
1-Kbyte
D-Cache
Data
MMU
Load/Store
Instruction
Bus
Parallel I/O
Baud Rate
Generators
Dual-Port
RAM
Interrupt
Controller
Four
Timers
20 Virtual
2 Virtual
32-Bit RISC Communications
Processor (CP) and Program ROM
SCC2
USB
SPI
Timer
Non-Multiplexed Serial Interface
MPC8xx
Core
Instruction
IDMA
Channels
Serial DMA
and
Channels
Unified Bus
Communications
Processor
Module
Peripheral Bus
SCC3
I
2
C
UTOPIA
Ports
(850SR & DSL)
SMC1
SMC2
Time Slot Assigner
TDMa

4
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
-- 2-Kbyte instruction cache and 1-Kbyte data cache (Harvard architecture)
≠ Caches are two-way, set-associative
≠ Physically addressed
≠ Cache blocks can be updated with a 4-word line burst
≠ Least-recently used (LRU) replacement algorithm
≠ Lockable one-line granularity
-- Memory management units (MMUs) with 8-entry translation lookaside buffers
(TLBs) and fully-associative instruction and data TLBs
-- MMUs support multiple page sizes of 4 Kbytes, 16 Kbytes, 256 Kbytes, 512
Kbytes, and 8 Mbytes; 16 virtual address spaces and eight protection groups
∑
Advanced on-chip emulation debug mode
∑
Data bus dynamic bus sizing for 8, 16, and 32-bit buses
-- Supports traditional 68000 big-endian, traditional x86 little-endian and modified
little-endian memory systems
-- Twenty-six external address lines
∑
Completely static design (0≠80 MHz operation)
∑
System integration unit (SIU)
-- Hardware bus monitor
-- Spurious interrupt monitor
-- Software watchdog
-- Periodic interrupt timer
-- Low-power stop mode
-- Clock synthesizer
-- Decrementer, time base, and real-time clock (RTC) from the PowerPC
architecture
-- Reset controller
-- IEEE 1149.1 test access port (JTAG)
∑
Memory controller (eight banks)
-- Glueless interface to DRAM single in-line memory modules (SIMMs),
synchronous DRAM (SDRAM), static random-access memory (SRAM),
electrically programmable read-only memory (EPROM), flash EPROM, etc.
-- Memory controller programmable to support most size and speed memory
interfaces
-- Boot chip-select available at reset (options for 8, 16, or 32-bit memory)
-- Variable block sizes, 32 Kbytes to 256 Mbytes

MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
5
-- Selectable write protection
-- On-chip bus arbiter supports one external bus master
-- Special features for burst mode support
∑
General-purpose timers
-- Four 16-bit timers or two 32-bit timers
-- Gate mode can enable/disable counting
-- Interrupt can be masked on reference match and event capture
∑
Interrupts
-- Eight external interrupt request (IRQ) lines
-- Twelve port pins with interrupt capability
-- Fifteen internal interrupt sources
-- Programmable priority among SCCs and USB
-- Programmable highest-priority request
∑
Single socket PCMCIA-ATA interface
-- Master (socket) interface, release 2.1 compliant
-- Single PCMCIA socket
-- Supports eight memory or I/O windows
∑
Communications processor module (CPM)
-- 32-bit, Harvard architecture, scalar RISC communications processor (CP)
-- Protocol-specific command sets (for example,
GRACEFUL
STOP
TRANSMIT
stops
transmission after the current frame is finished or immediately if no frame is
being sent and
CLOSE
RXBD
closes the receive buffer descriptor)
-- Supports continuous mode transmission and reception on all serial channels
-- Up to 8 Kbytes of dual-port RAM
-- Twenty serial DMA (SDMA) channels for the serial controllers, including eight
for the four USB endpoints
-- Three parallel I/O registers with open-drain capability
∑
Four independent baud-rate generators (BRGs)
-- Can be connected to any SCC, SMC, or USB
-- Allow changes during operation
-- Autobaud support option
∑
Two SCCs (serial communications controllers)
-- Ethernet/IEEE 802.3, supporting full 10-Mbps operation
-- HDLC/SDLCTM
(all channels supported at 2 Mbps)
-- HDLC bus (implements an HDLC-based local area network (LAN))

6
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
-- Asynchronous HDLC to support PPP (point-to-point protocol)
-- AppleTalk
Æ
-- Universal asynchronous receiver transmitter (UART)
-- Synchronous UART
-- Serial infrared (IrDA)
-- Totally transparent (bit streams)
-- Totally transparent (frame based with optional cyclic redundancy check (CRC))
∑
QUICC multichannel controller (QMC) microcode features
-- Up to 64 independent communication channels on a single SCC
-- Arbitrary mapping of 0≠31 channels to any of 0≠31 TDM time slots
-- Supports either transparent or HDLC protocols for each channel
-- Independent TxBDs/Rx and event/interrupt reporting for each channel
∑
One universal serial bus controller (USB)
-- Supports host controller and slave modes at 1.5 Mbps and 12 Mbps
∑
Two serial management controllers (SMCs)
-- UART
-- Transparent
-- General circuit interface (GCI) controller
-- Can be connected to the time-division-multiplexed (TDM) channel
∑
One serial peripheral interface (SPI)
-- Supports master and slave modes
-- Supports multimaster operation on the same bus
∑
One I
2
C
Æ
(interprocessor-integrated circuit) port
-- Supports master and slave modes
-- Supports multimaster environment
∑
Time slot assigner
-- Allows SCCs and SMCs to run in multiplexed operation
-- Supports T1, CEPT, PCM highway, ISDN basic rate, ISDN primary rate,
user-defined
-- 1- or 8-bit resolution
-- Allows independent transmit and receive routing, frame syncs, clocking
-- Allows dynamic changes
-- Can be internally connected to four serial channels (two SCCs and two SMCs)
∑
Low-power support

MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
7
-- Full high: all units fully powered at high clock frequency
-- Full low: all units fully powered at low clock frequency
-- Doze: core functional units disabled except time base, decrementer, PLL,
memory controller, real-time clock, and CPM in low-power standby
-- Sleep: all units disabled except real-time clock and periodic interrupt timer. PLL
is active for fast wake-up
-- Deep sleep: all units disabled including PLL, except the real-time clock and
periodic interrupt timer
-- Low-power stop: to provide lower power dissipation
-- Separate power supply input to operate internal logic at 2.2 V when operating at
or below 25 MHz
-- Can be dynamically shifted between high frequency (3.3 V internal) and low
frequency (2.2 V internal) operation
∑
Debug interface
-- Eight comparators: four operate on instruction address, two operate on data
address, and two operate on data
-- The MPC850 can compare using the =,
, <, and > conditions to generate
watchpoints
-- Each watchpoint can generate a breakpoint internally
∑
3.3-V operation with 5-V TTL compatibility on all general purpose I/O pins.
Part III Electrical and Thermal
Characteristics
This section provides the AC and DC electrical specifications and thermal characteristics
for the MPC850. Table 3-2 provides the maximum ratings.

8
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
This device contains circuitry protecting against damage due to high-static voltage or
electrical fields; however, it is advised that normal precautions be taken to avoid application
of any voltages higher than maximum-rated voltages to this high-impedance circuit.
Reliability of operation is enhanced if unused inputs are tied to an appropriate logic voltage
level (for example, either GND or V
CC
). Table 4-3 provides the package thermal
characteristics for the MPC850.
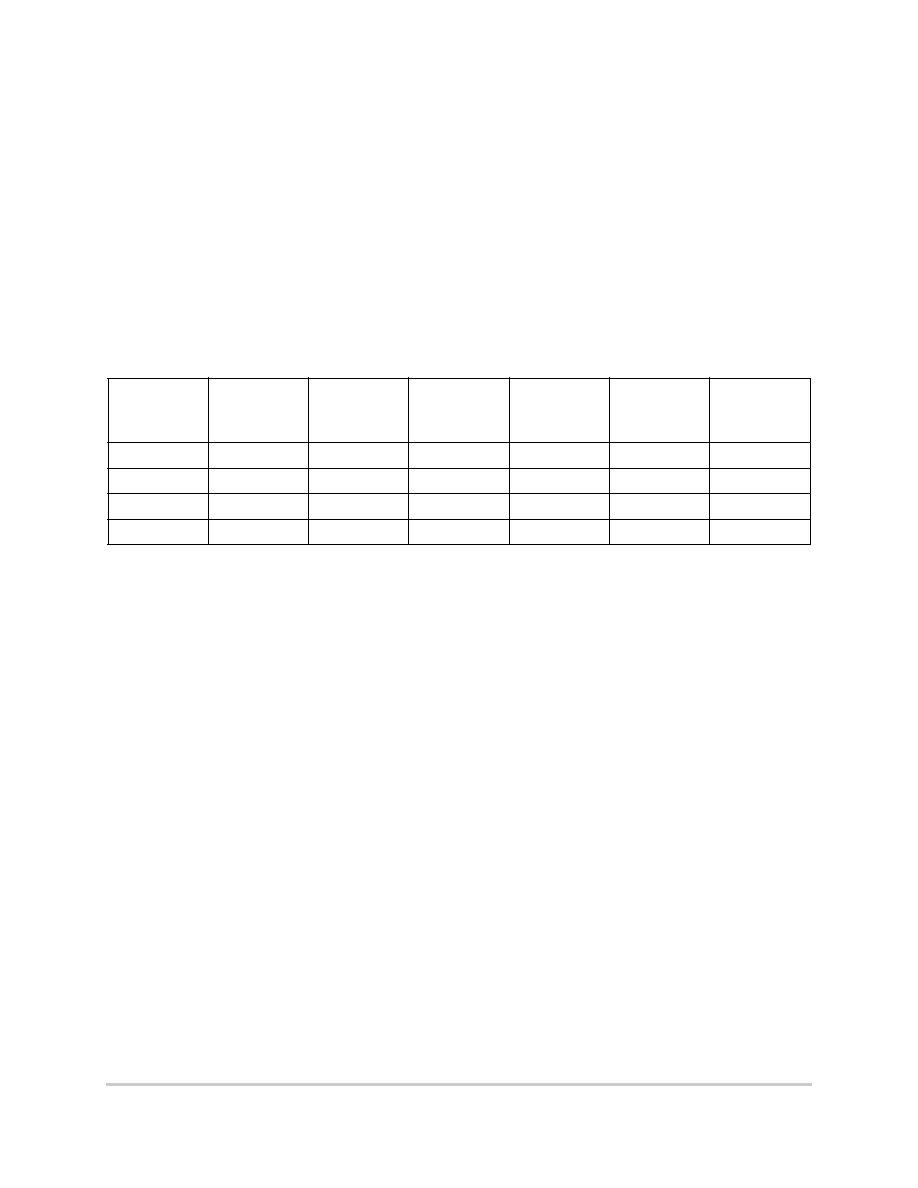
Table 3-2. Maximum Ratings
(GND = 0V)
Rating
Symbol
Value
Unit
Supply voltage
VDDH
-0.3 to 4.0
V
VDDL
-0.3 to 4.0
V
KAPWR
-0.3 to 4.0
V
VDDSYN
-0.3 to 4.0
V
Input voltage
1
1
Functional operating conditions are provided with the DC electrical specifications in Table 4-5. Absolute maximum
ratings are stress ratings only; functional operation at the maxima is not guaranteed. Stress beyond those listed may
affect device reliability or cause permanent damage to the device.
CAUTION: All inputs that tolerate 5 V cannot be more than 2.5 V greater than the supply voltage. This restriction
applies to power-up and normal operation (that is, if the MPC850 is unpowered, voltage greater than 2.5 V must not
be applied to its inputs).
V
in
GND-0.3 to VDDH + 2.5 V
V
Junction temperature
2
2
The MPC850, a high-frequency device in a BGA package, does not provide a guaranteed maximum ambient
temperature. Only maximum junction temperature is guaranteed. It is the responsibility of the user to consider power
dissipation and thermal management. Junction temperature ratings are the same regardless of frequency rating of
the device.
T
j
0 to 95 (standard)
-40 to 95 (extended)
∞C
Storage temperature range
T
stg
-55 to +150
∞C
MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
9
Part IV Thermal Characteristics
Table 4-3 shows the thermal characteristics for the MPC850.
Table 4-4 provides power dissipation information.
Table 4-5 provides the DC electrical characteristics for the MPC850.
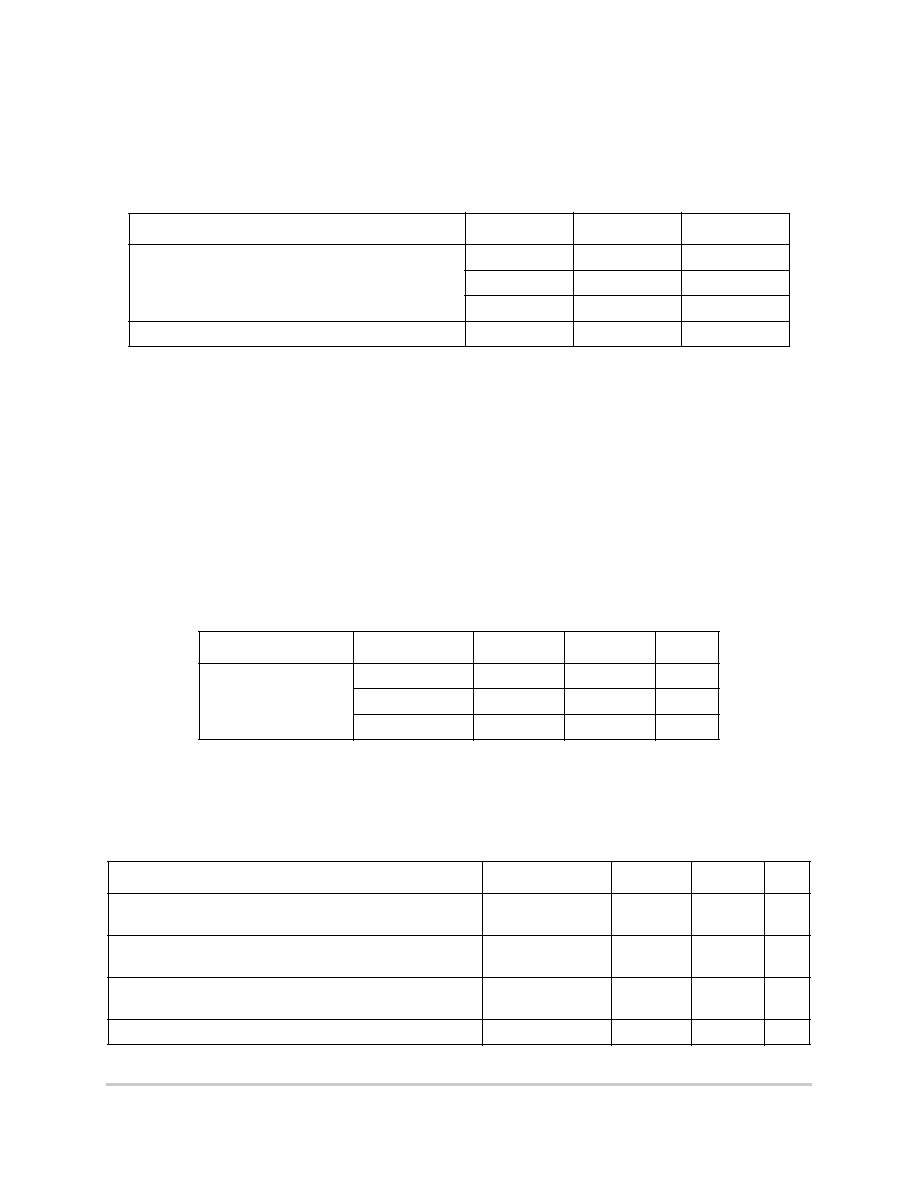
Table 4-3. Thermal Characteristics
Characteristic
Symbol
Value
Unit
Thermal resistance for BGA
1
1
For more information on the design of thermal vias on multilayer boards and BGA layout considerations in
general, refer to AN-1231/D,
Plastic Ball Grid Array Application Note
available from your local Motorola sales
office.
JA
40
2
2
Assumes natural convection and a single layer board (no thermal vias).
∞
C/W
JA
31
3
3
Assumes natural convection, a multilayer board with thermal vias
4
, 1 watt MPC850 dissipation, and a board
temperature rise of 20
∞
C above ambient.
∞
C/W
JA
24
4
4
Assumes natural convection, a multilayer board with thermal vias
4
, 1 watt MPC850 dissipation, and a board
temperature rise of 13
∞
C above ambient.
T
J
= T
A
+ (P
D
∑
JA
)
P
D
= (V
DD
∑
I
DD
) + P
I/O
where:
P
I/O
is the power dissipation on pins
∞
C/W
Thermal Resistance for BGA (junction-to-case)
JC
8
∞
C/W
Table 4-4. Power Dissipation (P
D
)
Characteristic
Frequency (MHz)
Typical
1
1
Typical power dissipation is measured at 3.3V
Maximum
2
2
Maximum power dissipation is measured at 3.65 V
Unit
Power Dissipation
All Revisions
(1:1) Mode
33
TBD
515
mW
40
TBD
590
mW
50
TBD
725
mW
Table 4-5. DC Electrical Specifications
Characteristic
Symbol
Min
Max
Unit
Operating voltage at 40 MHz or less
VDDH, VDDL,
KAPWR, VDDSYN
3.0
3.6
V
Operating voltage at 40 MHz or higher
VDDH, VDDL,
KAPWR, VDDSYN
3.135
3.465
V
Input high voltage (address bus, data bus, EXTAL, EXTCLK,
and all bus control/status signals)
VIH
2.0
3.6
V
Input high voltage (all general purpose I/O and peripheral pins)
VIH
2.0
5.5
V

10
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
Part V Power Considerations
The average chip-junction temperature
,
T
J
,
in
∞
C can be obtained from the equation:
T
J
= T
A
+ (P
D
∑
JA
)
(1)
where
T
A
= Ambient temperature
,
∞
C
JA
= Package thermal resistance
,
junction to ambient
,
∞
C/W
Input low voltage
VIL
GND
0.8
V
EXTAL, EXTCLK input high voltage
VIHC
0.7*(VCC)
VCC+0.3
V
Input leakage current, Vin = 5.5 V (Except TMS, TRST, DSCK
and DSDI pins)
I
in
--
100
µA
Input leakage current, Vin = 3.6V (Except TMS, TRST, DSCK
and DSDI pins)
I
In
--
10
µA
Input leakage current, Vin = 0V (Except TMS, TRST, DSCK and
DSDI pins)
I
In
--
10
µA
Input capacitance
C
in
--
20
pF
Output high voltage, IOH = -2.0 mA, VDDH = 3.0V
except XTAL, XFC, and open-drain pins
VOH
2.4
--
V
Output low voltage
IOL = 2.0 mA CLKOUT
IOL = 3.2 mA
1
IOL = 5.3 mA
2
IOL = 7.0 mA PA[14]/USBOE, PA[12]/TXD2
IOL = 8.9 mA TS, TA, TEA, BI, BB, HRESET, SRESET
VOL
--
0.5
V
1
A[6:31], TSIZ0/REG, TSIZ1, D[0:31], DP[0:3]/IRQ[3:6], RD/WR, BURST, RSV/IRQ2, IP_B[0:1]/IWP[0:1]/VFLS[0:1],
IP_B2/IOIS16_B/AT2, IP_B3/IWP2/VF2, IP_B4/LWP0/VF0, IP_B5/LWP1/VF1, IP_B6/DSDI/AT0, IP_B7/PTR/AT3,
PA[15]/USBRXD, PA[13]/RXD2, PA[9]/L1TXDA/SMRXD2, PA[8]/L1RXDA/SMTXD2,
PA[7]/CLK1/TIN1/L1RCLKA/BRGO1, PA[6]/CLK2/TOUT1/TIN3, PA[5]/CLK3/TIN2/L1TCLKA/BRGO2,
PA[4]/CLK4/TOUT2/TIN4, PB[31]/SPISEL, PB[30]/SPICLK/TXD3, PB[29]/SPIMOSI /RXD3,
PB[28]/SPIMISO/BRGO3, PB[27]/I2CSDA/BRGO1, PB[26]/I2CSCL/BRGO2, PB[25]/SMTXD1/TXD3,
PB[24]/SMRXD1/RXD3, PB[23]/SMSYN1/SDACK1, PB[22]/SMSYN2/SDACK2, PB[19]/L1ST1,
PB[18]/RTS2/L1ST2, PB[17]/L1ST3, PB[16]/L1RQa/L1ST4, PC[15]/DREQ0/L1ST5, PC[14]/DREQ1/RTS2/L1ST6,
PC[13]/L1ST7/RTS3, PC[12]/L1RQa/L1ST8, PC[11]/USBRXP, PC[10]/TGATE1/USBRXN, PC[9]/CTS2,
PC[8]/CD2/TGATE1, PC[7]/USBTXP, PC[6]/USBTXN, PC[5]/CTS3/L1TSYNCA/SDACK1, PC[4]/CD3/L1RSYNCA,
PD[15], PD[14], PD[13], PD[12], PD[11], PD[10], PD[9], PD[8], PD[7], PD[6], PD[5], PD[4], PD[3]
2
BDIP/GPL_B5, BR, BG, FRZ/IRQ6, CS[0:5], CS6/CE1_B, CS7/CE2_B, WE0/BS_AB0/IORD, WE1/BS_AB1/IOWR,
WE2/BS_AB2/PCOE, WE3/BS_AB3/PCWE, GPL_A0/GPL_B0, OE/GPL_A1/GPL_B1,
GPL_A[2:3]/GPL_B[2:3]/CS[2:3], UPWAITA/GPL_A4/AS, UPWAITB/GPL_B4, GPL_A5, ALE_B/DSCK/AT1,
OP2/MODCK1/STS, OP3/MODCK2/DSDO
Table 4-5. DC Electrical Specifications (continued)
Characteristic
Symbol
Min
Max
Unit

MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
11
Layout Practices
P
D
= P
INT
+ P
I/O
P
INT
= I
DD
x V
DD
,
watts--chip internal power
P
I/O
= Power dissipation on input and output pins--user determined
For most applications P
I/O
< 0.3
∑
P
INT
and can be neglected. If P
I/O
is neglected
,
an
approximate relationship between P
D
and T
J
is:
P
D
= K
˜
(T
J
+ 273
∞
C)
(2)
Solving equations (1) and (2) for K gives:
K = P
D
∑
(T
A
+ 273
∞
C) +
JA
∑ P
D
2
(3)
where K is a constant pertaining to the particular part. K can be determined from equation
(3) by measuring P
D
(at equilibrium) for a known T
A
. Using this value of K
,
the values of
P
D
and T
J
can be obtained by solving equations (1) and (2) iteratively for any value of T
A
.
5.1
Layout Practices
Each V
CC
pin on the MPC850 should be provided with a low-impedance path to the board's
supply. Each GND pin should likewise be provided with a low-impedance path to ground.
The power supply pins drive distinct groups of logic on chip. The V
CC
power supply should
be bypassed to ground using at least four 0.1 µF by-pass capacitors located as close as
possible to the four sides of the package. The capacitor leads and associated printed circuit
traces connecting to chip V
CC
and GND should be kept to less than half an inch per capacitor
lead. A four-layer board is recommended, employing two inner layers as V
CC
and GND
planes.
All output pins on the MPC850 have fast rise and fall times. Printed circuit (PC) trace
interconnection length should be minimized in order to minimize undershoot and
reflections caused by these fast output switching times. This recommendation particularly
applies to the address and data busses. Maximum PC trace lengths of six inches are
recommended. Capacitance calculations should consider all device loads as well as
parasitic capacitances due to the PC traces. Attention to proper PCB layout and bypassing
becomes especially critical in systems with higher capacitive loads because these loads
create higher transient currents in the V
CC
and GND circuits. Pull up all unused inputs or
signals that will be inputs during reset. Special care should be taken to minimize the noise
levels on the PLL supply pins.

12
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
Layout Practices
Part VI Bus Signal Timing
Table 6-6 provides the bus operation timing for the MPC850 at 50 MHz, 66 MHz, and 80
MHz. Timing information for other bus speeds can be interpolated by equation using the
MPC850 Electrical Specifications Spreadsheet found at http://www.mot.com/netcomm.
The maximum bus speed supported by the MPC850 is 50 MHz. Higher-speed parts must
be operated in half-speed bus mode (for example, an MPC850 used at 66 MHz must be
configured for a 33 MHz bus).
The timing for the MPC850 bus shown assumes a 50-pF load. This timing can be derated
by 1 ns per 10 pF. Derating calculations can also be performed using the MPC850 Electrical
Specifications Spreadsheet.
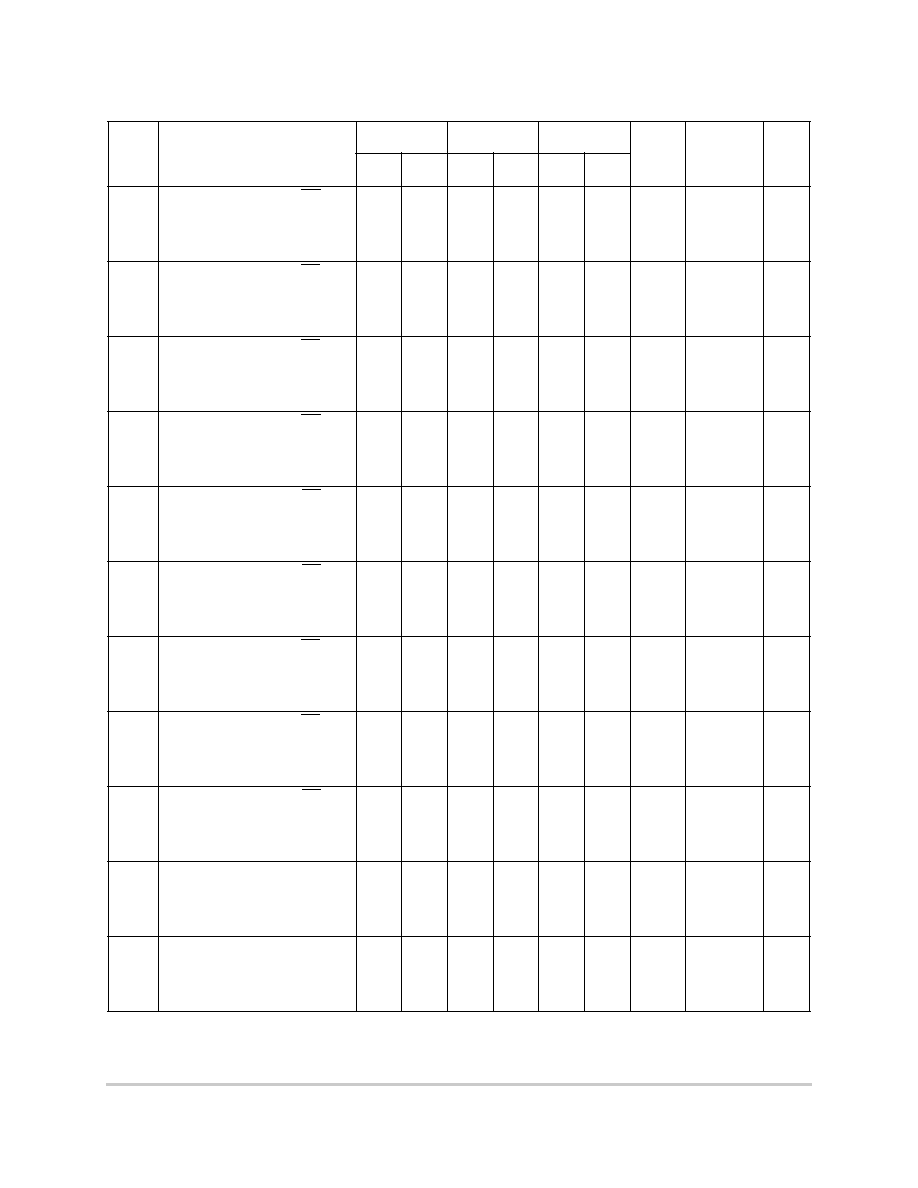
Table 6-6. Bus Operation Timing
1
Num
Characteristic
50 MHz
66 MHz
80 MHz
FFACT
Cap Load
(default
50 pF)
Unit
Min
Max
Min
Max
Min
Max
B1
CLKOUT period
20
--
30.30
--
25
--
--
--
ns
B1a
EXTCLK to CLKOUT phase
skew (EXTCLK > 15 MHz and
MF <= 2)
-0.90
0.90
-0.90
0.90
-0.90
0.90
--
50.00
ns
B1b
EXTCLK to CLKOUT phase
skew (EXTCLK > 10 MHz and
MF < 10)
-2.30
2.30
-2.30
2.30
-2.30
2.30
--
50.00
ns
B1c
CLKOUT phase jitter (EXTCLK
> 15 MHz and MF <= 2)
2
-0.60
0.60
-0.60
0.60
-0.60
0.60
--
50.00
ns
B1d
CLKOUT phase jitter
2
-2.00
2.00
-2.00
2.00
-2.00
2.00
--
50.00
ns
B1e
CLKOUT frequency jitter (MF <
10)
2
--
0.50
--
0.50
--
0.50
--
50.00
%
B1f
CLKOUT frequency jitter (10 <
MF < 500)
2
--
2.00
--
2.00
--
2.00
--
50.00
%
B1g
CLKOUT frequency jitter (MF >
500)
2
--
3.00
--
3.00
--
3.00
--
50.00
%
B1h
Frequency jitter on EXTCLK
3
--
0.50
--
0.50
--
0.50
--
50.00
%
B2
CLKOUT pulse width low
8.00
--
12.12
--
10.00
--
--
50.00
ns
B3
CLKOUT width high
8.00
--
12.12
--
10.00
--
--
50.00
ns
B4
CLKOUT rise time
--
4.00
--
4.00
--
4.00
--
50.00
ns
B5
CLKOUT fall time
--
4.00
--
4.00
--
4.00
--
50.00
ns
B7
CLKOUT to A[6≠31],
RD/WR, BURST, D[0≠31],
DP[0≠3] invalid
5.00
--
7.58
--
6.25
--
0.250
50.00
ns
B7a
CLKOUT to TSIZ[0≠1], REG,
RSV, AT[0≠3], BDIP, PTR invalid
5.00
--
7.58
--
6.25
--
0.250
50.00
ns

MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
13
Layout Practices
B7b
CLKOUT to BR, BG, FRZ,
VFLS[0≠1], VF[0≠2] IWP[0≠2],
LWP[0≠1], STS invalid
4
5.00
--
7.58
--
6.25
--
0.250
50.00
ns
B8
CLKOUT to A[6≠31],
RD/WR, BURST, D[0≠31],
DP[0≠3] valid
5.00
11.75
7.58
14.33
6.25
13.00
0.250
50.00
ns
B8a
CLKOUT to TSIZ[0≠1], REG,
RSV, AT[0≠3] BDIP, PTR valid
5.00
11.75
7.58
14.33
6.25
13.00
0.250
50.00
ns
B8b
CLKOUT to BR, BG, VFLS[0≠1],
VF[0≠2], IWP[0≠2], FRZ,
LWP[0≠1], STS valid
4
5.00
11.74
7.58
14.33
6.25
13.00
0.250
50.00
ns
B9
CLKOUT to A[6≠31] RD/WR,
BURST, D[0≠31], DP[0≠3],
TSIZ[0≠1], REG, RSV, AT[0≠3],
PTR high-Z
5.00
11.75
7.58
14.33
6.25
13.00
0.250
50.00
ns
B11
CLKOUT to TS, BB assertion
5.00
11.00
7.58
13.58
6.25
12.25
0.250
50.00
ns
B11a CLKOUT to TA, BI assertion,
(When driven by the memory
controller or PCMCIA interface)
2.50
9.25
2.50
9.25
2.50
9.25
--
50.00
ns
B12
CLKOUT to TS, BB negation
5.00
11.75
7.58
14.33
6.25
13.00
0.250
50.00
ns
B12a CLKOUT to TA, BI negation
(when driven by the memory
controller or PCMCIA interface)
2.50
11.00
2.50
11.00
2.50
11.00
--
50.00
ns
B13
CLKOUT to TS, BB high-Z
5.00
19.00
7.58
21.58
6.25
20.25
0.250
50.00
ns
B13a CLKOUT to TA, BI high-Z, (when
driven by the memory controller
or PCMCIA interface)
2.50
15.00
2.50
15.00
2.50
15.00
--
50.00
ns
B14
CLKOUT to TEA assertion
2.50
10.00
2.50
10.00
2.50
10.00
--
50.00
ns
B15
CLKOUT to TEA high-Z
2.50
15.00
2.50
15.00
2.50
15.00
--
50.00
ns
B16
TA, BI valid to CLKOUT(setup
time)
5
9.75
--
9.75
--
9.75
--
--
50.00
ns
B16a TEA, KR, RETRY, valid to
CLKOUT (setup time
) 5
10.00
--
10.00
--
10.00
--
--
50.00
ns
B16b BB, BG, BR valid to CLKOUT
(setup time)
6
8.50
--
8.50
--
8.50
--
--
50.00
ns
B17
CLKOUT to TA, TEA, BI, BB, BG,
BR valid (Hold time).
5
1.00
--
1.00
--
1.00
--
--
50.00
ns
B17a CLKOUT to KR, RETRY, except
TEA valid (hold time)
2.00
--
2.00
--
2.00
--
--
50.00
ns
B18
D[0≠31], DP[0≠3] valid to
CLKOUT rising edge (setup
time)
7
6.00
--
6.00
--
6.00
--
--
50.00
ns
Table 6-6. Bus Operation Timing
1
(continued)
Num
Characteristic
50 MHz
66 MHz
80 MHz
FFACT
Cap Load
(default
50 pF)
Unit
Min
Max
Min
Max
Min
Max

14
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
Layout Practices
B19
CLKOUT rising edge to D[0≠31],
DP[0≠3] valid (hold time)
7
1.00
--
1.00
--
1.00
--
--
50.00
ns
B20
D[0≠31], DP[0≠3] valid to
CLKOUT falling edge (setup
time)
8
4.00
--
4.00
--
4.00
--
--
50.00
ns
B21
CLKOUT falling edge to
D[0≠31], DP[0≠3] valid (hold
time)
8
2.00
--
2.00
--
2.00
--
--
--
--
B22
CLKOUT rising edge to CS
asserted GPCM ACS = 00
5.00
11.75
7.58
14.33
6.25
13.00
0.250
50.00
ns
B22a CLKOUT falling edge to CS
asserted GPCM ACS = 10,
TRLX = 0,1
--
8.00
--
8.00
--
8.00
--
50.00
ns
B22b CLKOUT falling edge to CS
asserted GPCM ACS = 11,
TRLX = 0, EBDF = 0
5.00
11.75
7.58
14.33
6.25
13.00
0.250
50.00
ns
B22c
CLKOUT falling edge to CS
asserted GPCM ACS = 11,
TRLX = 0, EBDF = 1
7.00
14.00 11.00 18.00
9.00
16.00
0.375
50.00
ns
B23
CLKOUT rising edge to CS
negated GPCM read access,
GPCM write access ACS = 00,
TRLX = 0 & CSNT = 0
2.00
8.00
2.00
8.00
2.00
8.00
--
50.00
ns
B24
A[6≠31] to CS asserted GPCM
ACS = 10, TRLX = 0.
3.00
--
6.00
--
4.00
--
0.250
50.00
ns
B24a A[6≠31] to CS asserted GPCM
ACS = 11, TRLX = 0
8.00
--
13.00
--
11.00
--
0.500
50.00
ns
B25
CLKOUT rising edge to OE,
WE[0≠3] asserted
--
9.00
--
9.00
--
9.00
--
50.00
ns
B26
CLKOUT rising edge to OE
negated
2.00
9.00
2.00
9.00
2.00
9.00
--
50.00
ns
B27
A[6≠31] to CS asserted GPCM
ACS = 10, TRLX = 1
23.00
--
36.00
--
29.00
--
1.250
50.00
ns
B27a A[6≠31] to CS asserted GPCM
ACS = 11, TRLX = 1
28.00
--
43.00
--
36.00
--
1.500
50.00
ns
B28
CLKOUT rising edge to WE[0≠3]
negated GPCM write access
CSNT = 0
--
9.00
--
9.00
--
9.00
--
50.00
ns
B28a CLKOUT falling edge to
WE[0≠3] negated GPCM write
access TRLX = 0,1 CSNT = 1,
EBDF = 0
5.00
12.00
8.00
14.00
6.00
13.00
0.250
50.00
ns
Table 6-6. Bus Operation Timing
1
(continued)
Num
Characteristic
50 MHz
66 MHz
80 MHz
FFACT
Cap Load
(default
50 pF)
Unit
Min
Max
Min
Max
Min
Max

MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
15
Layout Practices
B28b CLKOUT falling edge to CS
negated GPCM write access
TRLX = 0,1 CSNT = 1, ACS = 10
or ACS = 11, EBDF = 0
--
12.00
--
14.00
--
13.00
0.250
50.00
ns
B28c
CLKOUT falling edge to
WE[0≠3] negated GPCM write
access TRLX = 0,1 CSNT = 1
write access TRLX = 0, CSNT =
1, EBDF = 1
7.00
14.00 11.00 18.00
9.00
16.00
0.375
50.00
ns
B28d CLKOUT falling edge to CS
negated GPCM write access
TRLX = 0,1 CSNT = 1, ACS = 10
or ACS = 11, EBDF = 1
--
14.00
--
18.00
--
16.00
0.375
50.00
ns
B29
WE[0≠3] negated to D[0≠31],
DP[0≠3] high-Z GPCM write
access, CSNT = 0
3.00
--
6.00
--
4.00
--
0.250
50.00
ns
B29a WE[0≠3] negated to D[0≠31],
DP[0≠3] high-Z GPCM write
access, TRLX = 0 CSNT = 1,
EBDF = 0
8.00
--
13.00
--
11.00
--
0.500
50.00
ns
B29b CS negated to D[0≠31],
DP[0≠3], high-Z GPCM write
access, ACS = 00, TRLX = 0 &
CSNT = 0
3.00
--
6.00
--
4.00
--
0.250
50.00
ns
B29c CS negated to D[0≠31], DP[0≠3]
high-Z GPCM write access,
TRLX = 0, CSNT = 1, ACS = 10
or ACS = 11, EBDF = 0
8.00
--
13.00
--
11.00
--
0.500
50.00
ns
B29d WE[0≠3] negated to D[0≠31],
DP[0≠3] high-Z GPCM write
access, TRLX = 1, CSNT = 1,
EBDF = 0
28.00
--
43.00
--
36.00
--
1.500
50.00
ns
B29e CS negated to D[0≠31], DP[0≠3]
high-Z GPCM write access,
TRLX = 1, CSNT = 1, ACS = 10
or ACS = 11, EBDF = 0
28.00
--
43.00
--
36.00
--
1.500
50.00
ns
B29f
WE[0≠3] negated to D[0≠31],
DP[0≠3] high-Z GPCM write
access TRLX = 0, CSNT = 1,
EBDF = 1
5.00
--
9.00
--
7.00
--
0.375
50.00
ns
B29g CS negated to D[0≠31], DP[0≠3]
high-Z GPCM write access
TRLX = 0, CSNT = 1, ACS = 10
or ACS = 11, EBDF = 1
5.00
--
9.00
--
7.00
--
0.375
50.00
ns
Table 6-6. Bus Operation Timing
1
(continued)
Num
Characteristic
50 MHz
66 MHz
80 MHz
FFACT
Cap Load
(default
50 pF)
Unit
Min
Max
Min
Max
Min
Max

16
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
Layout Practices
B29h WE[0≠3] negated to D[0≠31],
DP[0≠3] high-Z GPCM write
access TRLX = 0, CSNT = 1,
EBDF = 1
25.00
--
39.00
--
31.00
--
1.375
50.00
ns
B29i
CS negated to D[0≠31], DP[0≠3]
high-Z GPCM write access,
TRLX = 1, CSNT = 1, ACS = 10
or ACS = 11, EBDF = 1
25.00
--
39.00
--
31.00
--
1.375
50.00
ns
B30
CS, WE[0≠3] negated to A[6≠31]
invalid
GPCM write access
9
3.00
--
6.00
--
4.00
--
0.250
50.00
ns
B30a WE[0≠3] negated to A[6≠31]
invalid
GPCM write access, TRLX = 0,
CSNT = 1, CS negated to
A[6≠31] invalid GPCM write
access TRLX = 0, CSNT =1,
ACS = 10 or ACS = 11, EBDF =
0
8.00
--
13.00
--
11.00
--
0.500
50.00
ns
B30b WE[0≠3] negated to A[6≠31]
invalid
GPCM write access, TRLX = 1,
CSNT = 1. CS negated to
A[6≠31] Invalid GPCM write
access TRLX = 1, CSNT = 1,
ACS = 10 or ACS = 11, EBDF =
0
28.00
--
43.00
--
36.00
--
1.500
50.00
ns
B30c
WE[0≠3] negated to A[6≠31]
invalid
GPCM write access, TRLX = 0,
CSNT = 1. CS negated to
A[6≠31] invalid GPCM write
access, TRLX = 0, CSNT = 1,
ACS = 10 or ACS = 11, EBDF =
1
5.00
--
8.00
--
6.00
--
0.375
50.00
ns
B30d WE[0≠3] negated to A[6≠31]
invalid GPCM write access
TRLX = 1, CSNT =1, CS
negated to A[6≠31] invalid
GPCM write access TRLX = 1,
CSNT = 1, ACS = 10 or ACS =
11, EBDF = 1
25.00
--
39.00
--
31.00
--
1.375
50.00
ns
B31
CLKOUT falling edge to CS valid
- as requested by control bit
CST4 in the corresponding word
in the UPM
1.50
6.00
1.50
6.00
1.50
6.00
--
50.00
ns
Table 6-6. Bus Operation Timing
1
(continued)
Num
Characteristic
50 MHz
66 MHz
80 MHz
FFACT
Cap Load
(default
50 pF)
Unit
Min
Max
Min
Max
Min
Max
MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
17
Layout Practices
B31a CLKOUT falling edge to CS valid
- as requested by control bit
CST1 in the corresponding word
in the UPM
5.00
12.00
8.00
14.00
6.00
13.00
0.250
50.00
ns
B31b CLKOUT rising edge to CS valid
- as requested by control bit
CST2 in the corresponding word
in the UPM
1.50
8.00
1.50
8.00
1.50
8.00
--
50.00
ns
B31c
CLKOUT rising edge to CS valid
- as requested by control bit
CST3 in the corresponding word
in the UPM
5.00
12.00
8.00
14.00
6.00
13.00
0.250
50.00
ns
B31d CLKOUT falling edge to CS valid
- as requested by control bit
CST1 in the corresponding word
in the UPM EBDF = 1
9.00
14.00 13.00 18.00 11.00 16.00
0.375
50.00
ns
B32
CLKOUT falling edge to BS valid
- as requested by control bit
BST4 in the corresponding word
in the UPM
1.50
6.00
1.50
6.00
1.50
6.00
--
50.00
ns
B32a CLKOUT falling edge to BS valid
- as requested by control bit
BST1 in the corresponding word
in the UPM, EBDF = 0
5.00
12.00
8.00
14.00
6.00
13.00
0.250
50.00
ns
B32b CLKOUT rising edge to BS valid
- as requested by control bit
BST2 in the corresponding word
in the UPM
1.50
8.00
1.50
8.00
1.50
8.00
--
50.00
ns
B32c
CLKOUT rising edge to BS valid
- as requested by control bit
BST3 in the corresponding word
in the UPM
5.00
12.00
8.00
14.00
6.00
13.00
0.250
50.00
ns
B32d CLKOUT falling edge to BS valid
- as requested by control bit
BST1 in the corresponding word
in the UPM, EBDF = 1
9.00
14.00 13.00 18.00 11.00 16.00
0.375
50.00
ns
B33
CLKOUT falling edge to GPL
valid - as requested by control
bit GxT4 in the corresponding
word in the UPM
1.50
6.00
1.50
6.00
1.50
6.00
--
50.00
ns
B33a CLKOUT rising edge to GPL
valid - as requested by control
bit GxT3 in the corresponding
word in the UPM
5.00
12.00
8.00
14.00
6.00
13.00
0.250
50.00
ns
Table 6-6. Bus Operation Timing
1
(continued)
Num
Characteristic
50 MHz
66 MHz
80 MHz
FFACT
Cap Load
(default
50 pF)
Unit
Min
Max
Min
Max
Min
Max

18
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
Layout Practices
B34
A[6≠31] and D[0≠31] to CS valid
- as requested by control bit
CST4 in the corresponding word
in the UPM
3.00
--
6.00
--
4.00
--
0.250
50.00
ns
B34a A[6≠31] and D[0≠31] to CS valid
- as requested by control bit
CST1 in the corresponding word
in the UPM
8.00
--
13.00
--
11.00
--
0.500
50.00
ns
B34b A[6≠31] and D[0≠31] to CS valid
- as requested by CST2 in the
corresponding word in UPM
13.00
--
21.00
--
17.00
--
0.750
50.00
ns
B35
A[6≠31] to CS valid - as
requested by control bit BST4 in
the corresponding word in UPM
3.00
--
6.00
--
4.00
--
0.250
50.00
ns
B35a A[6≠31] and D[0≠31] to BS valid
- as requested by BST1 in the
corresponding word in the UPM
8.00
--
13.00
--
11.00
--
0.500
50.00
ns
B35b A[6≠31] and D[0≠31] to BS valid
- as requested by control bit
BST2 in the corresponding word
in the UPM
13.00
--
21.00
--
17.00
--
0.750
50.00
ns
B36
A[6≠31] and D[0≠31] to GPL
valid - as requested by control
bit GxT4 in the corresponding
word in the UPM
3.00
--
6.00
--
4.00
--
0.250
50.00
ns
B37
UPWAIT valid to CLKOUT falling
edge
10
6.00
--
6.00
--
6.00
--
--
50.00
ns
B38
CLKOUT falling edge to
UPWAIT valid
10
1.00
--
1.00
--
1.00
--
--
50.00
ns
B39
AS valid to CLKOUT rising edge
11
7.00
--
7.00
--
7.00
--
--
50.00
ns
B40
A[6≠31], TSIZ[0≠1], RD/WR,
BURST, valid to CLKOUT rising
edge.
7.00
--
7.00
--
7.00
--
--
50.00
ns
B41
TS valid to CLKOUT rising edge
(setup time)
7.00
--
7.00
--
7.00
--
--
50.00
ns
B42
CLKOUT rising edge to TS valid
(hold time)
2.00
--
2.00
--
2.00
--
--
50.00
ns
B43
AS negation to memory
controller signals negation
--
TBD
--
TBD
TBD
--
--
50.00
ns
Table 6-6. Bus Operation Timing
1
(continued)
Num
Characteristic
50 MHz
66 MHz
80 MHz
FFACT
Cap Load
(default
50 pF)
Unit
Min
Max
Min
Max
Min
Max
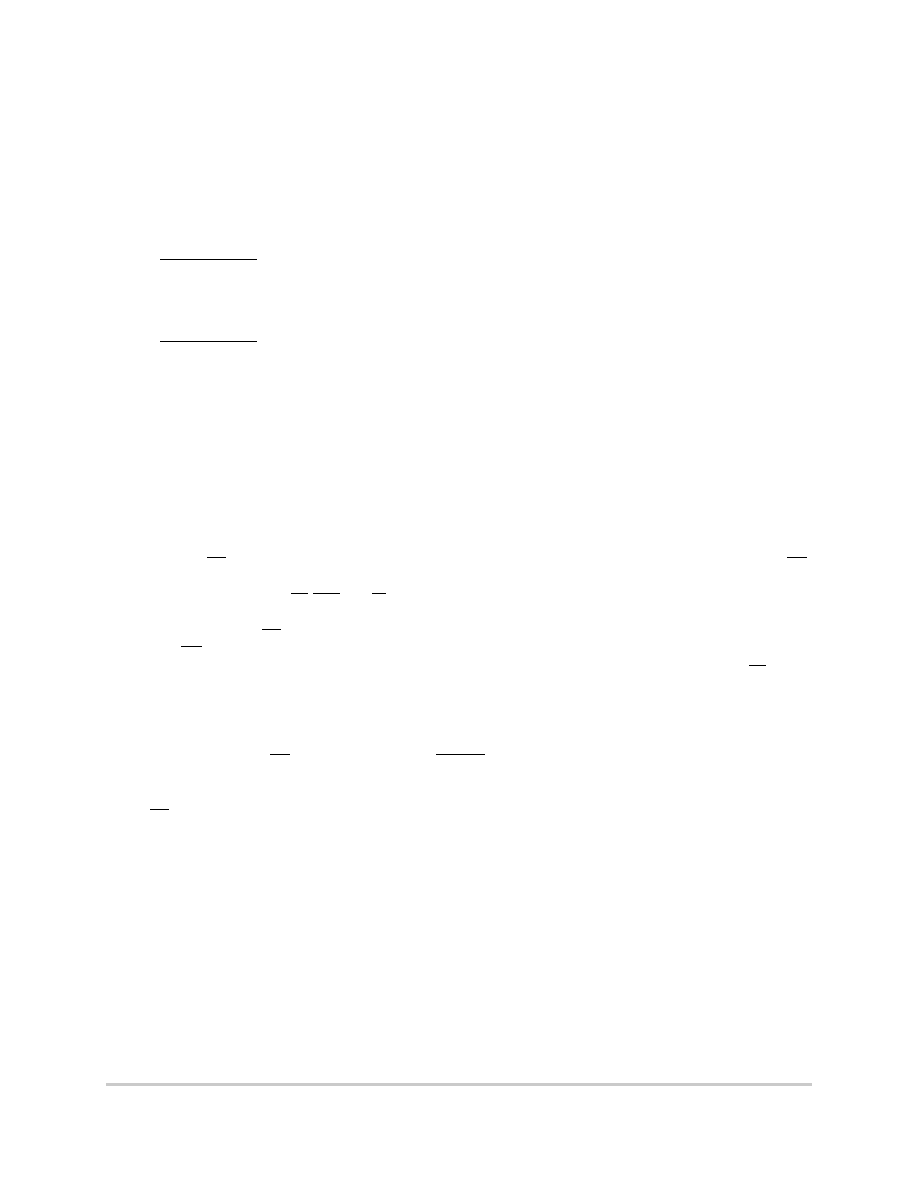
MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
19
Layout Practices
Figure 6-2 is the control timing diagram.
1
The minima provided assume a 0 pF load, whereas maxima assume a 50pF load. For frequencies not marked on the
part, new bus timing must be calculated for all frequency-dependent AC parameters. Frequency-dependent AC
parameters are those with an entry in the FFactor column. AC parameters without an FFactor entry do not need to
be calculated and can be taken directly from the frequency column corresponding to the frequency marked on the
part. The following equations should be used in these calculations.
For a frequency F, the following equations should be applied to each one of the above parameters:
For minima:
For maxima:
where:
D is the parameter value to the frequency required in ns
F is the operation frequency in MHz
D
50
is the parameter value defined for 50 MHz
CAP LOAD is the capacitance load on the signal in question.
FFACTOR is the one defined for each of the parameters in the table.
2
Phase and frequency jitter performance results are valid only if the input jitter is less than the prescribed value.
3
If the rate of change of the frequency of EXTAL is slow (i.e. it does not jump between the minimum and maximum
values in one cycle) or the frequency of the jitter is fast (i.e., it does not stay at an extreme value for a long time) then
the maximum allowed jitter on EXTAL can be up to 2%.
4
The timing for BR output is relevant when the MPC850 is selected to work with external bus arbiter. The timing for BG
output is relevant when the MPC850 is selected to work with internal bus arbiter.
5
The setup times required for TA, TEA, and BI are relevant only when they are supplied by an external device (and not
when the memory controller or the PCMCIA interface drives them).
6
The timing required for BR input is relevant when the MPC850 is selected to work with the internal bus arbiter. The
timing for BG input is relevant when the MPC850 is selected to work with the external bus arbiter.
7
The D[0≠31] and DP[0≠3] input timings B20 and B21 refer to the rising edge of the CLKOUT in which the TA input
signal is asserted.
8
The D[0:31] and DP[0:3] input timings B20 and B21 refer to the falling edge of CLKOUT. This timing is valid only for
read accesses controlled by chip-selects controlled by the UPM in the memory controller, for data beats where DLT3
= 1 in the UPM RAM words. (This is only the case where data is latched on the falling edge of CLKOUT.
9
The timing B30 refers to CS when ACS = '00' and to WE[0:3] when CSNT = '0'.
10
The signal UPWAIT is considered asynchronous to CLKOUT and synchronized internally. The timings specified in
B37 and B38 are specified to enable the freeze of the UPM output signals.
11
The AS signal is considered asynchronous to CLKOUT.
D =
FFACTOR x 1000
F
(D
50
- 20 x FFACTOR)
+
D =
FFACTOR x 1000
F
(D
50
-20 x FFACTOR)
+
+
1ns(CAP LOAD - 50) / 10

20
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
Layout Practices
Figure 6-2. Control Timing
CLKOUT
Outputs
A
B
2.0 V
0.8 V
0.8 V
2.0 V
2.0 V
0.8 V
2.0 V
0.8 V
Outputs
2.0 V
0.8 V
2.0 V
0.8 V
B
A
Inputs
2.0 V
0.8 V
2.0 V
0.8 V
D
C
Inputs
2.0 V
0.8 V
2.0 V
0.8 V
C
D
A
Maximum output delay specification
B
Minimum output hold time
C
Minimum input setup time specification
D
Minimum input hold time specification
MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
21
Layout Practices
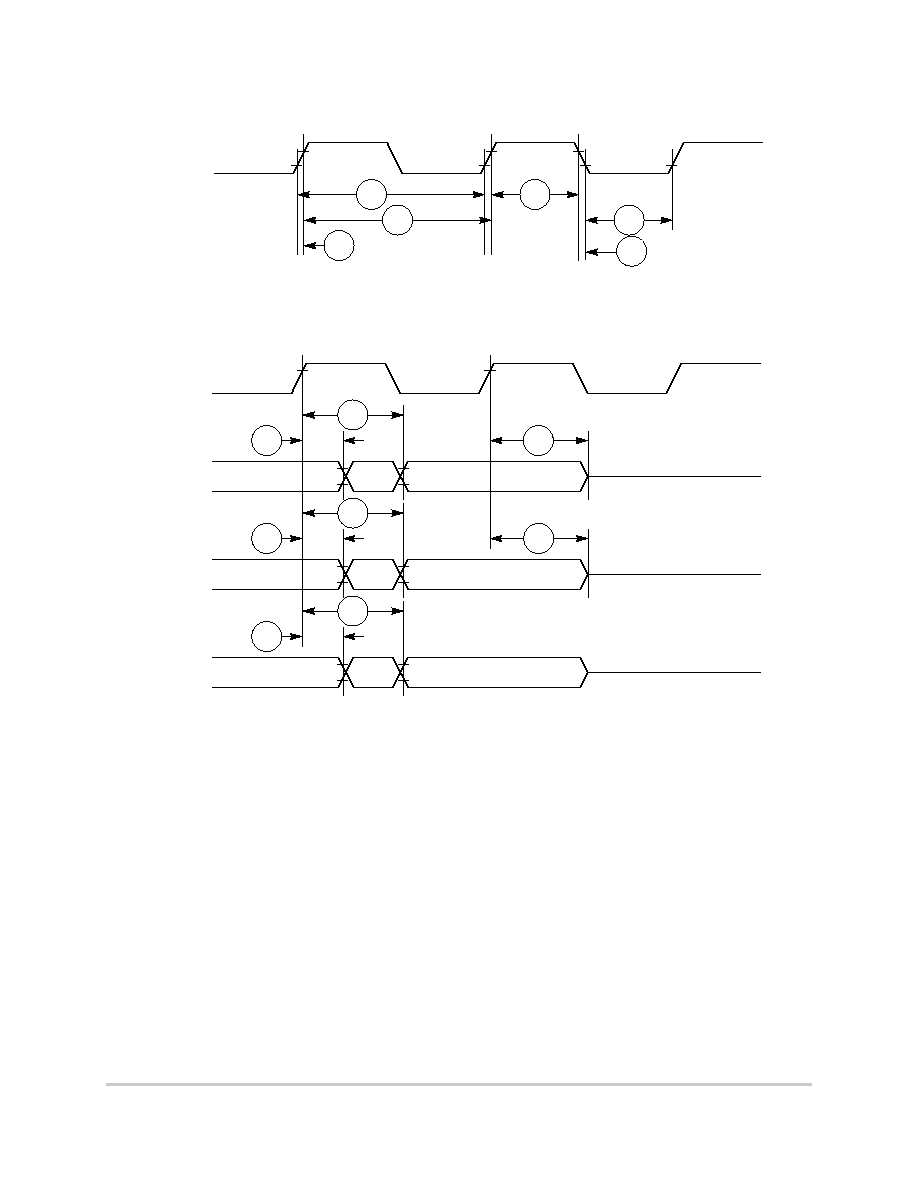
Figure 6-3 provides the timing for the external clock.
Figure 6-3. External Clock Timing
Figure 6-4 provides the timing for the synchronous output signals.
Figure 6-4. Synchronous Output Signals Timing
CLKOUT
B1
B5
B3
B4
B1
B2
CLKOUT
Output
Signals
Output
Signals
Output
Signals
B8
B7
B9
B8a
B9
B7a
B8b
B7b
22
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
Layout Practices
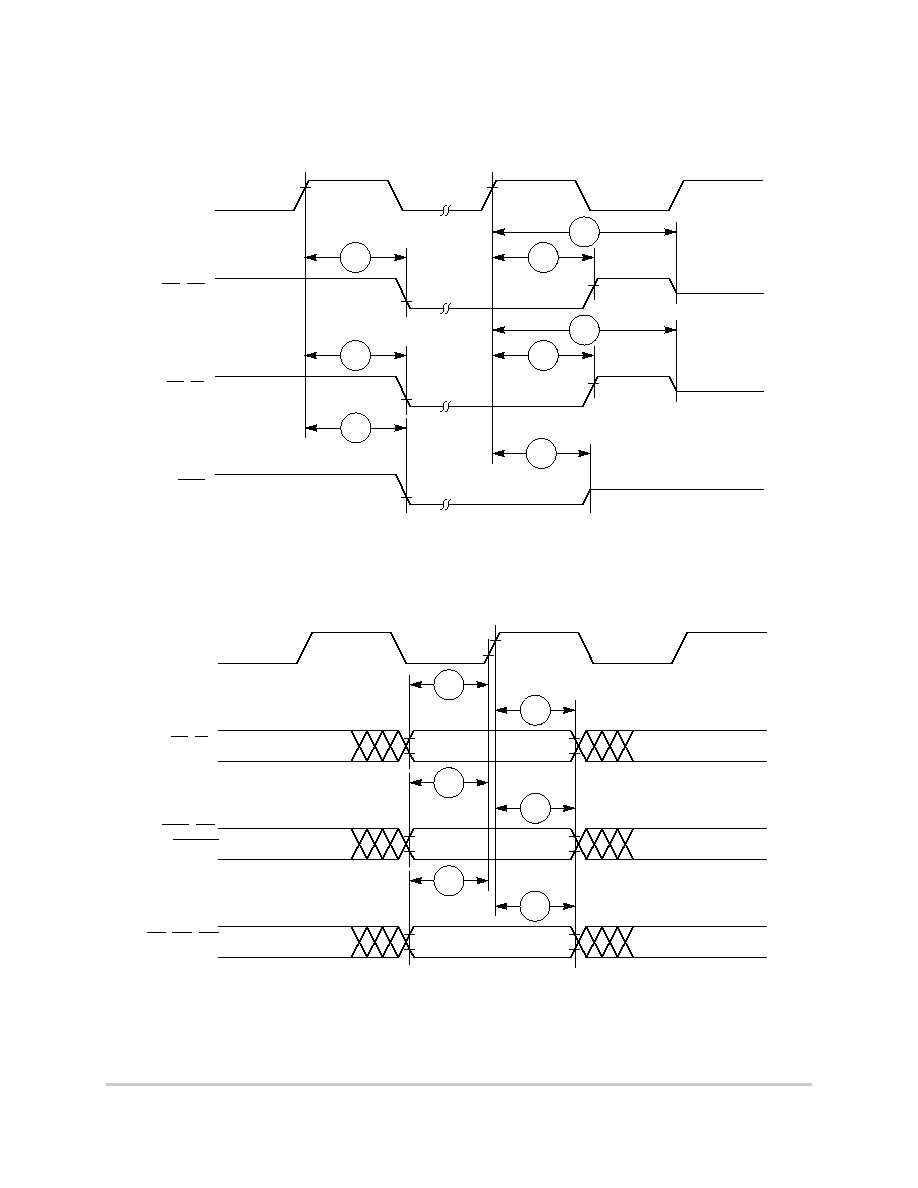
Figure 6-5 provides the timing for the synchronous active pull-up and open-drain output
signals.
Figure 6-5. Synchronous Active Pullup and Open-Drain Outputs Signals Timing
Figure 6-6 provides the timing for the synchronous input signals.
Figure 6-6. Synchronous Input Signals Timing
CLKOUT
TS, BB
TA, BI
TEA
B13
B12
B11
B11a
B12a
B13a
B15
B14
CLKOUT
TA
,
BI
TEA
,
KR
,
RETRY
BB
,
BG
,
BR
B16
B17
B16a
B17a
B16b
B17

MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
23
Layout Practices
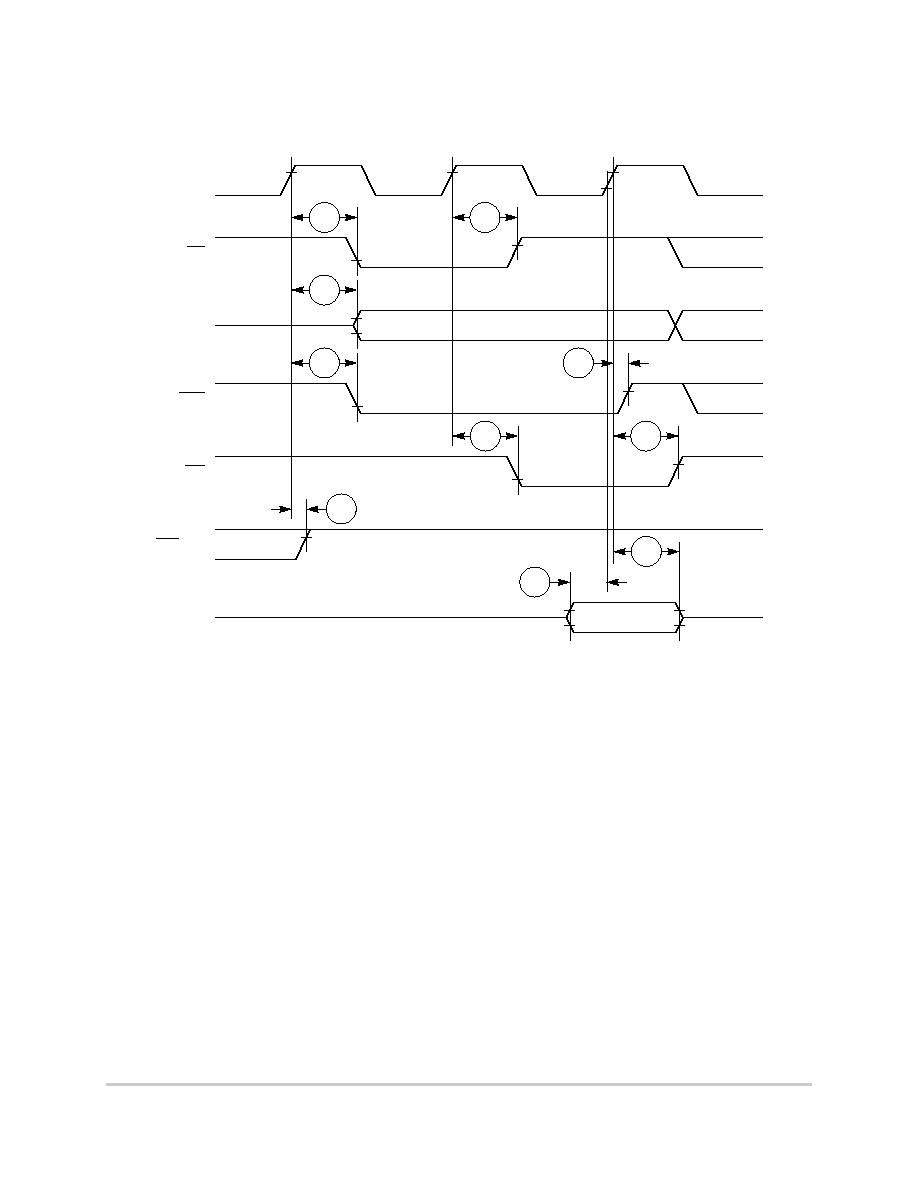
Figure 6-7 provides normal case timing for input data.
Figure 6-7. Input Data Timing in Normal Case
Figure 6-8 provides the timing for the input data controlled by the UPM in the memory
controller.
Figure 6-8. Input Data Timing when Controlled by UPM in the Memory Controller
CLKOUT
TA
D[0:31],
DP[0:3]
B16
B17
B19
B18
CLKOUT
TA
D[0:31],
DP[0:3]
B20
B21
24
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
Layout Practices
Figure 6-9 through Figure 6-12 provide the timing for the external bus read controlled by
various GPCM factors.
Figure 6-9. External Bus Read Timing (GPCM Controlled--ACS = 00)
CLKOUT
A[6:31]
CSx
OE
WE[0:3]
TS
D[0:31],
DP[0:3]
B11
B12
B23
B8
B22
B26
B19
B18
B25
B28

MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
25
Layout Practices
Figure 6-10. External Bus Read Timing (GPCM Controlled--TRLX = 0, ACS = 10)
Figure 6-11. External Bus Read Timing (GPCM Controlled--TRLX = 0, ACS = 11)
CLKOUT
A[6:31]
CSx
OE
TS
D[0:31],
DP[0:3]
B11
B12
B8
B22a
B23
B26
B19
B18
B25
B24
CLKOUT
A[6:31]
CSx
OE
TS
D[0:31],
DP[0:3]
B11
B12
B22b
B8
B22c
B23
B24a
B25
B26
B19
B18

26
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
Layout Practices
Figure 6-12. External Bus Read Timing (GPCM Controlled--TRLX = 1, ACS = 10,
ACS = 11)
CLKOUT
A[6:31]
CSx
OE
TS
D[0:31],
DP[0:3]
B11
B12
B8
B22a
B27
B27a
B22bB22c
B19
B18
B26
B23

MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
27
Layout Practices
Figure 6-13 through Figure 6-15 provide the timing for the external bus write controlled by
various GPCM factors.
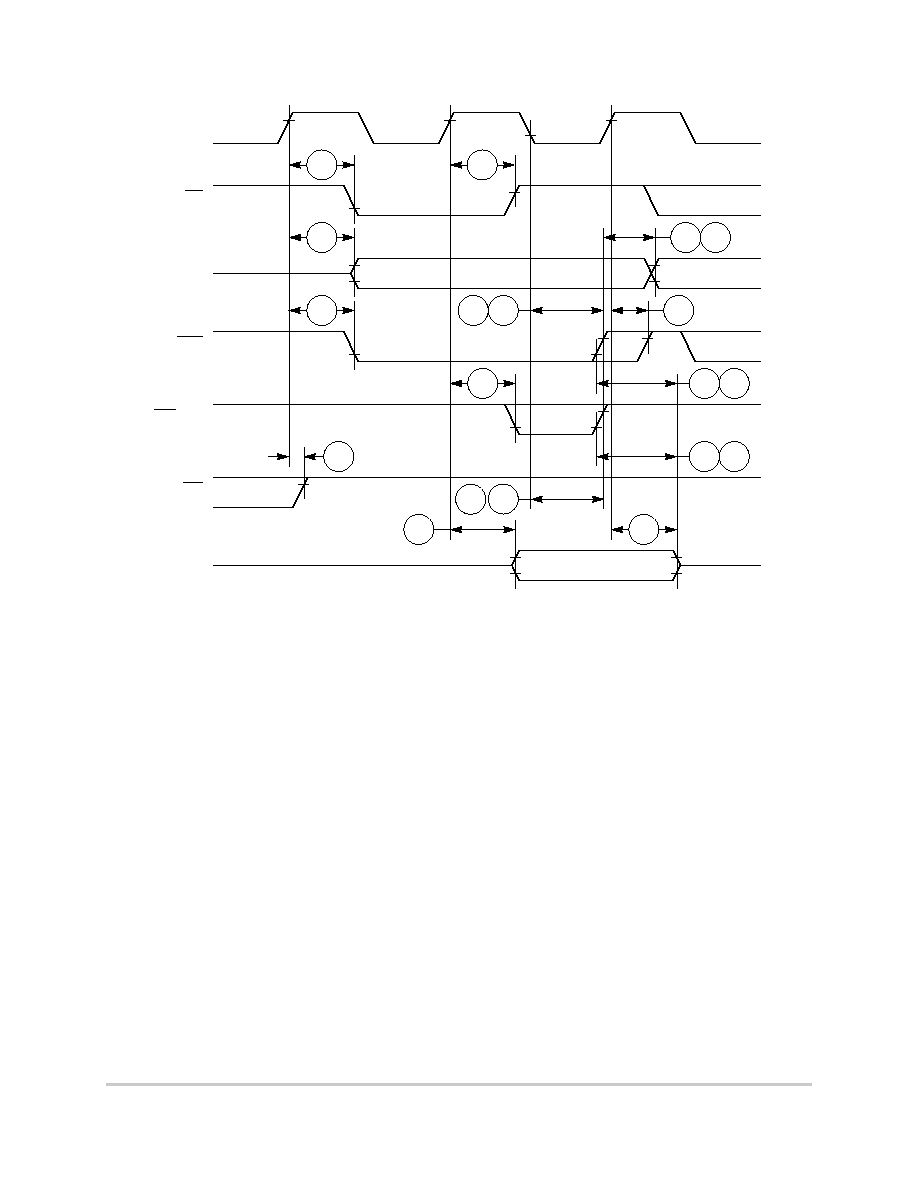
Figure 6-13. External Bus Write Timing (GPCM Controlled--TRLX = 0, CSNT = 0)
CLKOUT
A[6:31]
CSx
WE[0:3]
OE
TS
D[0:31],
DP[0:3]
B11
B8
B22
B23
B12
B30
B28
B25
B26
B8
B9
B29a
B29
28
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
Layout Practices
Figure 6-14. External Bus Write Timing (GPCM Controlled--TRLX = 0, CSNT = 1)
B23
B30aB30c
CLKOUT
A[6:31]
CSx
OE
WE[0:3]
TS
D[0:31],
DP[0:3]
B11
B8
B22
B12
B28bB28d
B25
B26
B8
B28a
B9
B28c
B29cB29g
B29aB29f
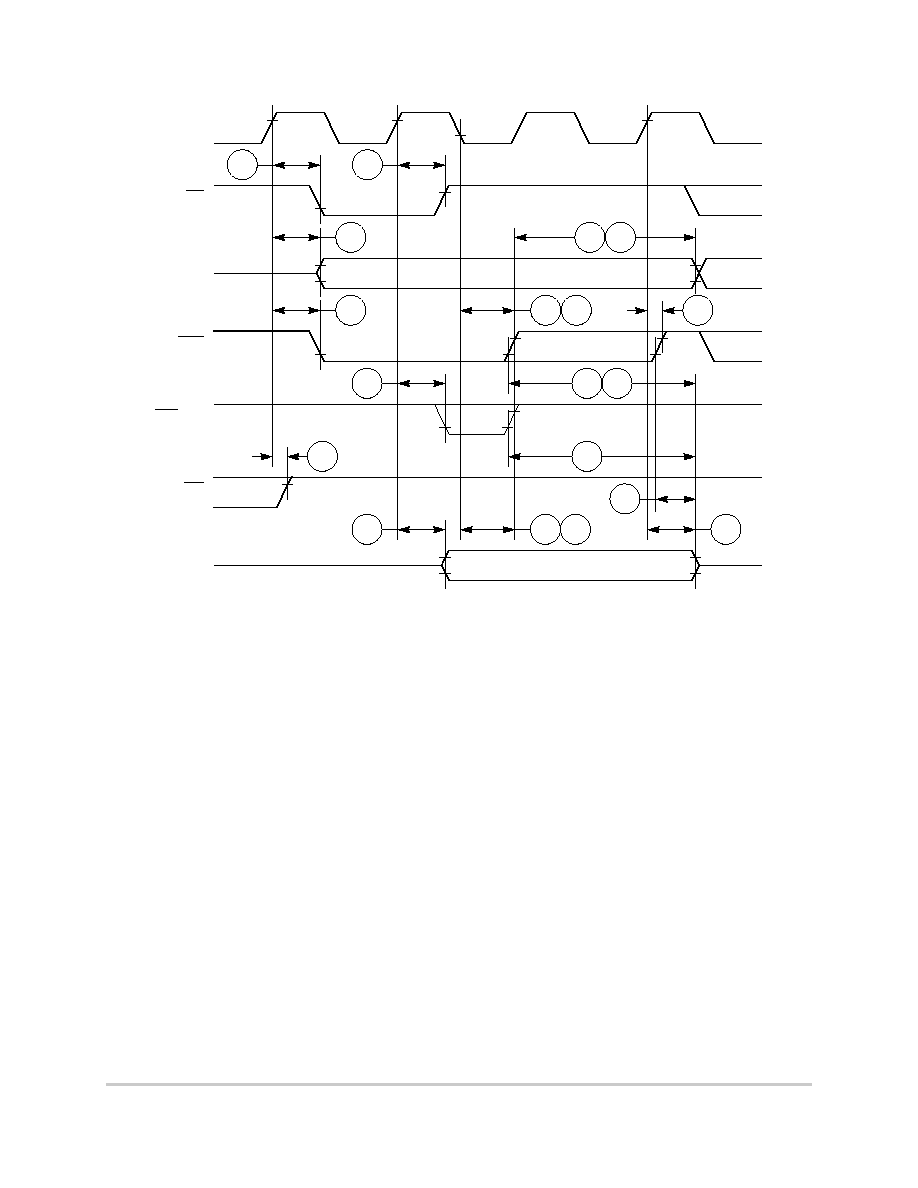
MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
29
Layout Practices
Figure 6-15. External Bus Write Timing (GPCM Controlled--TRLX = 1, CSNT = 1)
Figure 6-16 provides the timing for the external bus controlled by the UPM.
B23
B22
B8
B12
B11
CLKOUT
A[6:31]
CSx
WE[0:3]
TS
OE
D[0:31],
DP[0:3]
B30d
B30b
B28bB28d
B25
B29eB29i
B26
B29d
B28aB28c
B9
B8
B29
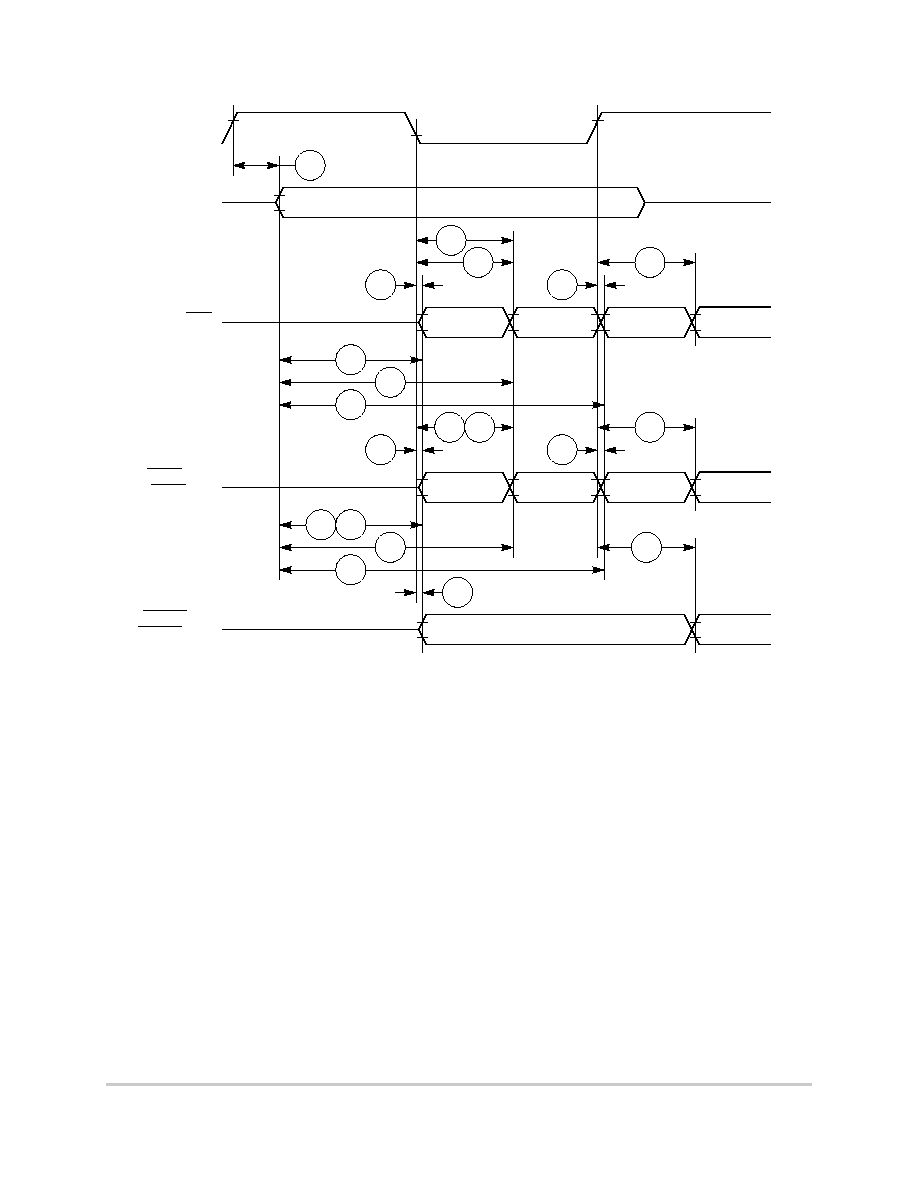
30
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
Layout Practices
Figure 6-16. External Bus Timing (UPM Controlled Signals)
Figure 6-17 provides the timing for the asynchronous asserted UPWAIT signal controlled
by the UPM.
CLKOUT
CSx
B31d
B8
B31
B34
B32b
GPL_A[0--5],
GPL_B[0--5]
BS_A[0:3],
BS_B[0:3]
A[6:31]
B31c
B31b
B34a
B32
B32aB32d
B34b
B36
B35b
B35a
B35
B33
B32c
B33a
B31a
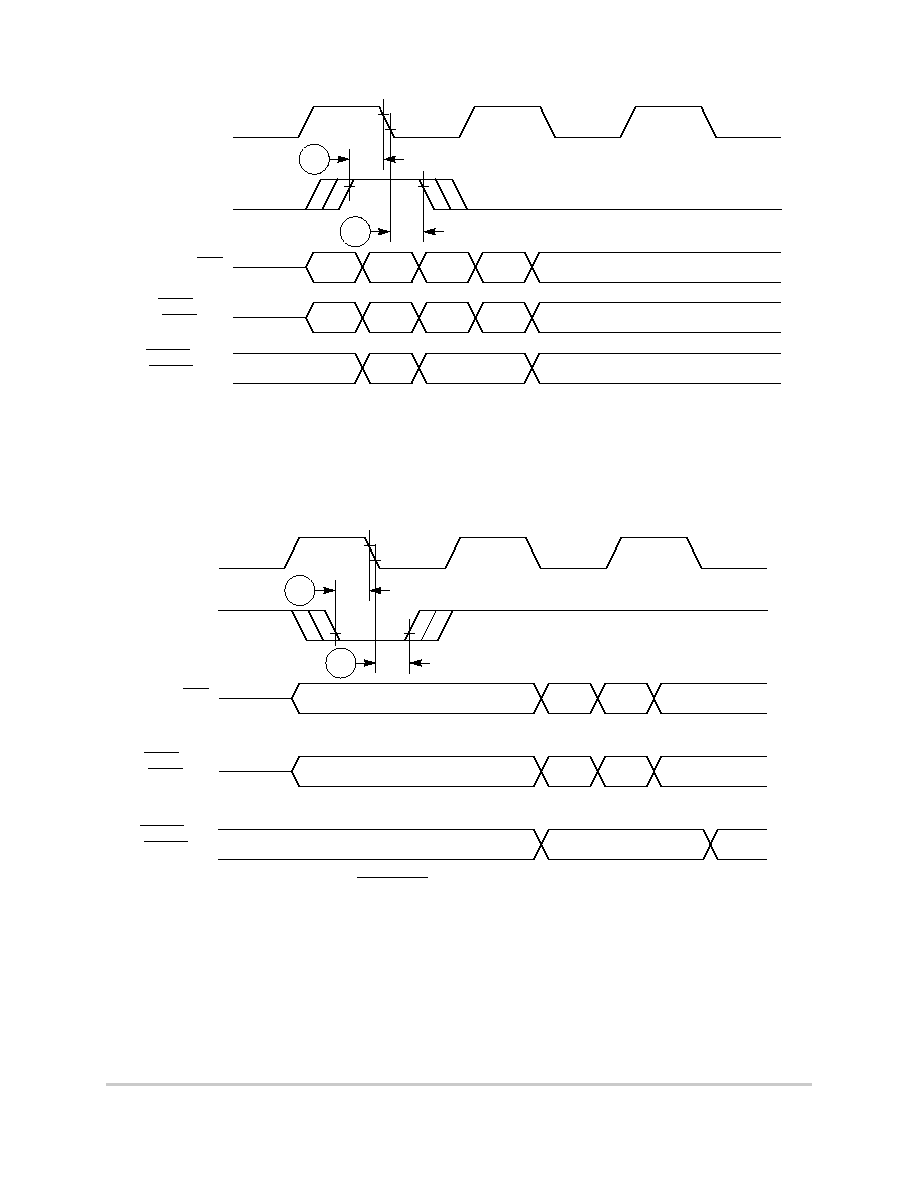
MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
31
Layout Practices
Figure 6-17. Asynchronous UPWAIT Asserted Detection in UPM Handled Cycles
Timing
Figure 6-18 provides the timing for the asynchronous negated UPWAIT signal controlled
by the UPM.
Figure 6-18. Asynchronous UPWAIT Negated Detection in UPM Handled Cycles
Timing
Figure 6-19 provides the timing for the synchronous external master access controlled by
the GPCM.
CLKOUT
CSx
UPWAIT
GPL_A[0--5],
GPL_B[0--5]
BS_A[0:3],
BS_B[0:3]
B37
B38
CLKOUT
CSx
UPWAIT
GPL_A[0--5],
GPL_B[0--5]
BS_A[0:3],
BS_B[0:3]
B37
B38

32
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
Layout Practices
Figure 6-19. Synchronous External Master Access Timing (GPCM Handled ACS =
00)
CLKOUT
TS
A[6:31],
TSIZ[0:1],
R/W, BURST
CSx
B41
B42
B40
B22

MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
33
Layout Practices
Figure 6-20 provides the timing for the asynchronous external master memory access
controlled by the GPCM.
Figure 6-20. Asynchronous External Master Memory Access Timing (GPCM
Controlled--ACS = 00)
Figure 6-21 provides the timing for the asynchronous external master control signals
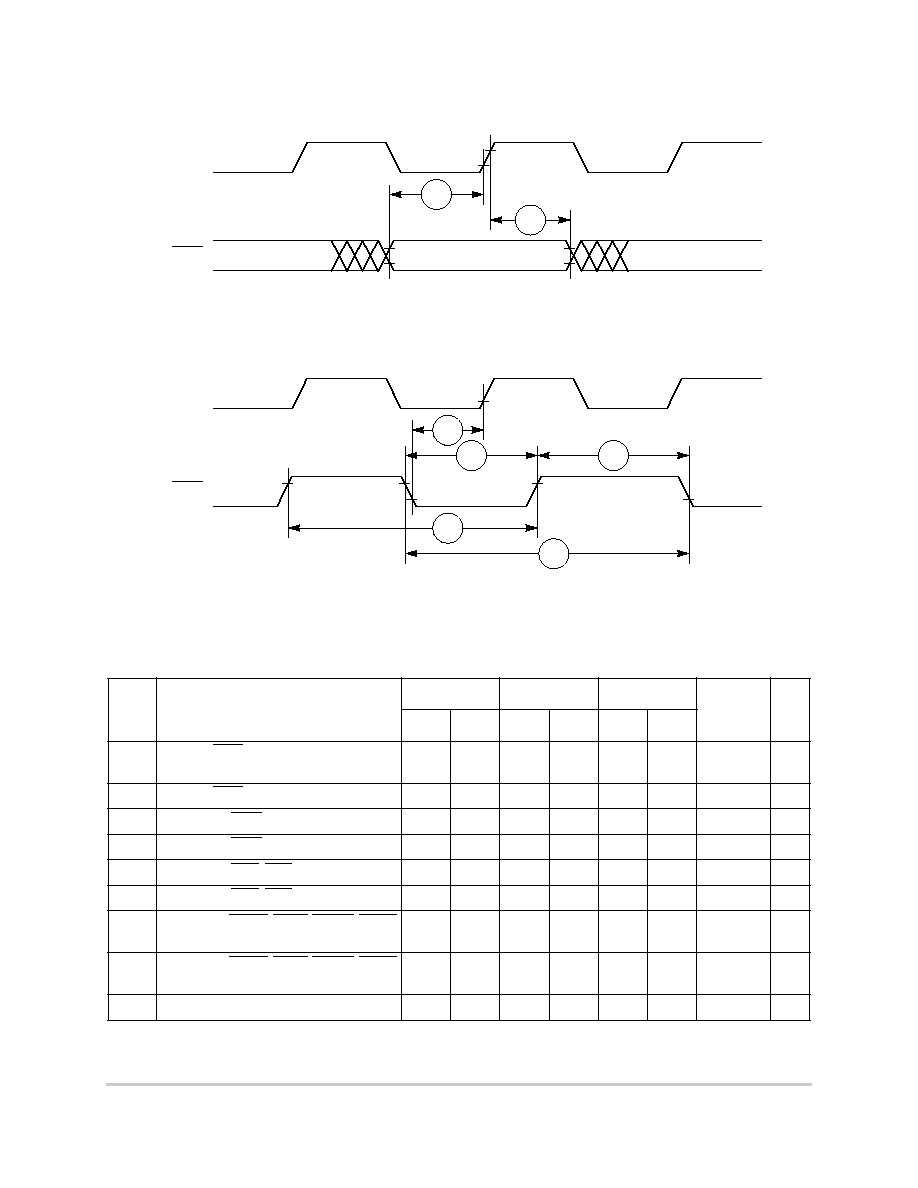
negation.
Figure 6-21. Asynchronous External Master--Control Signals Negation Timing
Table 6-7 provides interrupt timing for the MPC850.
Table 6-7. Interrupt Timing
Num
Characteristic
1
50 MHz
66MHz
80 MHz
Unit
Min
Max
Min
Max
Min
Max
I39
IRQx valid to CLKOUT rising edge (set up time)
6.00
--
6.00
--
6.00
--
ns
I40
IRQx hold time after CLKOUT.
2.00
--
2.00
--
2.00
--
ns
I41
IRQx pulse width low
3.00
--
3.00
--
3.00
--
ns
I42
IRQx pulse width high
3.00
--
3.00
--
3.00
--
ns
I43
IRQx edge-to-edge time
80.00
--
121.0
--
100.0
--
ns
CLKOUT
AS
A[6:31],
TSIZ[0:1],
R/W
CSx
B39
B40
B22
AS
CSx, WE[0:3],
OE, GPLx,
BS[0:3]
B43

34
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
Layout Practices
1
The timings I39 and I40 describe the testing conditions under which the IRQ lines are tested when being defined as
level sensitive. The IRQ lines are synchronized internally and do not have to be asserted or negated with reference
to the CLKOUT.
The timings I41, I42, and I43 are specified to allow the correct function of the IRQ lines detection circuitry, and has no
direct relation with the total system interrupt latency that the MPC850 is able to support
MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
35
Layout Practices
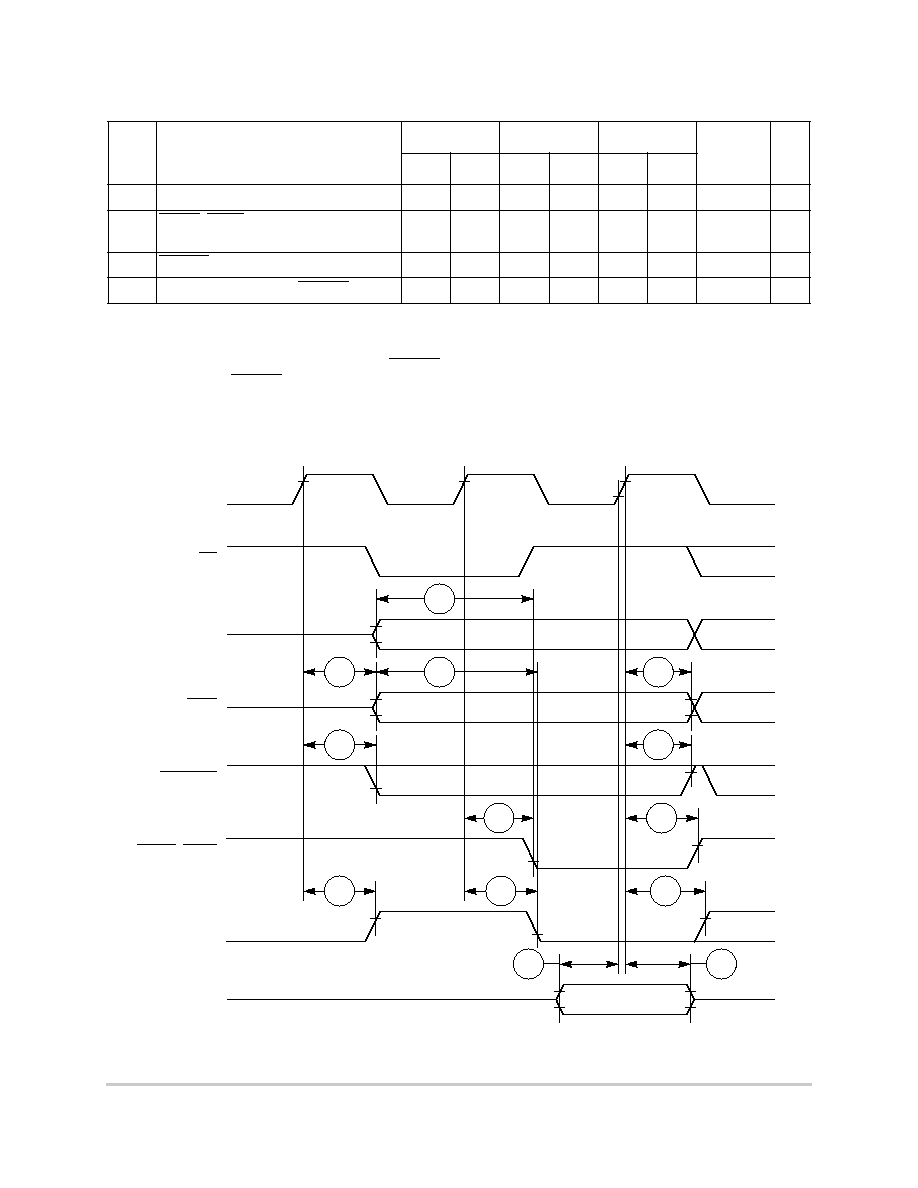
Figure 6-22 provides the interrupt detection timing for the external level-sensitive lines.
Figure 6-22. Interrupt Detection Timing for External Level Sensitive Lines
Figure 6-23 provides the interrupt detection timing for the external edge-sensitive lines.
Figure 6-23. Interrupt Detection Timing for External Edge Sensitive Lines
Table 6-8 shows the PCMCIA timing for the MPC850.
Table 6-8. PCMCIA Timing
Num
Characteristic
50MHz
66MHz
80 MHz
FFACTOR Unit
Min
Max
Min
Max
Min
Max
P44
A[6≠31], REG valid to PCMCIA strobe
asserted.
1
13.00
--
21.00
--
17.00
--
0.750
ns
P45
A[6≠31], REG valid to ALE negation.
1
18.00
--
28.00
--
23.00
--
1.000
ns
P46
CLKOUT to REG valid
5.00
13.00
8.00
16.00
6.00
14.00
0.250
ns
P47
CLKOUT to REG Invalid.
6.00
--
9.00
--
7.00
--
0.250
ns
P48
CLKOUT to CE1, CE2 asserted.
5.00
13.00
8.00
16.00
6.00
14.00
0.250
P49
CLKOUT to CE1, CE2 negated.
5.00
13.00
8.00
16.00
6.00
14.00
0.250
ns
P50
CLKOUT to PCOE, IORD, PCWE, IOWR
assert time.
--
11.00
--
11.00
--
11.00
--
ns
P51
CLKOUT to PCOE, IORD, PCWE, IOWR
negate time.
2.00
11.00
2.00
11.00
2.00
11.00
--
ns
P52
CLKOUT to ALE assert time
5.00
13.00
8.00
16.00
6.00
14.00
0.250
ns
CLKOUT
IRQx
I39
I40
CLKOUT
IRQx
I39
I41
I42
I43
I43
36
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
Layout Practices
Figure 6-24 provides the PCMCIA access cycle timing for the external bus read.
Figure 6-24. PCMCIA Access Cycles Timing External Bus Read
P53
CLKOUT to ALE negate time
--
13.00
--
16.00
--
14.00
0.250
ns
P54
PCWE, IOWR negated to D[0≠31]
invalid.
1
3.00
--
6.00
--
4.00
--
0.250
ns
P55
WAIT_B valid to CLKOUT rising edge.
1
8.00
--
8.00
--
8.00
--
--
ns
P56
CLKOUT rising edge to WAIT_B invalid.
1
2.00
--
2.00
--
2.00
--
--
ns
1
PSST = 1. Otherwise add PSST times cycle time.
PSHT = 0. Otherwise add PSHT times cycle time.
These synchronous timings define when the WAIT_B signal is detected in order to freeze (or relieve) the PCMCIA
current cycle. The WAIT_B assertion will be effective only if it is detected 2 cycles before the PSL timer expiration.
See PCMCIA Interface in the MPC850 PowerQUICC User's Manual.
Table 6-8. PCMCIA Timing (continued)
Num
Characteristic
50MHz
66MHz
80 MHz
FFACTOR Unit
Min
Max
Min
Max
Min
Max
CLKOUT
A[6:31]
REG
CE1/CE2
PCOE, IORD
TS
D[0:31]
ALE
B19
B18
P53
P52
P52
P51
P50
P48
P49
P46
P45
P44
P47

MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
37
Layout Practices
Figure 6-25 provides the PCMCIA access cycle timing for the external bus write.
Figure 6-25. PCMCIA Access Cycles Timing External Bus Write
Figure 6-26 provides the PCMCIA WAIT signals detection timing.
Figure 6-26. PCMCIA WAIT Signal Detection Timing
CLKOUT
A[6:31]
REG
CE1/CE2
PCWE, IOWR
TS
D[0:31]
ALE
B9
B8
P53
P52
P52
P51
P50
P48
P49
P46
P45
P44
P47
P54
CLKOUT
WAIT_B
P55
P56

38
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
Layout Practices
Table 6-9 shows the PCMCIA port timing for the MPC850.
Figure 6-27 provides the PCMCIA output port timing for the MPC850.
Figure 6-27. PCMCIA Output Port Timing
Figure 6-28 provides the PCMCIA output port timing for the MPC850.
Figure 6-28. PCMCIA Input Port Timing
Table 6-9. PCMCIA Port Timing
Num
Characteristic
50 MHz
66 MHz
80 MHz
Unit
Min
Max
Min
Max
Min
Max
P57
CLKOUT to OPx valid
--
19.00
--
19.00
--
19.00
ns
P58
HRESET negated to OPx drive
1
1
OP2 and OP3 only.
18.00
--
26.00
--
22.00
--
ns
P59
IP_Xx valid to CLKOUT rising edge
5.00
--
5.00
--
5.00
--
ns
P60
CLKOUT rising edge to IP_Xx invalid
1.00
--
1.00
--
1.00
--
ns
CLKOUT
HRESET
Output
Signals
OP2, OP3
P57
P58
CLKOUT
Input
Signals
P59
P60

MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
39
Layout Practices
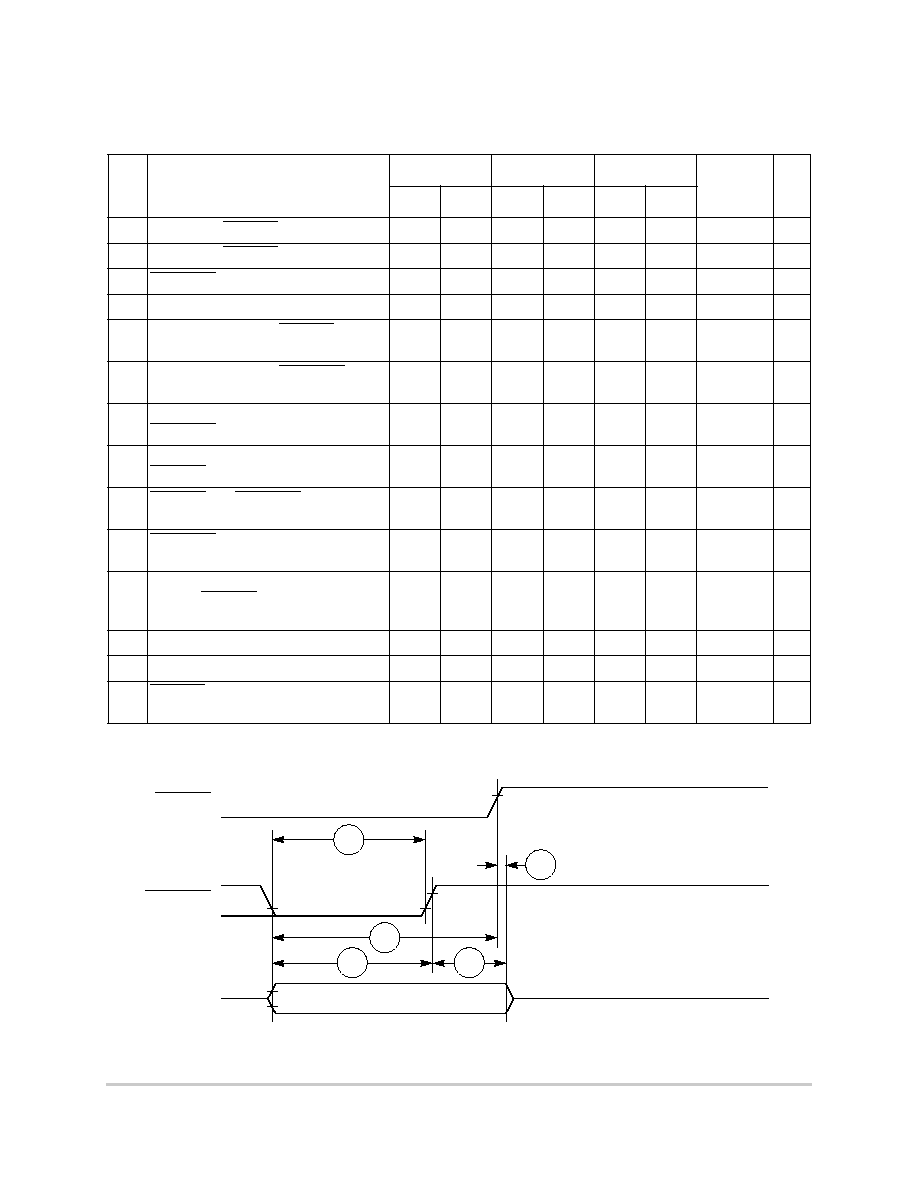
Table 6-10 shows the debug port timing for the MPC850.
Figure 6-29 provides the input timing for the debug port clock.
Figure 6-29. Debug Port Clock Input Timing
Figure 6-30 provides the timing for the debug port.
Figure 6-30. Debug Port Timings
Table 6-10. Debug Port Timing
Num
Characteristic
50 MHz
66 MHz
80 MHz
Unit
Min
Max
Min
Max
Min
Max
D61
DSCK cycle time
60.00
--
91.00
--
75.00
--
ns
D62
DSCK clock pulse width
25.00
--
38.00
--
31.00
--
ns
D63
DSCK rise and fall times
0.00
3.00
0.00
3.00
0.00
3.00
ns
D64
DSDI input data setup time
8.00
--
8.00
--
8.00
--
ns
D65
DSDI data hold time
5.00
--
5.00
--
5.00
--
ns
D66
DSCK low to DSDO data valid
0.00
15.00
0.00
15.00
0.00
15.00
ns
D67
DSCK low to DSDO invalid
0.00
2.00
0.00
2.00
0.00
2.00
ns
DSCK
D61
D63
D62
D62
D63
DSCK
DSDI
DSDO
D64
D65
D66
D67
40
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
Layout Practices
Table 6-11 shows the reset timing for the MPC850.
Figure 6-31 shows the reset timing for the data bus configuration.
Figure 6-31. Reset Timing--Configuration from Data Bus
Table 6-11. Reset Timing
Num
Characteristic
50 MHz
66MHz
80 MHz
FFACTOR Unit
Min
Max
Min
Max
Min
Max
R69
CLKOUT to HRESET high impedance
--
20.00
--
20.00
--
20.00
--
ns
R70
CLKOUT to SRESET high impedance
--
20.00
--
20.00
--
20.00
--
ns
R71
RSTCONF pulse width
340.00
--
515.00
--
425.00
--
17.000
ns
R72
--
--
--
--
--
--
--
R73
Configuration data to HRESET rising
edge set up time
350.00
--
505.00
--
425.00
--
15.000
ns
R74
Configuration data to RSTCONF rising
edge set up time
350.00
--
350.00
--
350.00
--
--
ns
R75
Configuration data hold time after
RSTCONF negation
0.00
--
0.00
--
0.00
--
--
ns
R76
Configuration data hold time after
HRESET negation
0.00
--
0.00
--
0.00
--
--
ns
R77
HRESET and RSTCONF asserted to
data out drive
--
25.00
--
25.00
--
25.00
--
ns
R78
RSTCONF negated to data out high
impedance.
--
25.00
--
25.00
--
25.00
--
ns
R79
CLKOUT of last rising edge before chip
tristates HRESET to data out high
impedance.
--
25.00
--
25.00
--
25.00
--
ns
R80
DSDI, DSCK set up
60.00
--
90.00
--
75.00
--
3.000
ns
R81
DSDI, DSCK hold time
0.00
--
0.00
--
0.00
--
--
ns
R82
SRESET negated to CLKOUT rising
edge for DSDI and DSCK sample
160.00
--
242.00
--
200.00
--
8.000
ns
HRESET
RSTCONF
D[0:31] (IN)
R71
R74
R73
R75
R76

MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
41
Layout Practices
Figure 6-32 provides the reset timing for the data bus weak drive during configuration.
Figure 6-32. Reset Timing--Data Bus Weak Drive during Configuration
Figure 6-33 provides the reset timing for the debug port configuration.
Figure 6-33. Reset Timing--Debug Port Configuration
CLKOUT
HRESET
D[0:31] (OUT)
(Weak)
RSTCONF
R69
R79
R77
R78
CLKOUT
SRESET
DSCK, DSDI
R70
R82
R80
R80
R81
R81

42
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
Layout Practices
Part VII IEEE 1149.1 Electrical
Specifications
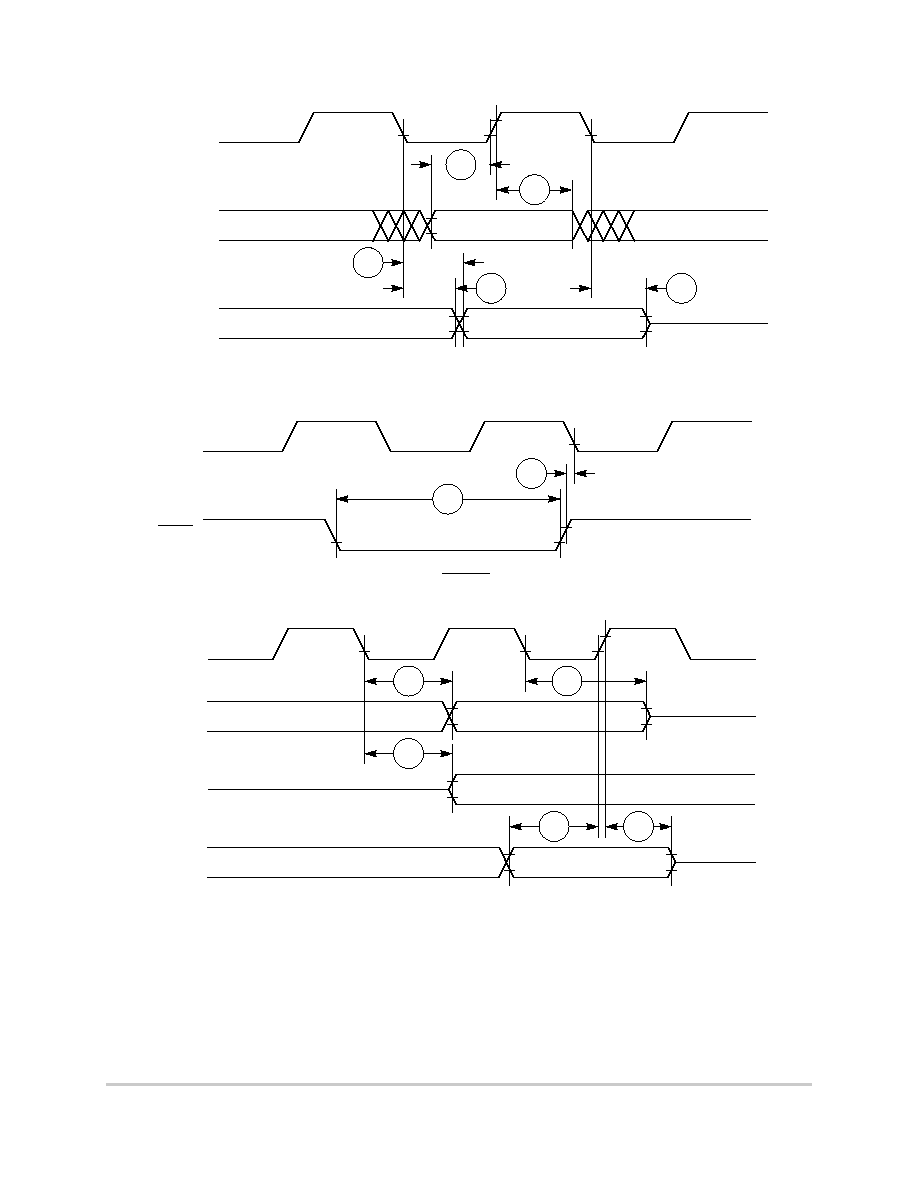
Table 7-12 provides the JTAG timings for the MPC850 as shown in Figure 7-34 to
Figure 7-37.
Figure 7-34. JTAG Test Clock Input Timing
Table 7-12. JTAG Timing
Num
Characteristic
50 MHz
66MHz
80 MHz
Unit
Min
Max
Min
Max
Min
Max
J82
TCK cycle time
100.00
--
100.00
--
100.00
--
ns
J83
TCK clock pulse width measured at 1.5 V
40.00
--
40.00
--
40.00
--
ns
J84
TCK rise and fall times
0.00
10.00
0.00
10.00
0.00
10.00
ns
J85
TMS, TDI data setup time
5.00
--
5.00
--
5.00
--
ns
J86
TMS, TDI data hold time
25.00
--
25.00
--
25.00
--
ns
J87
TCK low to TDO data valid
--
27.00
--
27.00
--
27.00
ns
J88
TCK low to TDO data invalid
0.00
--
0.00
--
0.00
--
ns
J89
TCK low to TDO high impedance
--
20.00
--
20.00
--
20.00
ns
J90
TRST assert time
100.00
--
100.00
--
100.00
--
ns
J91
TRST setup time to TCK low
40.00
--
40.00
--
40.00
--
ns
J92
TCK falling edge to output valid
--
50.00
--
50.00
--
50.00
ns
J93
TCK falling edge to output valid out of high
impedance
--
50.00
--
50.00
--
50.00
ns
J94
TCK falling edge to output high impedance
--
50.00
--
50.00
--
50.00
ns
J95
Boundary scan input valid to TCK rising edge
50.00
--
50.00
--
50.00
--
ns
J96
TCK rising edge to boundary scan input invalid
50.00
--
50.00
--
50.00
--
ns
TCK
J82
J83
J82
J83
J84
J84
MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
43
Layout Practices
Figure 7-35. JTAG Test Access Port Timing Diagram
Figure 7-36. JTAG TRST Timing Diagram
Figure 7-37. Boundary Scan (JTAG) Timing Diagram
Part VIII CPM Electrical Characteristics
This section provides the AC and DC electrical specifications for the communications
processor module (CPM) of the MPC850.
TCK
TMS, TDI
TDO
J85
J86
J87
J88
J89
TCK
TRST
J91
J90
TCK
Output
Signals
Output
Signals
Input
Signals
J92
J94
J93
J95
J96
44
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
PIO AC Electrical Specifications
8.1
PIO AC Electrical Specifications
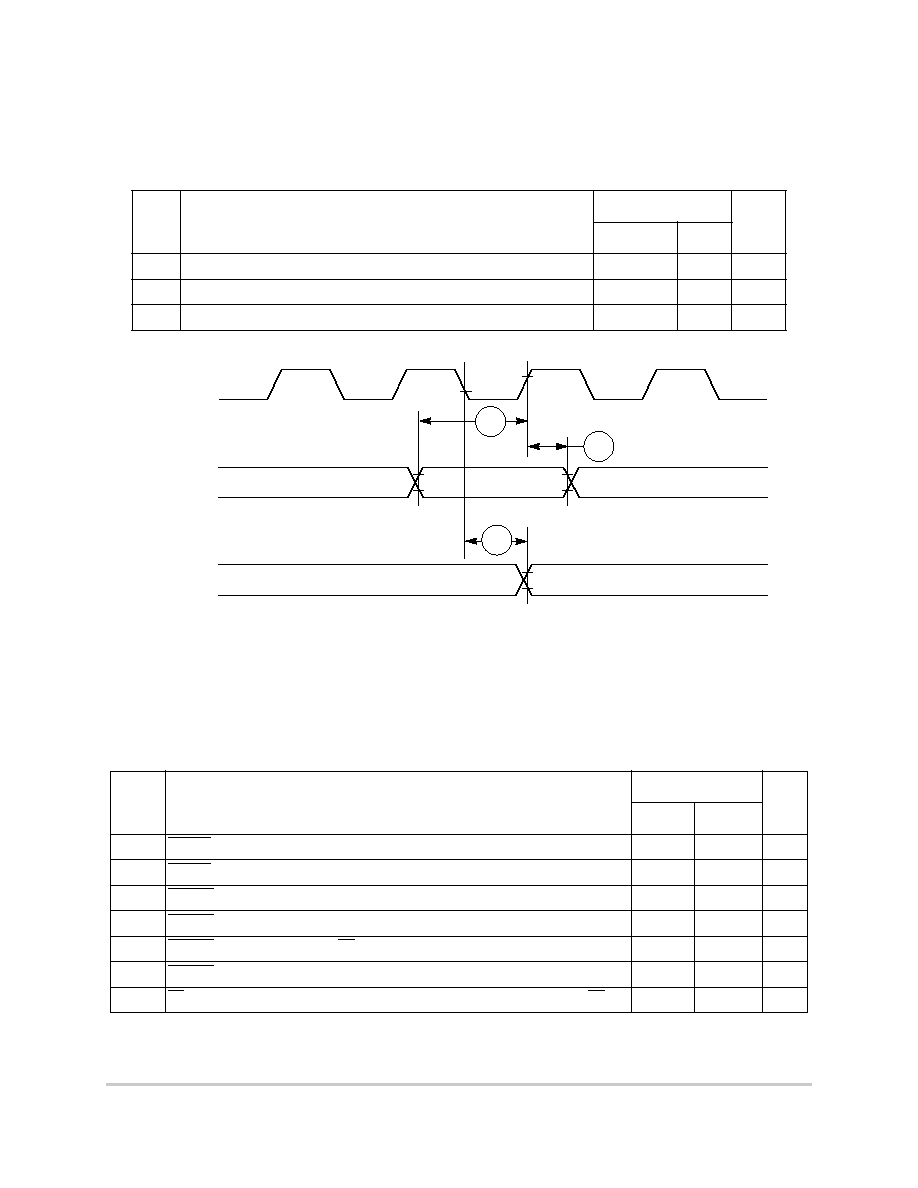
Table 8-13 provides the parallel I/O timings for the MPC850 as shown in Figure 8-38.
Figure 8-38. Parallel I/O Data-In/Data-Out Timing Diagram
8.2
IDMA Controller AC Electrical Specifications
Table 8-14 provides the IDMA controller timings as shown in Figure 8-39 to Figure 8-42.
Table 8-13. Parallel I/O Timing
Num
Characteristic
All Frequencies
Unit
Min
Max
29
Data-in setup time to clock high
15
--
ns
30
Data-in hold time from clock high
7.5
--
ns
31
Clock low to data-out valid (CPU writes data, control, or direction)
--
25
ns
Table 8-14. IDMA Controller Timing
Num
Characteristic
All Frequencies
Unit
Min
Max
40
DREQ setup time to clock high
7.00
--
ns
41
DREQ hold time from clock high
3.00
--
ns
42
SDACK assertion delay from clock high
--
12.00
ns
43
SDACK negation delay from clock low
--
12.00
ns
44
SDACK negation delay from TA low
--
20.00
ns
45
SDACK negation delay from clock high
--
15.00
ns
46
TA assertion to falling edge of the clock setup time (applies to external TA)
7.00
--
ns
CLKOUT
DATA-IN
29
31
30
DATA-OUT

MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
45
IDMA Controller AC Electrical Specifications
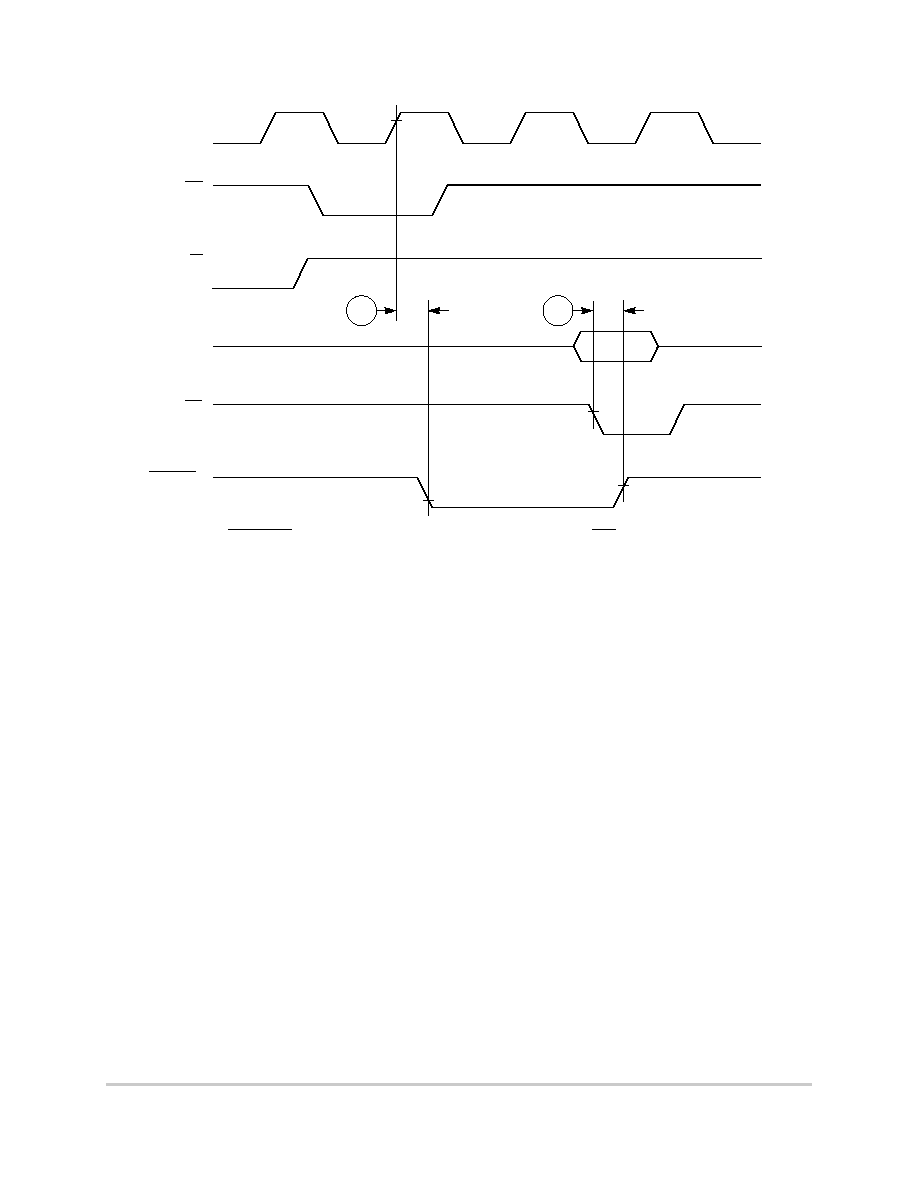
Figure 8-39. IDMA External Requests Timing Diagram
Figure 8-40. SDACK Timing Diagram--Peripheral Write, TA Sampled Low at the
Falling Edge
of the Clock
41
40
DREQ
(Input)
CLKOUT
(Output)
DATA
42
46
43
CLKOUT
(Output)
TS
(Output)
R/W
(Output)
TA
(Output)
SDACK
46
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
IDMA Controller AC Electrical Specifications
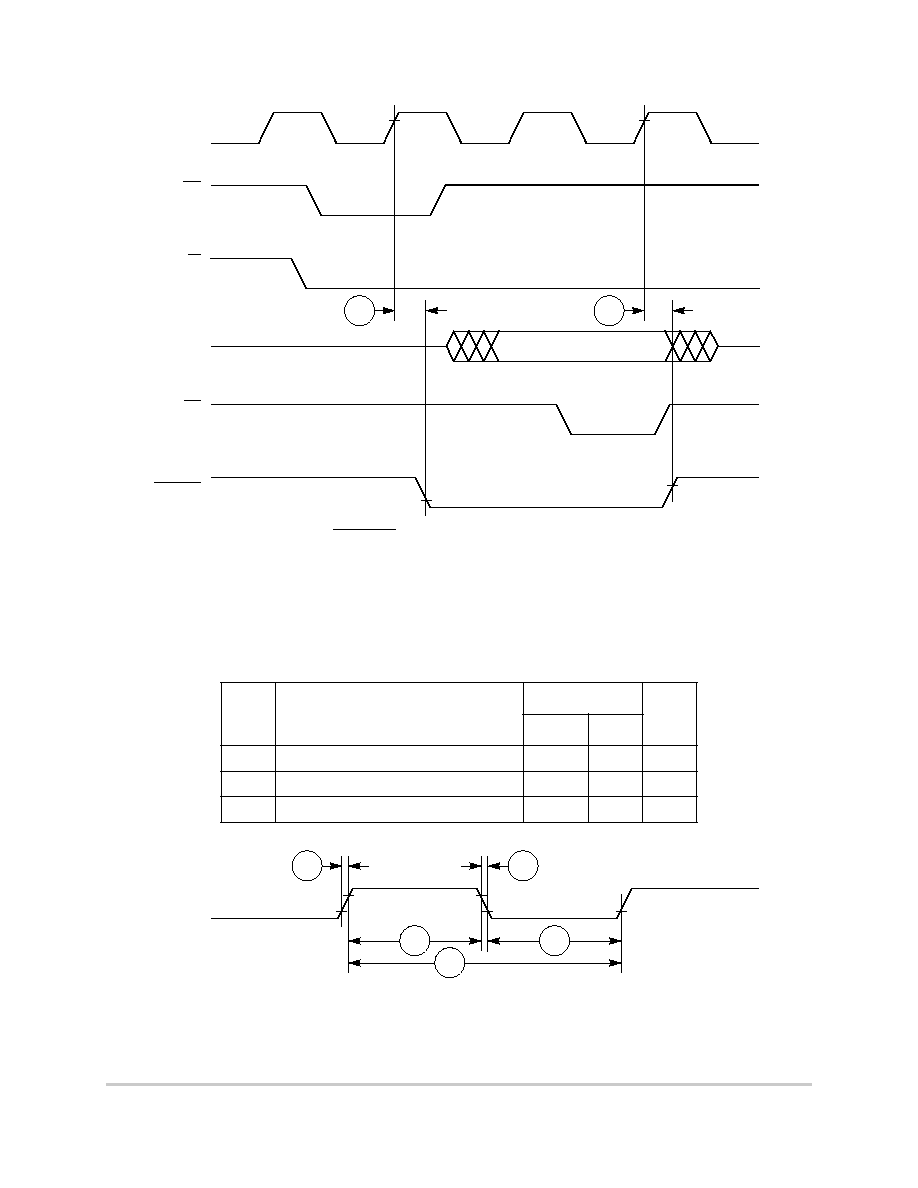
Figure 8-41. SDACK Timing Diagram--Peripheral Write, TA Sampled High at the
Falling Edge
of the Clock
DATA
42
44
CLKOUT
(Output)
TS
(Output)
R/W
(Output)
TA
(Output)
SDACK
MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
47
Baud Rate Generator AC Electrical Specifications
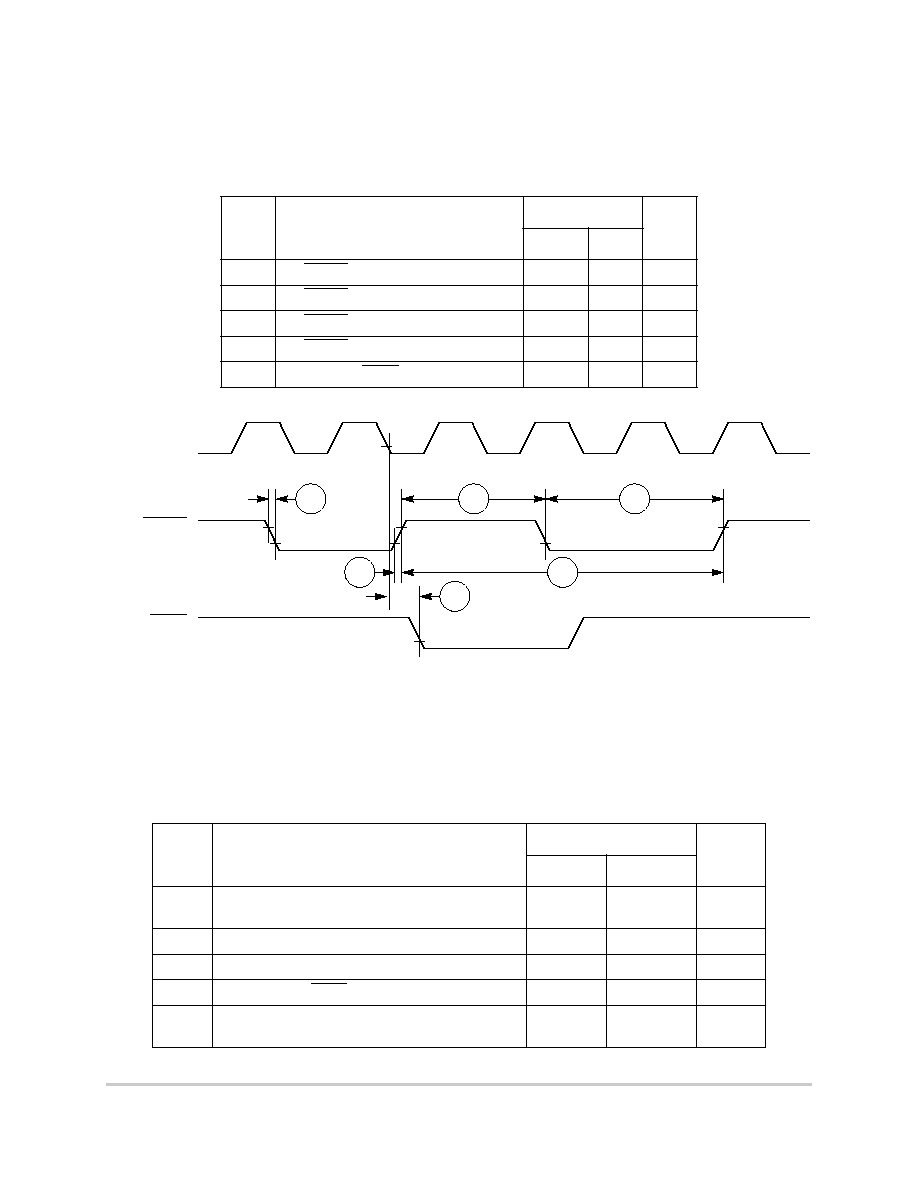
Figure 8-42. SDACK Timing Diagram--Peripheral Read
8.3
Baud Rate Generator AC Electrical Specifications
Table 8-15 provides the baud rate generator timings as shown in Figure 8-43.
Figure 8-43. Baud Rate Generator Timing Diagram
Table 8-15. Baud Rate Generator Timing
Num
Characteristic
All Frequencies
Unit
Min
Max
50
BRGO rise and fall time
--
10.00
ns
51
BRGO duty cycle
40.00
60.00
%
52
BRGO cycle
40.00
--
ns
DATA
42
45
CLKOUT
(Output)
TS
(Output)
R/W
(Output)
TA
(Output)
SDACK
52
50
51
BRGOn
50
51
48
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
Timer AC Electrical Specifications
8.4
Timer AC Electrical Specifications
Table 8-16 provides the baud rate generator timings as shown in Figure 8-44.
Figure 8-44. CPM General-Purpose Timers Timing Diagram
8.5
Serial Interface AC Electrical Specifications
Table 8-17 provides the serial interface timings as shown in Figure 8-45 to Figure 8-49.
Table 8-16. Timer Timing
Num
Characteristic
All Frequencies
Unit
Min
Max
61
TIN/TGATE rise and fall time
10.00
--
ns
62
TIN/TGATE low time
1.00
--
clk
63
TIN/TGATE high time
2.00
--
clk
64
TIN/TGATE cycle
time
3.00
--
clk
65
CLKO high to TOUT valid
3.00
25.00
ns
Table 8-17. SI Timing
Num
Characteristic
All Frequencies
Unit
Min
Max
70
L1RCLK, L1TCLK frequency (DSC = 0)
1,
2
--
SYNCCLK/2.
5
MHz
71
L1RCLK, L1TCLK width low (DSC = 0)
2
P + 10
--
ns
71a
L1RCLK, L1TCLK width high (DSC = 0)
3
P + 10
--
ns
72
L1TXD, L1STn, L1RQ, L1xCLKO rise/fall time
--
15.00
ns
73
L1RSYNC, L1TSYNC valid to L1xCLK edge Edge
(SYNC setup time)
20.00
--
ns
CLKOUT
TIN/TGATE
(Input)
TOUT
(Output)
64
65
61
62
63
61

MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
49
Serial Interface AC Electrical Specifications
74
L1xCLK edge to L1RSYNC, L1TSYNC, invalid
(SYNC hold time)
35.00
--
ns
75
L1RSYNC, L1TSYNC rise/fall time
--
15.00
ns
76
L1RXD valid to L1xCLK edge (L1RXD setup time)
17.00
--
ns
77
L1xCLK edge to L1RXD invalid (L1RXD hold time)
13.00
--
ns
78
L1xCLK edge to L1STn valid
4
10.00
45.00
ns
78A
L1SYNC valid to L1STn valid
10.00
45.00
ns
79
L1xCLK edge to L1STn invalid
10.00
45.00
ns
80
L1xCLK edge to L1TXD valid
10.00
55.00
ns
80A
L1TSYNC valid to L1TXD valid
4
10.00
55.00
ns
81
L1xCLK edge to L1TXD high impedance
0.00
42.00
ns
82
L1RCLK, L1TCLK frequency (DSC =1)
--
16.00 or
SYNCCLK/2
MHz
83
L1RCLK, L1TCLK width low (DSC =1)
P + 10
--
ns
83A
L1RCLK, L1TCLK width high (DSC = 1)
3
P + 10
--
ns
84
L1CLK edge to L1CLKO valid (DSC = 1)
--
30.00
ns
85
L1RQ valid before falling edge of L1TSYNC
4
1.00
--
L1TCLK
86
L1GR setup time
2
42.00
--
ns
87
L1GR hold time
42.00
--
ns
88
L1xCLK edge to L1SYNC valid (FSD = 00) CNT =
0000, BYT = 0, DSC = 0)
--
0.00
ns
1
The ratio SyncCLK/L1RCLK must be greater than 2.5/1.
2
These specs are valid for IDL mode only.
3
Where P = 1/CLKOUT. Thus for a 25-MHz CLKO1 rate, P = 40 ns.
4
These strobes and TxD on the first bit of the frame become valid after L1CLK edge or L1SYNC,
whichever is later.
Table 8-17. SI Timing (continued)
Num
Characteristic
All Frequencies
Unit
Min
Max

50
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
Serial Interface AC Electrical Specifications
Figure 8-45. SI Receive Timing Diagram with Normal Clocking (DSC = 0)
L1RxD
(Input)
79
76
77
74
L1RCLK
(FE=0, CE=0)
(Input)
L1RCLK
(FE=1, CE=1)
(Input)
L1RSYNC
(Input)
L1STn
(Output)
71
70
RFSD=1
75
72
73
78
BIT0
71a

MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
51
Serial Interface AC Electrical Specifications
Figure 8-46. SI Receive Timing with Double-Speed Clocking (DSC = 1)
L1RXD
(Input)
L1RCLK
(FE=1, CE=1)
(Input)
L1RCLK
(FE=0, CE=0)
(Input)
L1RSYNC
(Input)
L1ST(4-1)
(Output)
72
RFSD=1
75
73
74
77
78
76
79
83a
82
L1CLKO
(Output)
84
BIT0
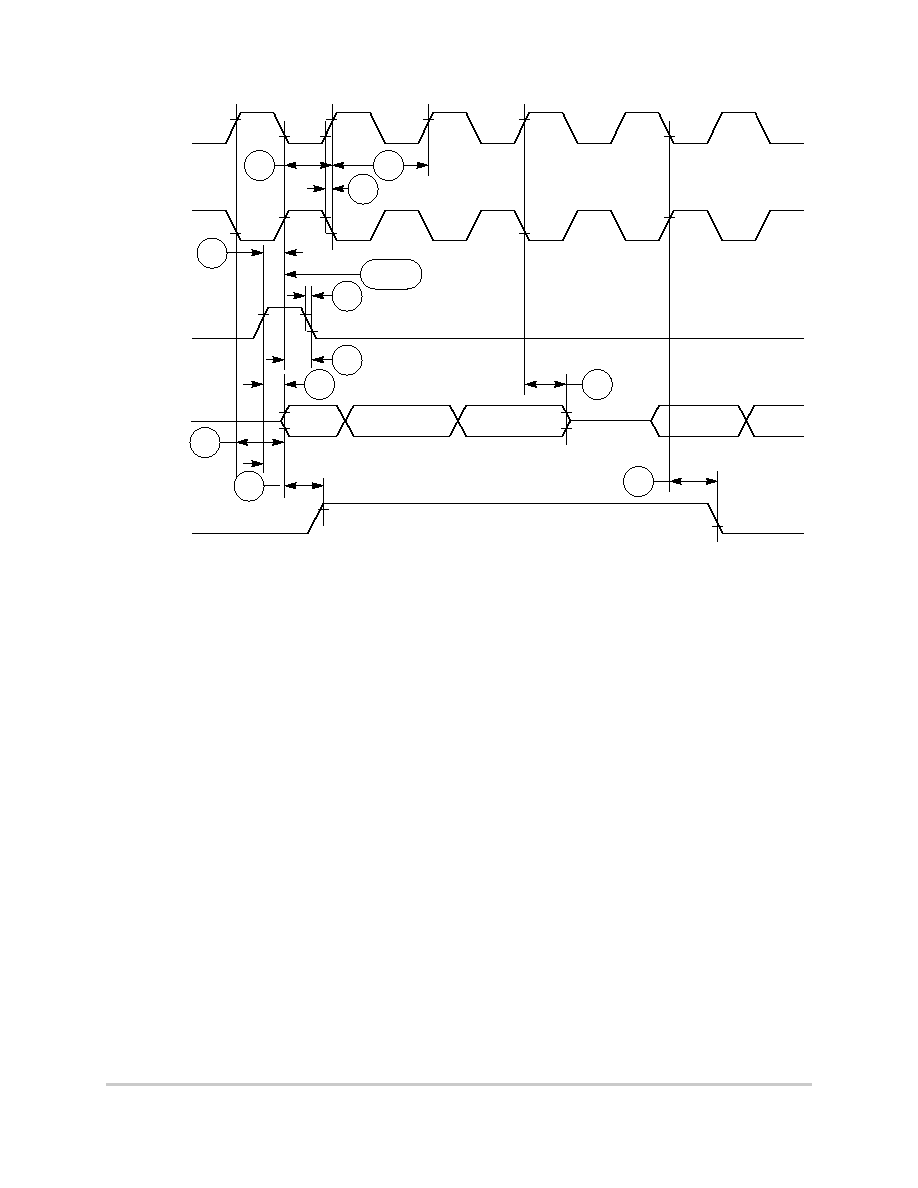
52
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
Serial Interface AC Electrical Specifications
Figure 8-47. SI Transmit Timing Diagram
L1TxD
(Output)
79
81
80a
L1TCLK
(FE=0, CE=0)
(Input)
L1TCLK
(FE=1, CE=1)
(Input)
L1TSYNC
(Input)
L1STn
(Output)
70
TFSD=0
75
72
74
80
BIT0
71
73
78
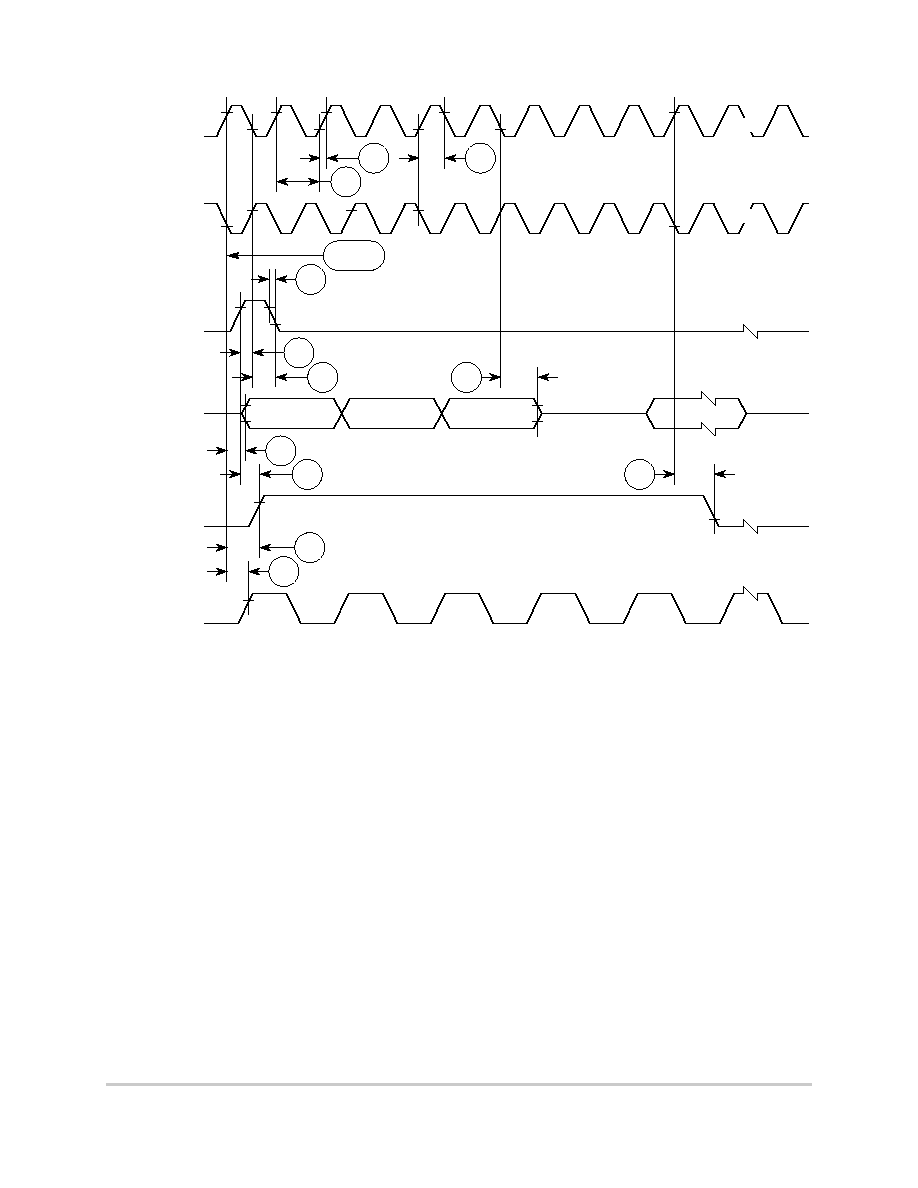
MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
53
Serial Interface AC Electrical Specifications
Figure 8-48. SI Transmit Timing with Double Speed Clocking (DSC = 1)
L1TXD
(Output)
L1RCLK
(FE=0, CE=0)
(Input)
L1RCLK
(FE=1, CE=1)
(Input)
L1RSYNC
(Input)
L1ST(4-1)
(Output)
72
TFSD=0
75
73
74
78a
80
79
83a
82
L1CLKO
(Output)
84
BIT0
78
81
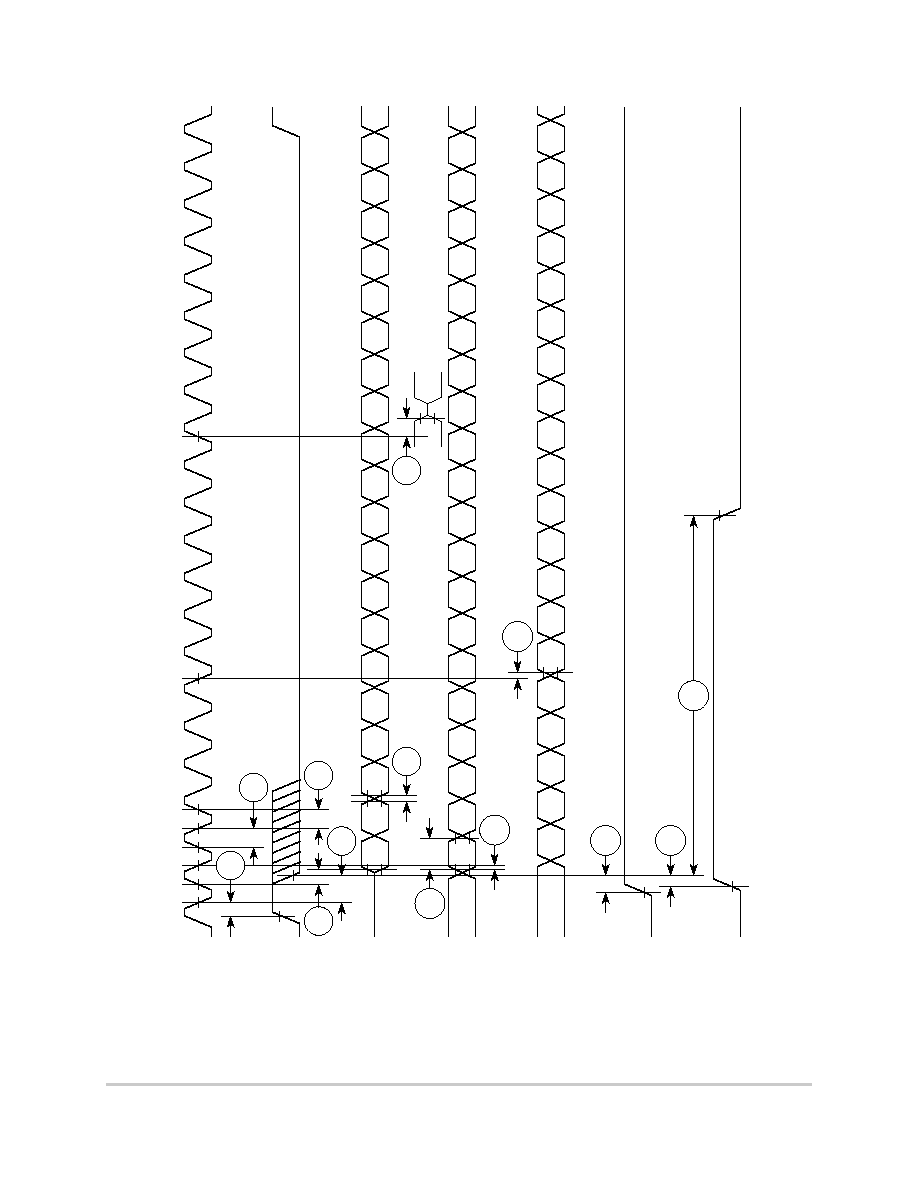
54
MPC850 (Re
v
.
A/B/C) Har
d
ware Specifications
MO
T
O
R
OLA
Serial Interface AC Electrical Specifications
Figure 8-49.
IDL
Timing
B17 B16
B14
B13
B12 B11 B10
D1
A
B27
B26
B25
B24
B23
B22
B21
B20
D2
M
B15
L1RXD
(Input)
L1TXD
(Output)
L1ST(4-1)
(Output)
L1RQ
(Output)
73
77
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
74
80
B17 B16
B15 B14
B13
B12 B11 B10
D1
A
B27 B26
B25
B24
B23
B22
B21
B20
D2
M
71
71
L1GR
(Input)
78
85
72
76
87
86
L1RSYNC
(Input)
L1RCLK
(Input)
81

MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
55
SCC in NMSI Mode Electrical Specifications
8.6
SCC in NMSI Mode Electrical Specifications
Table 8-18 provides the NMSI external clock timing.
Table 8-19 provides the NMSI internal clock timing.
Table 8-18. NMSI External Clock Timing
Num
Characteristic
All Frequencies
Unit
Min
Max
100
RCLKx and TCLKx frequency
1
(x = 2, 3 for all specs in this
table)
1
The ratios SyncCLK/RCLKx and SyncCLK/TCLKx must be greater than or equal to 2.25/1.
1/SYNCCLK
--
ns
101
RCLKx and TCLKx width low
1/SYNCCLK +5
--
ns
102
RCLKx and TCLKx rise/fall time
--
15.00
ns
103
TXDx active delay (from TCLKx falling edge)
0.00
50.00
ns
104
RTSx active/inactive delay (from TCLKx falling edge)
0.00
50.00
ns
105
CTSx setup time to TCLKx rising edge
5.00
--
ns
106
RXDx setup time to RCLKx rising edge
5.00
--
ns
107
RXDx hold time from RCLKx rising edge
2
2
Also applies to CD and CTS hold time when they are used as an external sync signal.
5.00
--
ns
108 CDx setup time to RCLKx rising edge
5.00
--
ns
Table 8-19. NMSI Internal Clock Timing
Num
Characteristic
All Frequencies
Unit
Min
Max
100
RCLKx and TCLKx frequency
1
(x = 2, 3 for all specs in this table)
1
The ratios SyncCLK/RCLKx and SyncCLK/TCLK1x must be greater or equal to 3/1.
0.00
SYNCCLK/3
MHz
102
RCLKx and TCLKx rise/fall time
--
--
ns
103
TXDx active delay (from TCLKx falling edge)
0.00
30.00
ns
104
RTSx active/inactive delay (from TCLKx falling edge)
0.00
30.00
ns
105
CTSx setup time to TCLKx rising edge
40.00
--
ns
106
RXDx setup time to RCLKx rising edge
40.00
--
ns
107
RXDx hold time from RCLKx rising edge
2
2
Also applies to CD and CTS hold time when they are used as an external sync signals.
0.00
--
ns
108
CDx setup time to RCLKx rising edge
40.00
--
ns

56
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
SCC in NMSI Mode Electrical Specifications
Figure 8-50 through Figure 8-52 show the NMSI timings.
Figure 8-50. SCC NMSI Receive Timing Diagram
Figure 8-51. SCC NMSI Transmit Timing Diagram
RCLKx
CDx
(Input)
102
100
107
108
107
RXDx
(Input)
CDx
(SYNC Input)
102
101
106
TCLKx
CTSx
(Input)
102
100
104
107
TXDx
(Output)
CTSx
(SYNC Input)
102
101
RTSx
(Output)
105
103
104

MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
57
Ethernet Electrical Specifications
Figure 8-52. HDLC Bus Timing Diagram
8.7
Ethernet Electrical Specifications
Table 8-20 provides the Ethernet timings as shown in Figure 8-53 to Figure 8-55.
Table 8-20. Ethernet Timing
Num
Characteristic
All Frequencies
Unit
Min
Max
120
CLSN width high
40.00
--
ns
121
RCLKx rise/fall time (x = 2, 3 for all specs in this table)
--
15.00
ns
122
RCLKx width low
40.00
--
ns
123
RCLKx clock period
1
80.00
120.00
ns
124
RXDx setup time
20.00
--
ns
125
RXDx hold time
5.00
--
ns
126
RENA active delay (from RCLKx rising edge of the last data bit)
10.00
--
ns
127
RENA width low
100.00
--
ns
128
TCLKx rise/fall time
--
15.00
ns
129
TCLKx width low
40.00
--
ns
130
TCLKx clock period
1
99.00
101.00
ns
131
TXDx active delay (from TCLKx rising edge)
10.00
50.00
ns
132
TXDx inactive delay (from TCLKx rising edge)
10.00
50.00
ns
TCLKx
CTSx
(Echo Input)
102
100
104
TXDx
(Output)
102
101
RTSx
(Output)
103
104
107
105
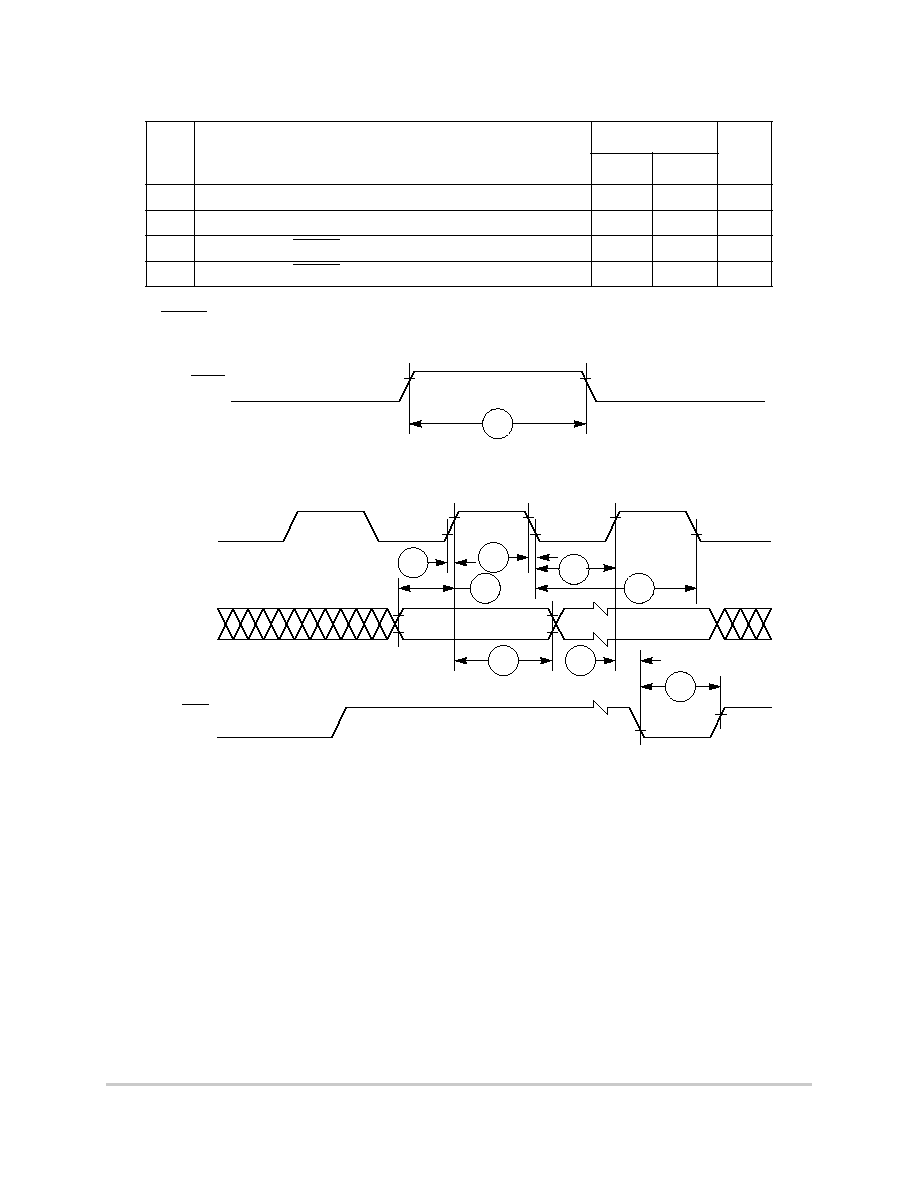
58
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
Ethernet Electrical Specifications
Figure 8-53. Ethernet Collision Timing Diagram
Figure 8-54. Ethernet Receive Timing Diagram
133
TENA active delay (from TCLKx rising edge)
10.00
50.00
ns
134
TENA inactive delay (from TCLKx rising edge)
10.00
50.00
ns
138
CLKOUT low to SDACK asserted
2
--
20.00
ns
139
CLKOUT low to SDACK negated
2
--
20.00
ns
1
The ratios SyncCLK/RCLKx and SyncCLK/TCLKx must be greater or equal to 2/1.
2
SDACK is asserted whenever the SDMA writes the incoming frame destination address into memory.
Table 8-20. Ethernet Timing (continued)
Num
Characteristic
All Frequencies
Unit
Min
Max
CLSN(CTSx)
120
(Input)
RCLKx
121
RXDx
(Input)
121
RENA(CDx)
(Input)
125
124
123
127
126
Last Bit
122
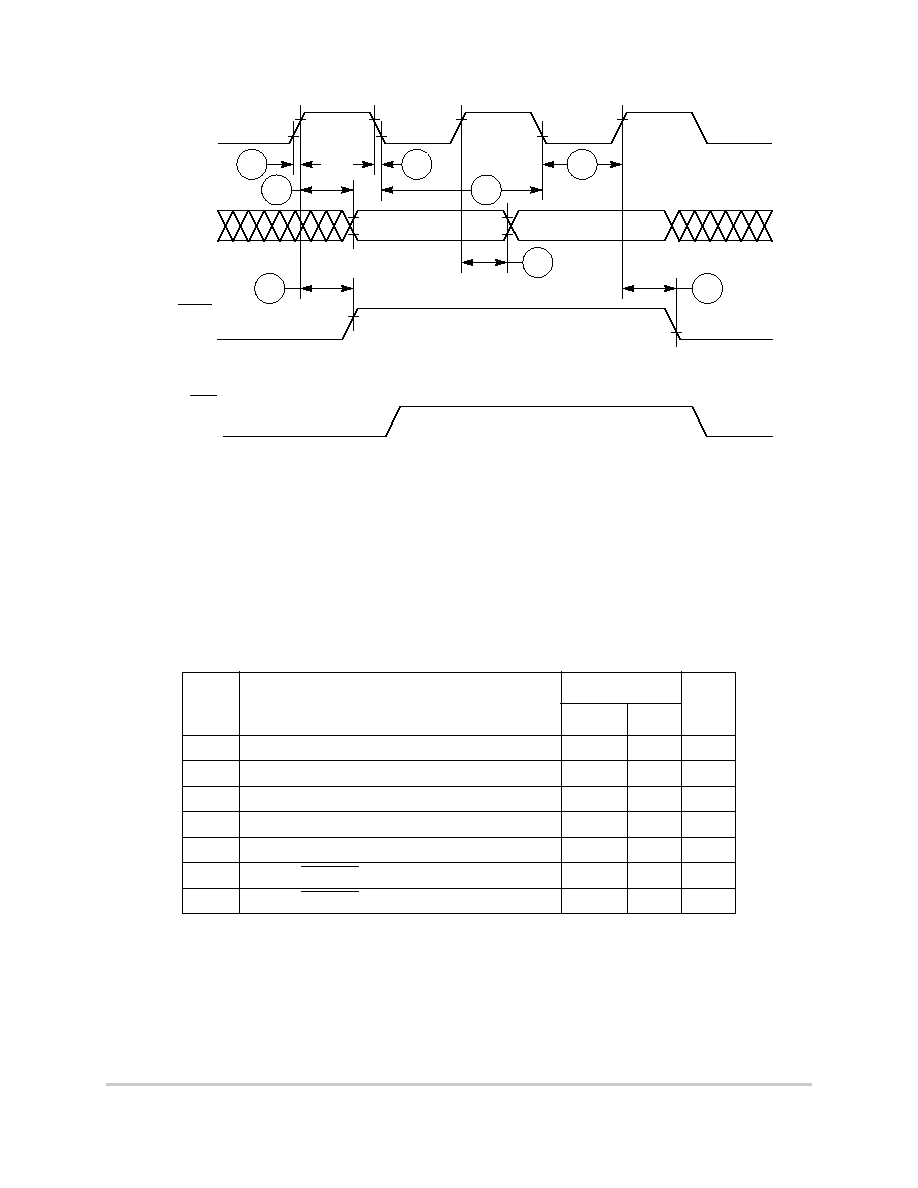
MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
59
SMC Transparent AC Electrical Specifications
Figure 8-55. Ethernet Transmit Timing Diagram
8.8
SMC Transparent AC Electrical Specifications
Figure 8-21 provides the SMC transparent timings as shown in Figure 8-56.
Table 8-21. Serial Management Controller Timing
Num
Characteristic
All Frequencies
Unit
Min
Max
150
SMCLKx clock period
1
1
The ratio SyncCLK/SMCLKx must be greater or equal to 2/1.
100.00
--
ns
151
SMCLKx width low
50.00
--
ns
151a
SMCLKx width high
50.00
--
ns
152
SMCLKx rise/fall time
--
15.00
ns
153
SMTXDx active delay (from SMCLKx falling edge)
10.00
50.00
ns
154
SMRXDx/SMSYNx setup time
20.00
--
ns
155
SMRXDx/SMSYNx hold time
5.00
--
ns
TCLKx
128
TxDx
(Output)
128
TENA(RTSx)
(Input)
NOTES:
Transmit clock invert (TCI) bit in GSMR is set.
If RENA is deasserted before TENA, or RENA is not asserted at all during transmit, then the
CSL bit is set in the buffer descriptor at the end of the frame transmission.
1.
2.
RENA(CDx)
(Input)
133
134
132
131
130
129
(NOTE 2)

60
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
SPI Master AC Electrical Specifications
Figure 8-56. SMC Transparent Timing Diagram
8.9
SPI Master AC Electrical Specifications
Table 8-22 provides the SPI master timings as shown in Figure 8-57 and Figure 8-58.
Table 8-22. SPI Master Timing
Num
Characteristic
All Frequencies
Unit
Min
Max
160
MASTER cycle time
4
1024
t
cyc
161
MASTER clock (SCK) high or low time
2
512
t
cyc
162
MASTER data setup time (inputs)
50.00
--
ns
163
Master data hold time (inputs)
0.00
--
ns
164
Master data valid (after SCK edge)
--
20.00
ns
165
Master data hold time (outputs)
0.00
--
ns
166
Rise time output
--
15.00
ns
167
Fall time output
--
15.00
ns
SMCLKx
SMRXDx
(Input)
152
150
SMTXDx
(Output)
152
151
151a
154
153
155
154
155
NOTE
NOTE:
This delay is equal to an integer number of character-length clocks.
1.
SMSYNx

MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
61
SPI Master AC Electrical Specifications
Figure 8-57. SPI Master (CP = 0) Timing Diagram
Figure 8-58. SPI Master (CP = 1) Timing Diagram
SPIMOSI
(Output)
SPICLK
(CI=0)
(Output)
SPICLK
(CI=1)
(Output)
SPIMISO
(Input)
162
Data
166
167
161
161
160
msb
lsb
msb
msb
Data
lsb
msb
167
166
163
166
167
165
164
SPIMOSI
(Output)
SPICLK
(CI=0)
(Output)
SPICLK
(CI=1)
(Output)
SPIMISO
(Input)
Data
166
167
161
161
160
msb
lsb
msb
msb
Data
lsb
msb
167
166
163
166
167
165
164
162

62
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
SPI Slave AC Electrical Specifications
8.10 SPI Slave AC Electrical Specifications
Table 8-23 provides the SPI slave timings as shown in Figure 8-59 and Figure 8-60.
Table 8-23. SPI Slave Timing
Num
Characteristic
All Frequencies
Unit
Min
Max
170
Slave cycle time
2
--
t
cyc
171
Slave enable lead time
15.00
--
ns
172
Slave enable lag time
15.00
--
ns
173
Slave clock (SPICLK) high or low time
1
--
t
cyc
174
Slave sequential transfer delay (does not require deselect)
1
--
t
cyc
175
Slave data setup time (inputs)
20.00
--
ns
176
Slave data hold time (inputs)
20.00
--
ns
177
Slave access time
--
50.00
ns
178
Slave SPI MISO disable time
--
50.00
ns
179
Slave data valid (after SPICLK edge)
--
50.00
ns
180
Slave data hold time (outputs)
0.00
--
ns
181
Rise time (input)
--
15.00
ns
182
Fall time (input)
--
15.00
ns
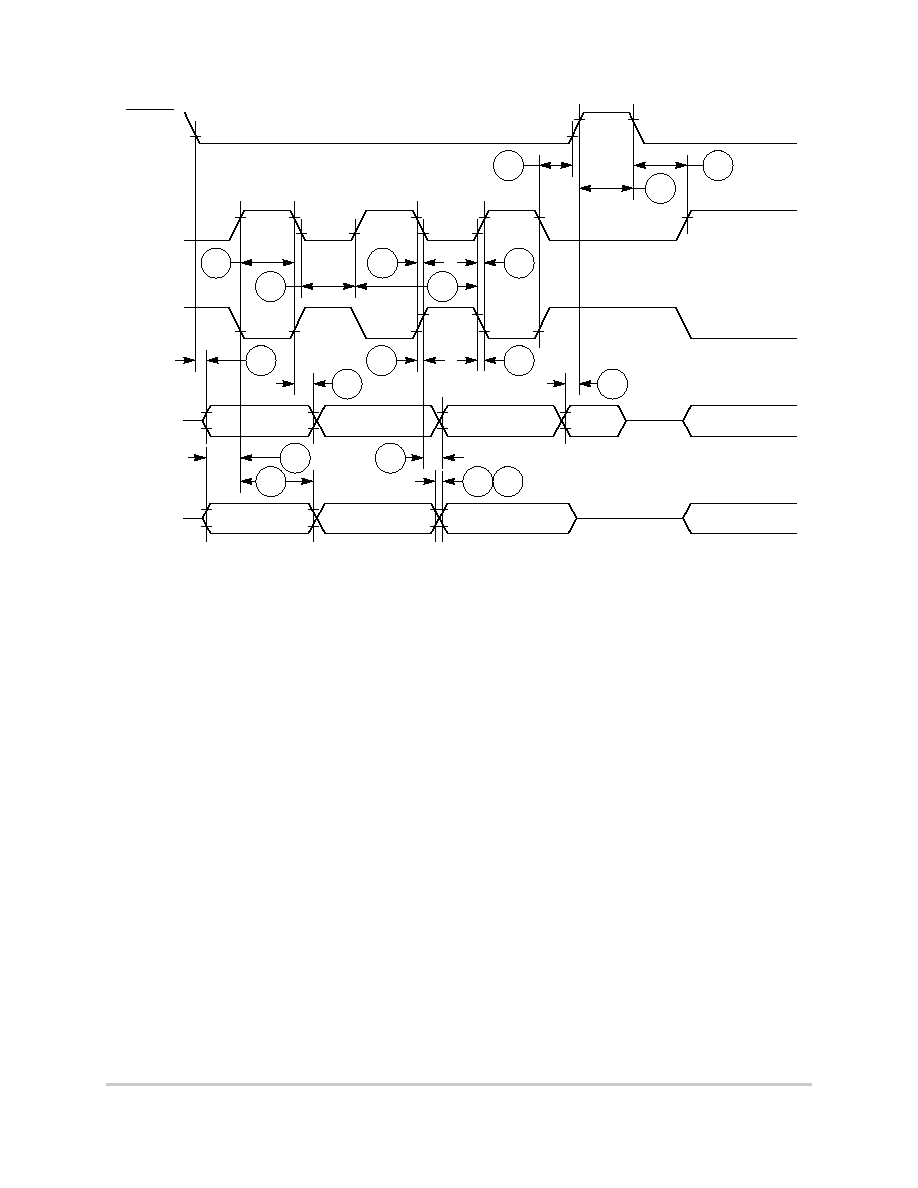
MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
63
SPI Slave AC Electrical Specifications
Figure 8-59. SPI Slave (CP = 0) Timing Diagram
SPIMOSI
(Input)
SPICLK
(CI=0)
(Input)
SPICLK
(CI=1)
(Input)
SPIMISO
(Output)
180
Data
181
182
173
173
170
msb
lsb
msb
181
177
182
175
179
SPISEL
(Input)
171
172
174
Data
msb
lsb
msb
Undef
181
178
176
182

64
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
I2C AC Electrical Specifications
Figure 8-60. SPI Slave (CP = 1) Timing Diagram
8.11 I
2
C AC Electrical Specifications
Table 8-24 provides the I
2
C (SCL < 100 KHz) timings.
Table 8-24. I
2
C Timing (SCL < 100 KH
Z
)
Num
Characteristic
All Frequencies
Unit
Min
Max
200
SCL clock frequency (slave)
0.00
100.00
KHz
200
SCL clock frequency (master)
1
1.50
100.00
KHz
202
Bus free time between transmissions
4.70
--
µ
s
203
Low period of SCL
4.70
--
µ
s
204
High period of SCL
4.00
--
µ
s
205
Start condition setup time
4.70
--
µ
s
206
Start condition hold time
4.00
--
µ
s
207
Data hold time
0.00
--
µ
s
SPIMOSI
(Input)
SPICLK
(CI=0)
(Input)
SPICLK
(CI=1)
(Input)
SPIMISO
(Output)
180
Data
181
182
msb
lsb
181
177
182
175
179
SPISEL
(Input)
174
Data
msb
lsb
Undef
178
176
182
msb
msb
172
173
173
171
170
181

MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
65
I2C AC Electrical Specifications
Table 8-25 provides the I
2
C (SCL > 100 KHz) timings.
208
Data setup time
250.00
--
ns
209
SDL/SCL rise time
--
1.00
µ
s
210
SDL/SCL fall time
--
300.00
ns
211
Stop condition setup time
4.70
--
µ
s
1
SCL frequency is given by SCL = BRGCLK_frequency / ((BRG register + 3) * pre_scaler * 2).
The ratio SyncClk/(BRGCLK/pre_scaler) must be greater or equal to 4/1.
Table 8-25. I
2
C Timing (SCL > 100 KH
Z
)
Num
Characteristic
Expression
All Frequencies
Unit
Min
Max
200
SCL clock frequency (slave)
fSCL
0
BRGCLK/48
Hz
200
SCL clock frequency (master)
1
1
SCL frequency is given by SCL = BrgClk_frequency / ((BRG register + 3) * pre_scaler * 2).
The ratio SyncClk/(Brg_Clk/pre_scaler) must be greater or equal to 4/1.
fSCL
BRGCLK/16512
BRGCLK/48
Hz
202
Bus free time between transmissions
1/(2.2 * fSCL)
--
s
203
Low period of SCL
1/(2.2 * fSCL)
--
s
204
High period of SCL
1/(2.2 * fSCL)
--
s
205
Start condition setup time
1/(2.2 * fSCL)
--
s
206
Start condition hold time
1/(2.2 * fSCL)
--
s
207
Data hold time
0
--
s
208
Data setup time
1/(40 * fSCL)
--
s
209
SDL/SCL rise time
--
1/(10 * fSCL)
s
210
SDL/SCL fall time
--
1/(33 * fSCL)
s
211
Stop condition setup time
1/2(2.2 * fSCL)
--
s
Table 8-24. I
2
C Timing (SCL < 100 KH
Z
) (
CONTINUED
)
Num
Characteristic
All Frequencies
Unit
Min
Max
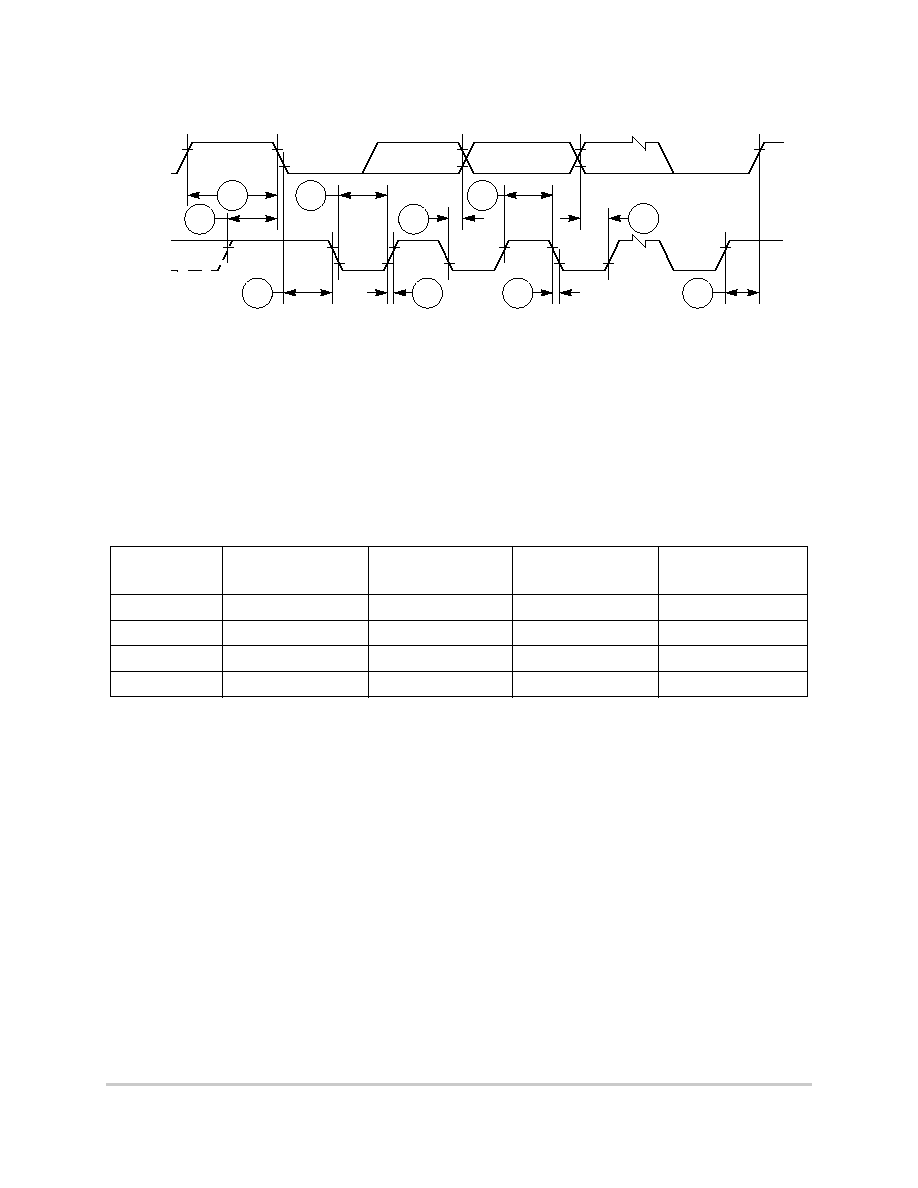
66
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
I2C AC Electrical Specifications
Figure 8-61 shows the I
2
C bus timing.
Figure 8-61. I
2
C Bus Timing Diagram
Part IX Mechanical Data and Ordering
Information
Table 9-26 provides information on the MPC850 derivative devices.
Table 9-26. MPC850 Family Derivatives
Device
Ethernet Support
Number of SCCs
1
1
Serial Communication Controller (SCC)
32-Channel HDLC
Support
64-Channel HDLC
Support
2
2
50 MHz version supports 64 time slots on a time division multiplexed line using one SCC
MPC850
N/A
One
N/A
N/A
MPC850DE
Yes
Two
N/A
N/A
MPC850SR
Yes
Two
N/A
Yes
MPC850DSL
Yes
Two
No
No
SCL
202
205
203
207
204
208
206
209
211
210
SDA
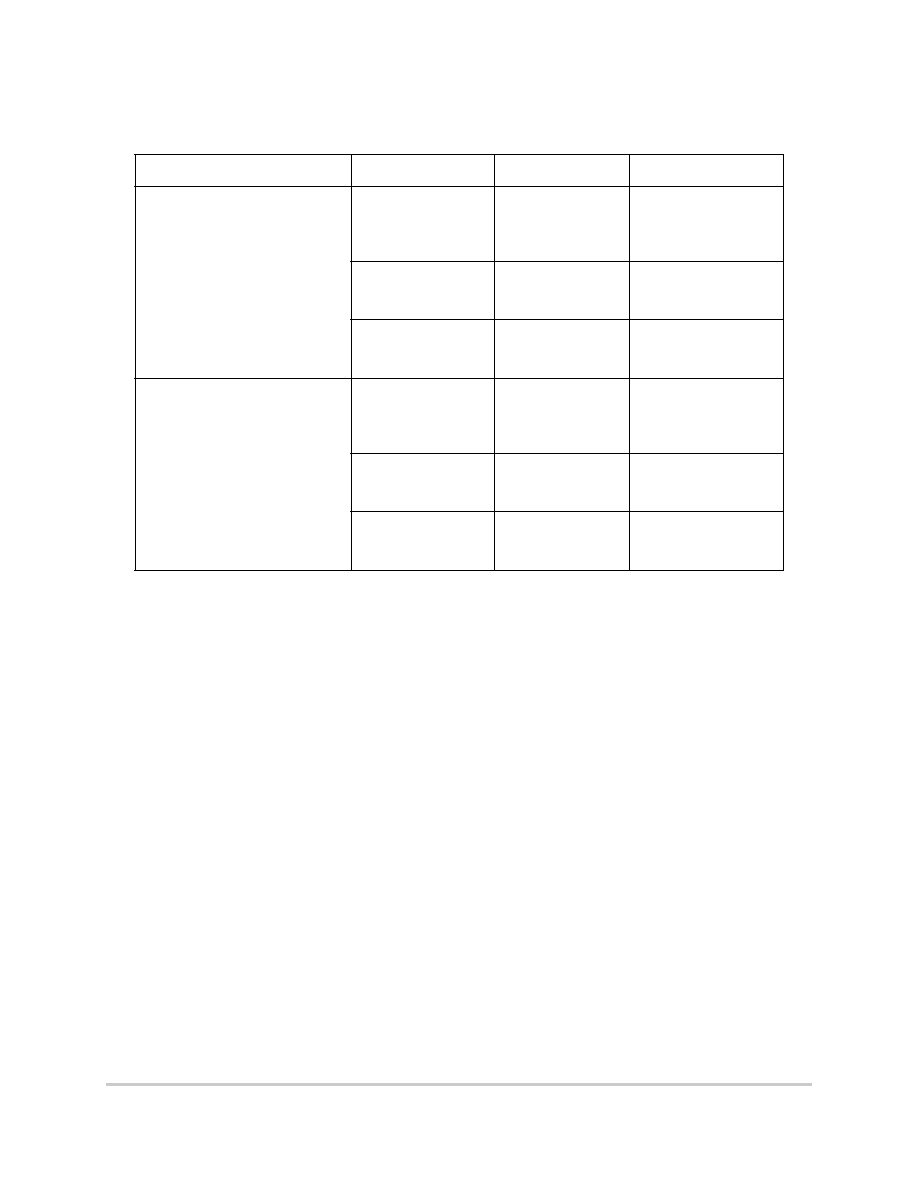
67
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
Pin Assignments and Mechanical Dimensions of the PBGA
Table 9-27 identifies the packages and operating frequencies available for the MPC850.
9.1
Pin Assignments and Mechanical Dimensions of
the PBGA
The original pin numbering of the MPC850 conformed to a Motorola proprietary pin
numbering scheme that has since been replaced by the JEDEC pin numbering standard for
this package type. To support customers that are currently using the non-JEDEC pin
numbering scheme, two sets of pinouts, JEDEC and non-JEDEC, are presented in this
document.
Table 9-27. MPC850 Package/Frequency/Availability
Package Type
Frequency (MHz)
Temperature (Tj)
Order Number
256-Lead Plastic Ball Grid Array
(ZT suffix)
50
0∞C to 95∞C
XPC850ZT50BU
XPC850DEZT50BU
XPC850SRZT50BU
XPC850DSLZT50BU
66
0∞C to 95∞C
XPC850ZT66BU
XPC850DEZT66BU
XPC850SRZT66BU
80
0∞C to 95∞C
XPC850ZT80BU
XPC850DEZT80BU
XPC850SRZT80BU
256-Lead Plastic Ball Grid Array
(CZT suffix)
50
-40∞C to 95∞C
XPC850CZT50BU
XPC850DECZT50BU
XPC850SRCZT50BU
XPC850DSLCZT50BU
66
XPC850CZT66BU
XPC850DECZT66BU
XPC850SRCZT66BU
80
XPC850CZT80B
XPC850DECZT80B
XPC850SRCZT80B
68
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
Pin Assignments and Mechanical Dimensions of the PBGA
Figure 9-62 shows the non-JEDEC pinout of the PBGA package as viewed from the top
surface.
Figure 9-62. Pin Assignments for the PBGA (Top View)--non-JEDEC Standard
PC14
PB28
PB27
PC12
TCK
PB24
PB23
PA8
PA7
VDDL
PA5
PC7
PC4
PD14
PD10
PD8
PC15
PA14
PA13
PA12
TMS
PB26
PA15
PB30
PB29
PC13
TRST
N/C
PC10
PA6
PB18
PC5
PD13
PD9
PD4
PD5
A8
A7
PB31
TDO
TDI
PC11
PB22
PC9
PB25
PA9
PC8
A11
A9
A12
PB19
PA4
PB16
PD15
PD12
PD7
PD6
PB17
PC6
PD11
PD3
IRQ7
IRQ1
IRQ0
T
R
P
N
M
A15
A14
A13
A27
A19
A16
VDDL
A20
A21
A29
A23
A25
A28
A30
A22
A31
TSIZ0
A26
WE1
TSIZ1
WE0
WE2
GPLA3
GPLA1 GPLA2
CS6
D8
D0
D4
D1
D9
D11
D2
D3
K
J
H
L
D16
D5
D19
VDDL
D21
D6
D29
D7
D30
CLKOUT
DP3
N/C
GND
G
F
VDDH
E
D
CS4
CS7
CS2
XFC VDDSYN
BI
N/C
CS3
CS1
BDIP
BURST IPB4
ALEB
IRQ4 MODCK2HRESETSRESETPORESET
VSSSYN1VSSSYN
BR
BB
IRQ6
IPB3
IPB0
VDDL EXTCLKEXTAL XTAL KAPWR
C
B
A
TA
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
A6
A10
A17
A24
A18
WE3
GPLA0
CS5
WR
GPLB4
CS0
TS
IRQ2
IPB7
IPB2 MODCK1 TEXP
DP1
DP2
GPLA4
TEA
BG
IPB5
IPB1
IPB6
RSTCONFWAITB DP0
GPLA5
D12
D13
D23
D27
D17
D10
D15
D14
D22
D18
D25
D20
D28
D24
D26
D31
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C

MOTOROLA
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
69
Pin Assignments and Mechanical Dimensions of the PBGA
Figure 9-63 shows the JEDEC pinout of the PBGA package as viewed from the top surface.
Figure 9-63. Pin Assignments for the PBGA (Top View)--JEDEC Standard
For more information on the printed circuit board layout of the PBGA package, including
thermal via design and suggested pad layout, please refer to AN-1231/D, Plastic Ball Grid
Array Application Note available from your local Motorola sales office.
PC14
PB28
PB27
PC12
TCK
PB24
PB23
PA8
PA7
VDDL
PA5
PC7
PC4
PD14
PD10
PD8
PC15
PA14
PA13
PA12
TMS
PB26
PA15
PB30
PB29
PC13
TRST
N/C
PC10
PA6
PB18
PC5
PD13
PD9
PD4
PD5
A8
A7
PB31
TDO
TDI
PC11
PB22
PC9
PB25
PA9
PC8
A11
A9
A12
PB19
PA4
PB16
PD15
PD12
PD7
PD6
PB17
PC6
PD11
PD3
IRQ7
IRQ1
IRQ0
U
T
R
P
N
A15
A14
A13
A27
A19
A16
VDDL
A20
A21
A29
A23
A25
A28
A30
A22
A31
TSIZ0
A26
WE1
TSIZ1
WE0
WE2
GPLA3
GPLA1 GPLA2
CS6
D8
D0
D4
D1
D9
D11
D2
D3
L
K
J
M
D16
D5
D19
VDDL
D21
D6
D29
D7
D30
CLKOUT
DP3
N/C
GND
H
G
VDDH
F
E
CS4
CS7
CS2
XFC VDDSYN
BI
N/C
CS3
CS1
BDIP
BURST IPB4
ALEB
IRQ4 MODCK2HRESETSRESETPORESET
VSSSYN1VSSSYN
BR
BB
IRQ6
IPB3
IPB0
VDDL EXTCLKEXTAL XTAL KAPWR
D
C
B
TA
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
A6
A10
A17
A24
A18
WE3
GPLA0
CS5
WR
GPLB4
CS0
TS
IRQ2
IPB7
IPB2 MODCK1 TEXP
DP1
DP2
GPLA4
TEA
BG
IPB5
IPB1
IPB6
RSTCONFWAITB DP0
GPLA5
D12
D13
D23
D27
D17
D10
D15
D14
D22
D18
D25
D20
D28
D24
D26
D31
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C
N/C

70
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
Pin Assignments and Mechanical Dimensions of the PBGA
Figure 9-64 shows the non-JEDEC package dimensions of the PBGA.
Figure 9-64. Package Dimensions for the Plastic Ball Grid Array
(PBGA)--non-JEDEC Standard
T
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
256X
BOTTOM VIEW
E
0.20
6
5
4
3
2
1
b
0.15
C
D
D2
E2
A
B
0.30
C A B
SIDE VIEW
DIM
MIN
MAX
MILLIMETERS
A
1.91
2.35
A1
0.50
0.70
A2
1.12
1.22
A3
0.29
0.43
b
0.60
0.90
D
23.00 BSC
D1
19.05 REF
D2
E
23.00 BSC
E1
19.05 REF
E2
19.00
20.00
NOTES:
1.
DIMENSIONING AND TOLERANCING PER ASME
Y14.5M, 1994.
2.
DIMENSIONS IN MILLIMETERS.
3.
DIMENSION b IS MEASURED AT THE MAXIMUM
SOLDER BALL DIAMETER, PARALLEL TO PRIMARY
DATUM C.
4.
PRIMARY DATUM C AND THE SEATING PLANE ARE
DEFINED BY THE SPHERICAL CROWNS OF THE
SOLDER BALLS.
4X
7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
M
M
TOP VIEW
(D1)
15X
e
15X
e
(E1)
4X
e /2
0.20 C
0.35 C
A3
256X
C
A
A1
A2
SEATING
PLANE
e
1.27 BSC
19.00
20.00
16

71
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
Pin Assignments and Mechanical Dimensions of the PBGA
Figure 9-65 shows the JEDEC package dimensions of the PBGA.
Figure 9-65. Package Dimensions for the Plastic Ball Grid Array (PBGA)--JEDEC
Standard
U
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
M
N
P
R
T
256X
BOTTOM VIEW
E
0.20
7
6
5
4
3
2
b
0.15
C
D
D2
E2
A
B
0.30
C A B
SIDE VIEW
DIM
MIN
MAX
MILLIMETERS
A
1.91
2.35
A1
0.50
0.70
A2
1.12
1.22
A3
0.29
0.43
b
0.60
0.90
D
23.00 BSC
D1
19.05 REF
D2
E
23.00 BSC
E1
19.05 REF
E2
19.00
20.00
NOTES:
1.
DIMENSIONING AND TOLERANCING PER ASME
Y14.5M, 1994.
2.
DIMENSIONS IN MILLIMETERS.
3.
DIMENSION b IS MEASURED AT THE MAXIMUM
SOLDER BALL DIAMETER, PARALLEL TO PRIMARY
DATUM C.
4.
PRIMARY DATUM C AND THE SEATING PLANE ARE
DEFINED BY THE SPHERICAL CROWNS OF THE
SOLDER BALLS.
4X
8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
M
M
TOP VIEW
(D1)
15X
e
15X
e
(E1)
4X
e /2
0.20 C
0.35 C
A3
256X
C
A
A1
A2
SEATING
PLANE
e
1.27 BSC
19.00
20.00
17
CASE 1130-01
ISSUE B

72
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
Pin Assignments and Mechanical Dimensions of the PBGA
Part X Document Revision History
Table 10-28 lists significant changes between revisions of this document.
Table 10-28. Document Revision History
Revision
Date
Change
0.1
11/2001
Removed reference to 5 Volt tolerance capability on peripheral interface pins.
Replaced SI and IDL timing diagrams with better images. Updated to new
template, added this revision table.
0.2
04/2002
Updated power numbers and added Rev. C
1
10/2002
Added MPC850DSL. Corrected Figure 6-25 on page 37.

73
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
Pin Assignments and Mechanical Dimensions of the PBGA
THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK

74
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
Pin Assignments and Mechanical Dimensions of the PBGA
THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK

75
MPC850 (Rev. A/B/C) Hardware Specifications
MOTOROLA
Pin Assignments and Mechanical Dimensions of the PBGA
THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK

MPC850ABEC/D
HOW TO REACH US:
USA/EUROPE/LOCATIONS NOT LISTED:
Motorola Literature Distribution
P.O. Box 5405, Denver, Colorado 80217
1-303-675-2140 or 1-800-441-2447
JAPAN:
Motorola Japan Ltd.
SPS, Technical Information Center
3-20-1, Minami-Azabu Minato-ku
Tokyo 106-8573 Japan
81-3-3440-3569
ASIA/PACIFIC:
Motorola Semiconductors H.K. Ltd.
Silicon Harbour Centre, 2 Dai King Street
Tai Po Industrial Estate, Tai Po, N.T., Hong Kong
852-26668334
TECHNICAL INFORMATION CENTER:
800-521-6274
HOME PAGE:
www.motorola.com/semiconductors
Information in this document is provided solely to enable system and software implementers to use
Motorola products. There are no express or implied copyright licenses granted hereunder to design
or fabricate any integrated circuits or integrated circuits based on the information in this document.
Motorola reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products herein.
Motorola makes no warranty, representation or guarantee regarding the suitability of its products
for any particular purpose, nor does Motorola assume any liability arising out of the application or
use of any product or circuit, and specifically disclaims any and all liability, including without
limitation consequential or incidental damages. "Typical" parameters which may be provided in
Motorola data sheets and/or specifications can and do vary in different applications and actual
performance may vary over time. All operating parameters, including "Typicals" must be validated
for each customer application by customer's technical experts. Motorola does not convey any
license under its patent rights nor the rights of others. Motorola products are not designed,
intended, or authorized for use as components in systems intended for surgical implant into the
body, or other applications intended to support or sustain life, or for any other application in which
the failure of the Motorola product could create a situation where personal injury or death may
occur. Should Buyer purchase or use Motorola products for any such unintended or unauthorized
application, Buyer shall indemnify and hold Motorola and its officers, employees, subsidiaries,
affiliates, and distributors harmless against all claims, costs, damages, and expenses, and
reasonable attorney fees arising out of, directly or indirectly, any claim of personal injury or death
associated with such unintended or unauthorized use, even if such claim alleges that Motorola was
negligent regarding the design or manufacture of the part.
Motorola and the Stylized M Logo are registered in the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office.
digital dna is a trademark of Motorola, Inc. All other product or service names are the property of
their respective owners. Motorola, Inc. is an Equal Opportunity/Affirmative Action Employer.
© Motorola, Inc. 2002