Document Outline
- COVER
- Features
- Ordering Information
- Pin Configuration
- Block Diagram
- Electrical Specifications
- Package Drawing

The information in this document is subject to change without notice. Before using this document, please
confirm that this is the latest version.
Not all devices/types available in every country. Please check with local NEC representative for
availability and additional information.
©
2000
Document No. M15085EJ5V0DS00 (5th edition)
Date Published October 2001 NS CP (K)
Printed in Japan
MOS INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112
16M-BIT CMOS MOBILE SPECIFIED RAM
1M-WORD BY 16-BIT
DATA SHEET
The mark
5
5
5
5
shows major revised points.
5
5
Description
The
µ
PD4616112 is a high speed, low power, 16,777,216 bits (1,048,576 words by 16 bits) CMOS mobile specified
RAM featuring low power static RAM compatible function and pin configuration.
The
µ
PD4616112 is fabricated with advanced CMOS technology using one-transistor memory cell.
The
µ
PD4616112 is packed in 48-pin TAPE FBGA.
Features
∑
1,048,576 words by 16 bits organization
∑
Fast access time: 80, 90 ns (MAX.)
∑
Byte data control: /LB (I/O0 - I/O7), /UB (I/O8 - I/O15)
∑
Low voltage operation: V
CC
= 2.6 to 3.0 V
∑
Operating ambient temperature: T
A
= ≠20 to +70 ∞C
∑
Output Enable input for easy application
∑
Chip Enable input: /CS pin
∑
Standby Mode input: MODE pin
∑
Standby Mode1: Normal standby (Memory cell data hold valid)
∑
Standby Mode2: Memory cell data hold invalid
Product name
Access time
Operating supply Operating ambient
Supply current
ns (MAX.)
Voltage
temperature
At operating
At standby
∞C
mA (MAX.)
µ
A (MAX.)
µ
PD4616112-BCxx
80, 90
2.6 to 3.0
≠20 to +70
35
100 / 10

Data Sheet M15085EJ5V0DS
2
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112
5
5
Ordering Information
Part number
Package
Access time
Operating
Operating
Remark
ns (MAX.)
supply voltage
temperature
V
∞C
µ
PD4616112F9-BC80-BC2
48-pin TAPE FBGA (8 x 6)
80
2.6 to 3.0
≠20 to +70
BC version
µ
PD4616112F9-BC90-BC2
90
Marking Image
Part number
Marking (XX)
µ
PD4616112F9-BC80-BC2
B1
µ
PD4616112F9-BC90-BC2
B2
J
MS16M0-XX
Index mark
Lot number

Data Sheet M15085EJ5V0DS
3
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112
Pin Configuration
/xxx indicates active low signal.
48-pin TAPE FBGA (8 x 6)
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
1
2
3
4
5
6
Bottom View
6
5
4
3
2
1
Top View
Remark Refer to Package Drawing for the index mark.
A0 - A19
: Address inputs
I/O0 - I/O15
: Data inputs / outputs
/CS
: Chip Select
MODE
: Standby mode
/WE
: Write enable
/OE
: Output enable
/LB, /UB
: Byte data select
V
CC
: Power supply
GND
: Ground
1
2
3
4
5
6
A
/LB
/OE
A0
A1
A2
MODE
B
I/O8
/UB
A3
A4
/CS
I/O0
C
I/O9
I/O10
A5
A6
I/O1
I/O2
D
GND
I/O11
A17
A7
I/O3
V
CC
E
V
CC
I/O12
GND
A16
I/O4
GND
F
I/O14
I/O13
A14
A15
I/O5
I/O6
G
I/O15
A19
A12
A13
/WE
I/O7
H
A18
A8
A9
A10
A11
GND
6
5
4
3
2
1
A
MODE
A2
A1
A0
/OE
/LB
B
I/O0
/CS
A4
A3
/UB
I/O8
C
I/O2
I/O1
A6
A5
I/O10
I/O9
D
V
CC
I/O3
A7
A17
I/O11
GND
E
GND
I/O4
A16
GND
I/O12
V
CC
F
I/O6
I/O5
A15
A14
I/O13
I/O14
G
I/O7
/WE
A13
A12
A19
I/O15
H
GND
A11
A10
A9
A8
A18

Data Sheet M15085EJ5V0DS
4
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112
Block Diagram
Address buffer
Memory cell array
16,777,216 bits
Input data
controller
A0
A19
I/O8 - I/O15
Sense amplifier / Switching circuit
Column decoder
/WE
/OE
/UB
/LB
Output data
controller
I/O0 - I/O7
V
CC
GND
/CS
MODE
Address
buffer
Refresh
counter
Row
decoder
Refresh
control
Standby mode control

Data Sheet M15085EJ5V0DS
5
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112
5
Truth Table
/CS
MODE
/OE
/WE
/LB
/UB
Mode
I/O
Supply current
I/O0 - I/O7
I/O8 - I/O15
H
H
◊
◊
◊
◊
Not selected (Standby Mode 1)
High impedance
High impedance
I
SB1
H
L
◊
◊
◊
◊
Not selected (Standby Mode 2)
High impedance
High impedance
I
SB2
L
H
H
H
◊
◊
Output disable
High impedance
High impedance
I
CCA
L
H
L
L
Word read
D
OUT
D
OUT
L
H
Lower byte read
D
OUT
High impedance
H
L
Upper byte read
High impedance
D
OUT
H
H
Output disable
High impedance
High impedance
◊
L
L
L
Word write
D
IN
D
IN
L
H
Lower byte write
D
IN
High impedance
H
L
Upper byte write
High impedance
D
IN
H
H
Write abort
High impedance
High impedance
Caution MODE pin must be fixed to High except Standby Mode 2.
Remark
◊
: V
IH
or V
IL
Initialization
The
µ
PD4616112 is initialized in the power-on sequence according to the following.
(1) To stabilize internal circuits, before turning on the power, a 200
µ
s or longer wait time must precede any signal
toggling.
(2) After the wait time, read operation must be performed at least 3 times. After that, it can be normal operation.
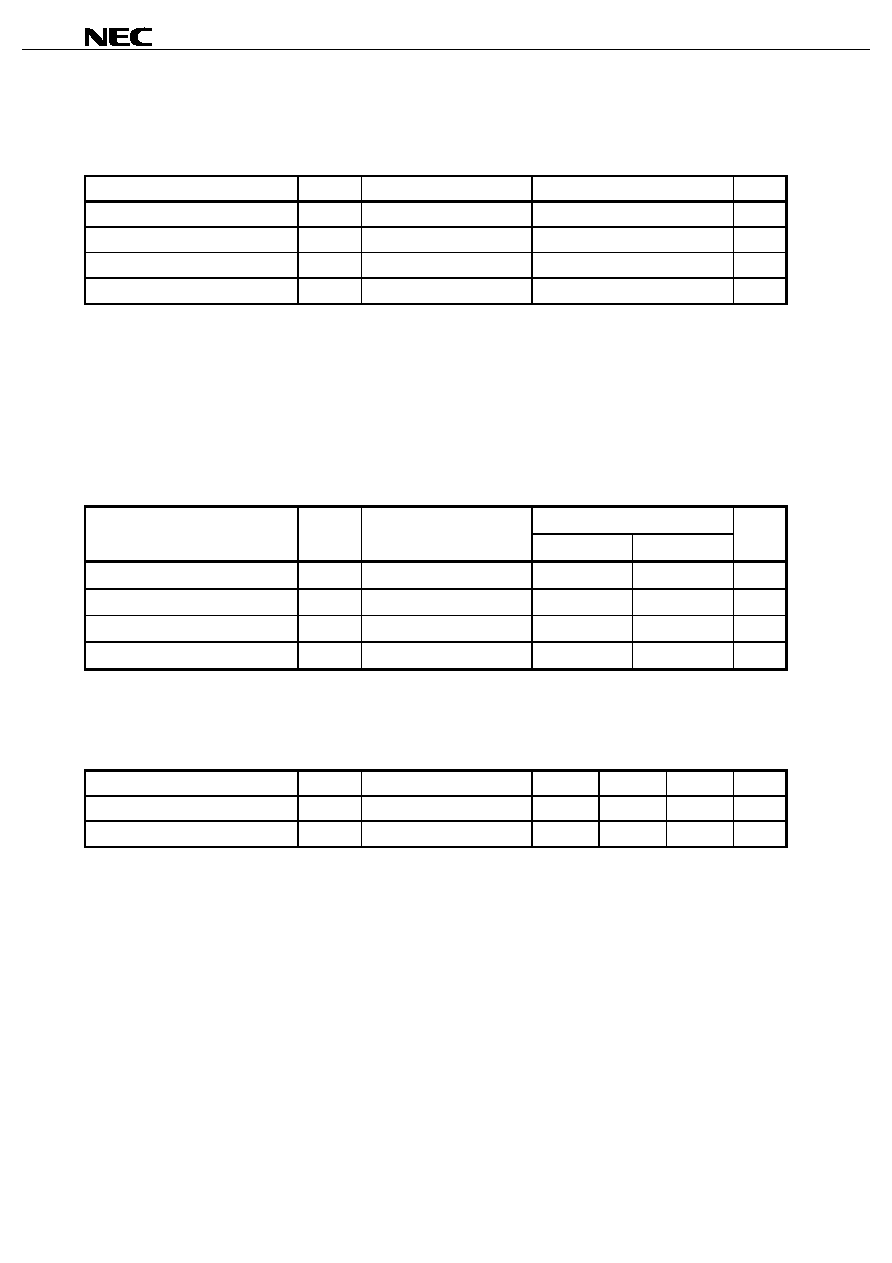
Initialization Timing Chart
V
CC
V
CC
(MIN.)
V
IH
(MIN.)
V
IH
(MIN.)
t
RC
t
CP
200 s
Address (Input)
/CS (Input)
MODE (Input)
Wait Time
Power On
Read Operation 3 times
Normal
Operation
µ
Cautions 1. Following power application, make MODE and /CS high level during the wait time interval.
2.
Following power application, make MODE high level during the wait time and three read
operations.
3. The read operation must satisfy the specs described on page 10 (Read Cycle (BC Version)).
4. The address is don't care (V
IH
or V
IL
) during read operation.
5. Read operation must be executed with toggled the /CS pin.
6. To prevent bus contention, it is recommended to set /OE to high level.
7. Do not input data to the I/O pins if /OE is low level during a read operation.
Data Sheet M15085EJ5V0DS
6
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112
Electrical Specifications
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
Rating
Unit
Supply voltage
V
CC
≠0.5
Note
to +3.3
V
Input / Output voltage
V
T
≠0.5
Note
to V
CC
+ 0.4 (3.3 V MAX).
V
Operating ambient temperature
T
A
≠20 to +70
∞
C
Storage temperature
T
stg
≠55 to +125
∞
C
Note ≠1.0 V (MIN.) (Pulse width: 30 ns)
Caution
Exposing the device to stress above those listed in Absolute Maximum Rating could cause
permanent damage. The device is not meant to be operated under conditions outside the limits
described in the operational section of this specification. Exposure to Absolute Maximum Rating
conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Recommended Operating Conditions
Parameter
Symbol
Condition
µ
PD4616112-BCxx
Unit
MIN.
MAX.
Supply voltage
V
CC
2.6
3.0
V
High level input voltage
V
IH
0.8V
CC
V
CC
+0.3
V
Low level input voltage
V
IL
≠0.3
Note
0.2V
CC
V
Operating ambient temperature
T
A
≠20
+70
∞
C
Note ≠0.5 V (MIN.) (Pulse width: 30 ns)
Capacitance (T
A
= 25
∞
∞
∞
∞
C, f = 1 MHz)
Parameter
Symbol
Test condition
MIN.
TYP.
MAX.
Unit
Input capacitance
C
IN
V
IN
= 0 V
8
pF
Input / Output capacitance
C
I/O
V
I/O
= 0 V
10
pF
Remarks 1. V
IN
: Input voltage
V
I/O
: Input / Output voltage
2. These parameters are not 100% tested.

Data Sheet M15085EJ5V0DS
7
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112
DC Characteristics (Recommended Operating Conditions Unless Otherwise Noted)
Parameter
Symbol
Test condition
µ
PD4616112-BCxx
Unit
MIN.
TYP.
MAX.
Input leakage current
I
LI
V
IN
= 0 V to V
CC
≠1.0
+1.0
µ
A
I/O leakage current
I
LO
V
I/O
= 0 V to V
CC
, /CS = V
IH
or
≠1.0
+1.0
µ
A
/WE = V
IL
or /OE = V
IH
Operating supply current
I
CCA
/CS = V
IL
, Minimum cycle time,
35
mA
I
I/O
= 0 mA
Standby supply current
I
SB1
/CS
V
CC
-
0.2 V, MODE
V
CC
-
0.2 V
100
µ
A
I
SB2
/CS
V
CC
-
0.2 V, MODE
0.2 V
10
High level output voltage
V
OH
I
OH
= ≠0.5 mA
0.8V
CC
V
Low level output voltage
V
OL
I
OL
= 1 mA
0.2V
CC
V
Remarks 1. V
IN
: Input voltage
V
I/O
: Input / Output voltage
2. These DC characteristics are in common regardless of product classifications.

Data Sheet M15085EJ5V0DS
8
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112
5
Standby Mode State Machine
/CS = V
IH
,
MODE = V
IH
MODE = V
IH
/CS = V
IH
,
MODE = V
IH
/CS = V
IH
,
MODE = V
IL
/CS = V
IH
, MODE = V
IL
/CS = V
IL
,
MODE = V
IH
/CS = V
IH
,
MODE = V
IH
/CS = V
IL
Power on
µ
Wait 200 s
Dummy read operation (3 times)
Initial State
Active
Standby
Mode1
Standby
Mode2
Standby Mode Characteristics
Standby Mode
Memory Cell Data Hold
Standby Supply Current (
µ
A)
Mode 1
Valid
100 (I
SB1
)
Mode 2
Invalid
10 (I
SB2
)

Data Sheet M15085EJ5V0DS
9
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112
5
AC Characteristics (Recommended Operating Conditions Unless Otherwise Noted)
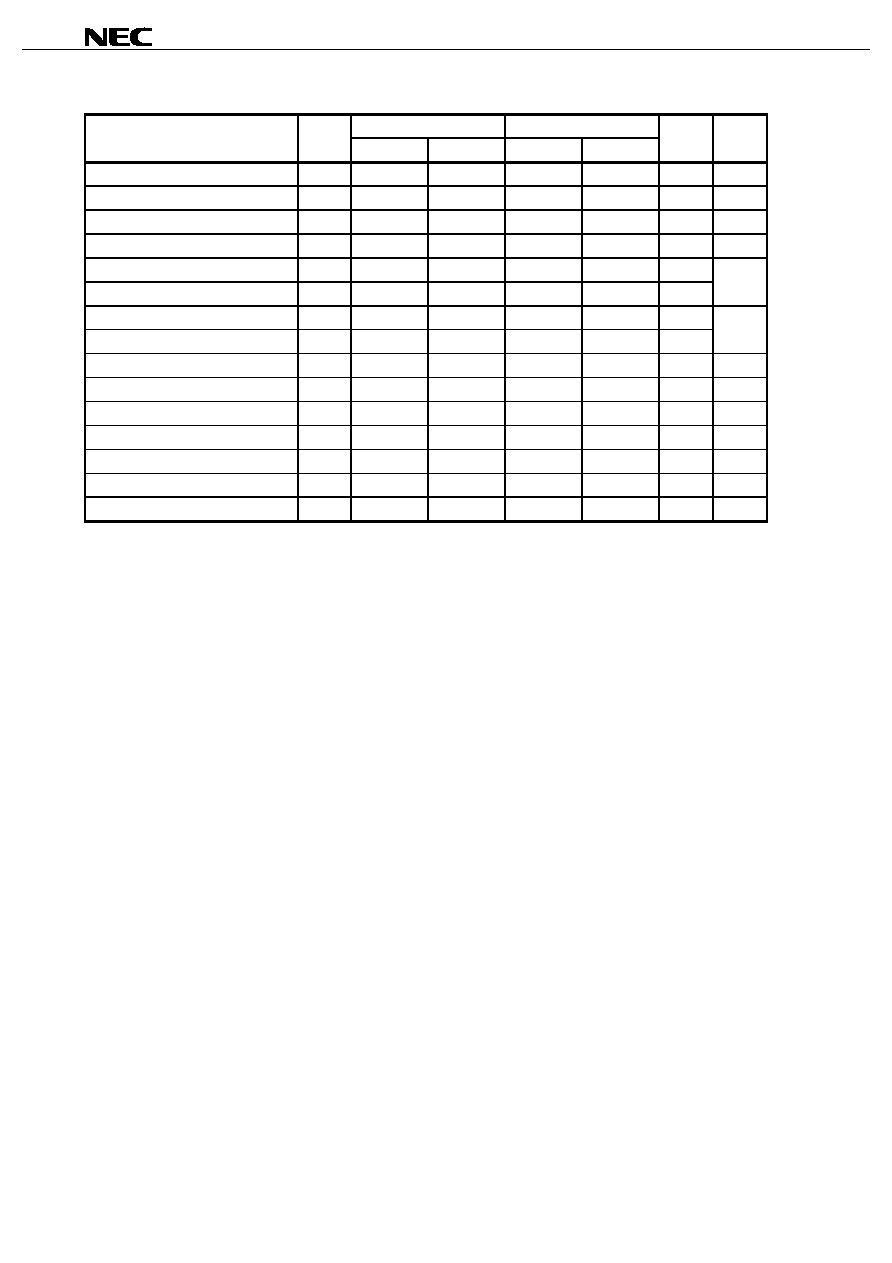
AC Test Conditions
[
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112-BC80,
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112-BC90 ]
Input Waveform (Rise and Fall Time
5 ns)
Test points
0.2 Vcc
0.8 Vcc
Vcc/2
Vcc/2
Vcc
GND
5ns
Output Waveform
Test points
Vcc/2
Vcc/2
Output Load
AC characteristics directed with the note should be measured with the output load shown in Figure 1
.
Figure 1
C
L
: 50 pF
5 pF (t
CLZ
, t
OLZ
, t
BLZ
, t
CHZ
, t
OHZ
, t
BHZ
, t
WHZ
, t
OW
)
I/O (Output)
50
Z
O
= 50
C
L
V
CC
/2
Data Sheet M15085EJ5V0DS
10
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112
5
5
5
5
Read Cycle (BC version)
Parameter
Symbol
µ
PD4616112-BC80
µ
PD4616112-BC90
Unit
Notes
MIN.
MAX.
MIN.
MAX.
Read cycle time
t
RC
80
10,000
90
10,000
ns
1
Identical address read cycle time
t
RC1
80
10,000
90
10,000
ns
2
Address skew time
t
SKEW
10
20
ns
3
/CS pulse width
t
CP
10
10
ns
Address access time
t
AA
80
90
ns
4
/CS access time
t
ACS
80
90
ns
/OE to output valid
t
OE
35
40
ns
5
/LB, /UB to output valid
t
BA
35
40
ns
Output hold from address change
t
OH
10
10
ns
/CS to output in low impedance
t
CLZ
10
10
ns
/OE to output in low impedance
t
OLZ
5
5
ns
/LB, /UB to output in low impedance
t
BLZ
5
5
ns
/CS to output in high impedance
t
CHZ
25
25
ns
/OE to output in high impedance
t
OHZ
25
25
ns
/LB, /UB to output in high impedance
t
BHZ
25
25
ns
Notes 1. One read cycle (t
RC
) must satisfy the minimum value (t
RC(MIN.)
) and maximum value (t
RC(MAX.)
= 10
µ
s). t
RC
indicates the time from the /CS low level input point or address change start point, whichever is later, to
the /CS high level input point or the next address change start point, whichever is earlier. As a result,
there are the following four conditions for t
RC
.
1) Time from address change start point to /CS high level input point
(address access)
2) Time from address change start point to next address change start point
(address access)
3) Time from /CS low level input point to next address change start point
(/CS access)
4) Time from /CS low level input point to /CS high level input point
(/CS access)
2. The identical address read cycle time (t
RC1
) is the cycle time of one read operation when performing
continuous read operations toggling /OE , /LB, and /UB with the address fixed and /CS low level. Perform
settings so that the sum (t
RC
) of the identical address read cycle times (t
RC1
) is 10
µ
s or less.
3. t
SKEW
indicates the following three types of time depending on the condition.
1) When switching /CS from high level to low level, t
SKEW
is the time from the /CS low level input point until
the next address is determined.
2) When switching /CS from low level to high level, t
SKEW
is the time from the address change start point to
the /CS high level input point.
3) When /CS is fixed to low level, t
SKEW
is the time from the address change start point until the next address
is determined.
Since specs are defined for t
SKEW
only when /CS is active, t
SKEW
is not subject to limitations when /CS is
switched from high level to low level following address determination, or when the address is changed after
/CS is switched from low level to high level.
4. Regarding t
AA
and t
ACS
, only t
AA
is satisfied during address access (refer to 1) and 2) of Note 1), and only
t
ACS
is satisfied during /CS access (refer to 3) of Note 1).
5. Regarding t
BA
and t
OE
, only t
BA
is satisfied if /OE becomes active later than /UB and /LB, and only t
OE
is
satisfied if /UB and /LB become active before /OE.

Data Sheet M15085EJ5V0DS
11
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112
5
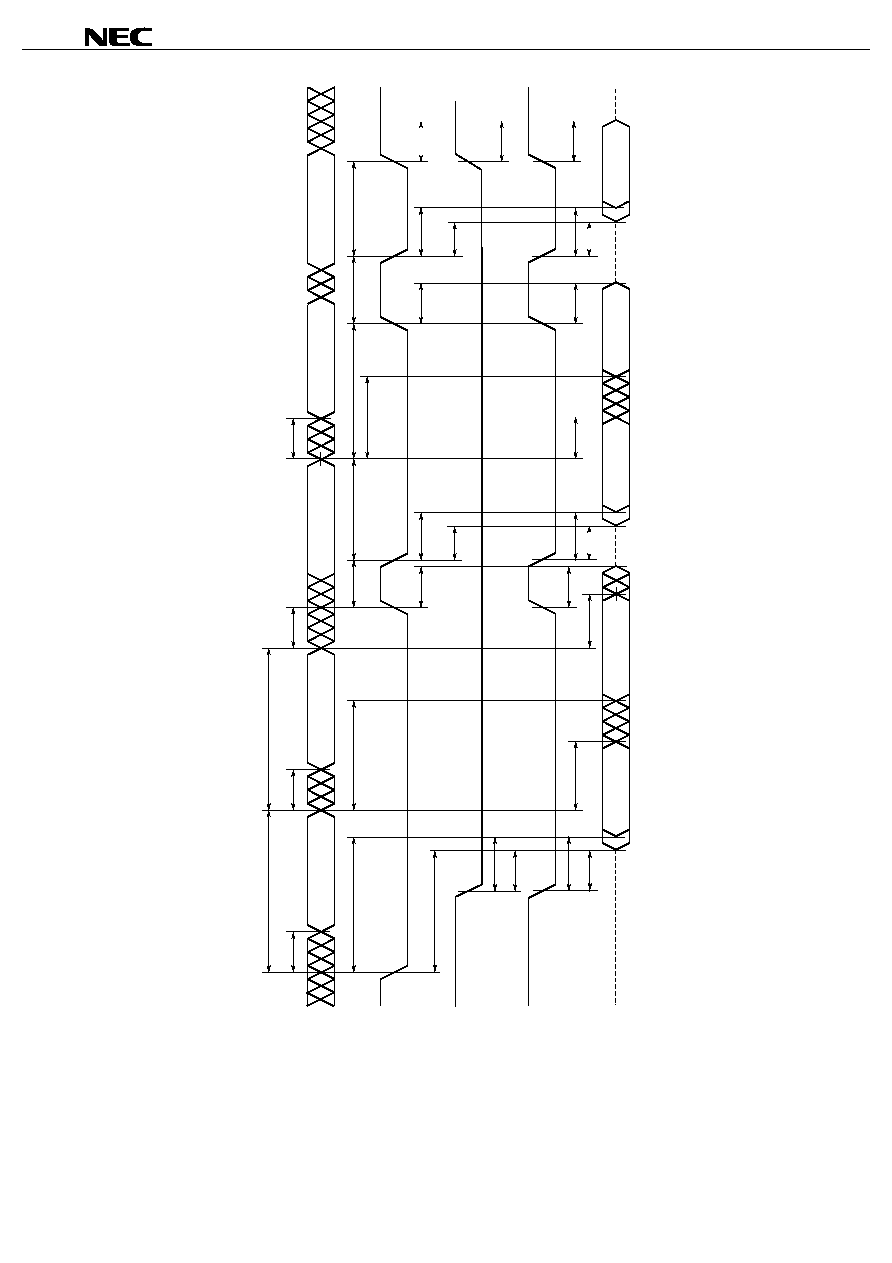
Read Cycle Timing Chart 1
t
CHZ
t
OH
t
CLZ
t
ACS
/CS
(Input)
I/O
(Output)
t
BLZ
t
BA
t
BHZ
/OE
(Input)
/LB, /UB
(Input)
t
OE
t
SKEW
t
SKEW
t
CP
t
CP
t
RC
t
OLZ
t
OHZ
t
CHZ
t
CLZ
t
ACS
I/O
(Output)
t
BLZ
t
BA
t
BHZ
/OE
(Input)
/LB, /UB
(Input)
t
OE
t
SKEW
t
CP
t
CP
t
RC
t
OLZ
t
OHZ
/CS
(Input)
t
SKEW
High impedance
High impedance
Address (Input)
Address (Input)
Data out
Data out
Caution If the address is changed using a value that is either lower than the minimum value or higher than
the maximum value for the read cycle time (t
RC
), none of the data can be guaranteed.
Remark In read cycle, /WE should be fixed to High.
D
a
ta S
heet M15085E
J5V
0
D
S
12
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112
5
t
ACS
/CS
(Input)
Address (Input)
I/O
(Output)
/OE
(Input)
t
SKEW
t
SKEW
t
SKEW
/LB, /UB
(Input)
Data out
Data out
Data out
Data out
Data out
High impedance
t
RC
t
RC
t
AA
t
OE
t
OLZ
t
BLZ
t
OH
t
CP
t
RC
t
CHZ
t
ACS
t
CLZ
t
BHZ
t
BA
t
BLZ
t
SKEW
t
CP
t
RC
t
CHZ
t
ACS
t
CLZ
t
BHZ
t
BA
t
BLZ
t
BHZ
t
CHZ
t
OH
t
AA
t
OHZ
t
RC
t
CLZ
t
BA
t
OH
Caution If the address is changed using a value that is either lower than the minimum value or higher than the maximum value for the read cycle
time (t
RC
), none of the data can be guaranteed.
Remark In read cycle, /WE should be fixed to High.
Read Cycle Timing Chart 2

D
a
ta S
heet M15085E
J5V
0
D
S
13
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112
5
t
ACS
/CS
(Input)
Address (Input)
I/O8~15
(Output)
/OE
(Input)
t
SKEW
/LB
(Input)
t
CLZ
t
SKEW
t
SKEW
t
SKEW
t
SKEW
t
RC
t
RC
t
RC
t
RC
t
RC
I/O0~7
(Output)
/UB
(Input)
Data out
Data out
Data out
Data out
Hi-Z
High impedance
t
BLZ
t
BLZ
t
OLZ
t
OE
t
BA
t
BA
t
OH
t
BHZ
t
BHZ
t
OHZ
t
OH
t
OH
t
BHZ
t
OHZ
t
OH
t
BHZ
t
OHZ
t
AA
t
BLZ
t
OLZ
t
OE
t
BA
t
BLZ
t
OLZ
t
OE
t
BA
t
AA
Caution If the address is changed using a value that is either lower than the minimum value or higher than the maximum value for the read cycle
time (t
RC
), none of the data can be guaranteed.
Remark In read cycle, /WE should be fixed to High.
Read Cycle Timing Chart 3

Data Sheet M15085EJ5V0DS
14
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112
5
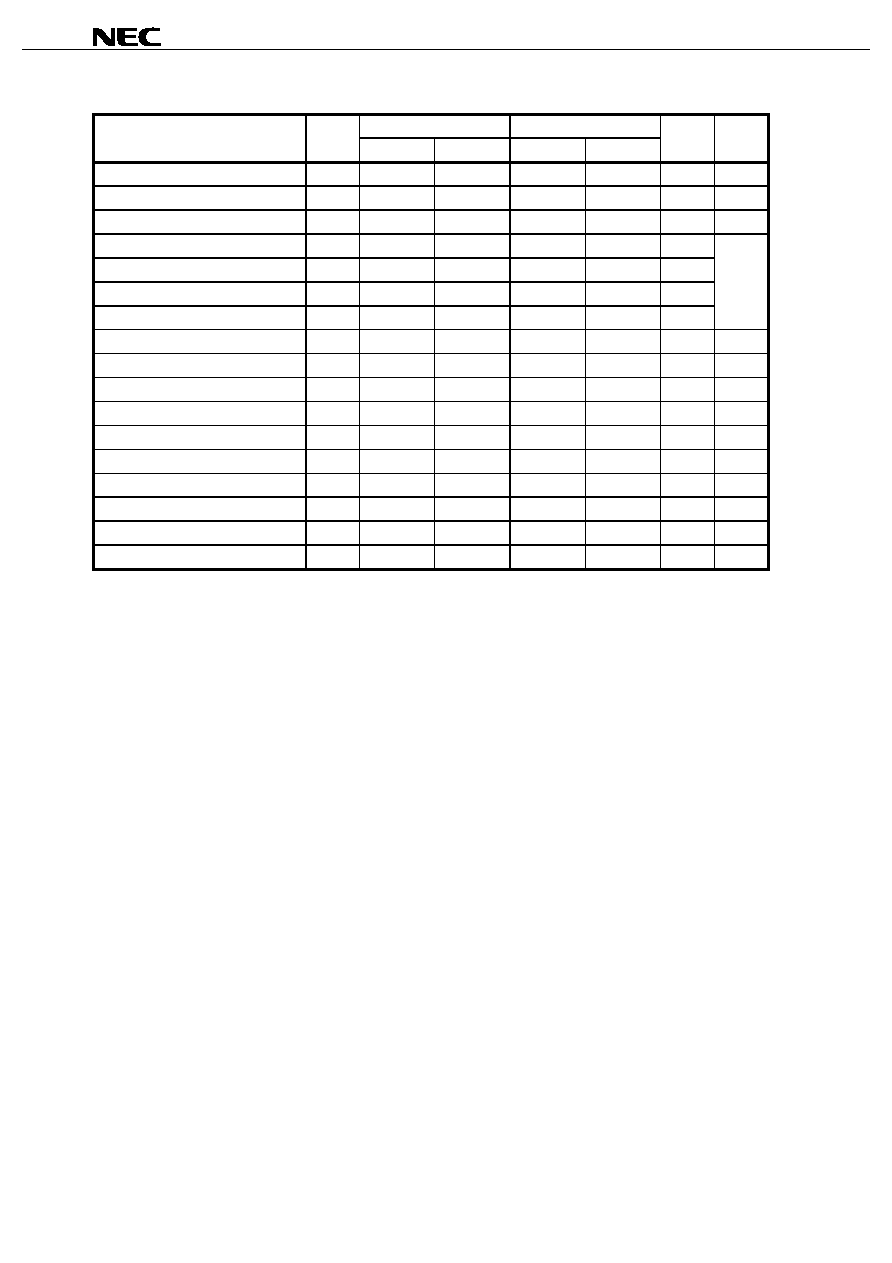
Read Cycle Timing Chart 4
/CS
(Input)
Address (Input)
/LB, /UB
(Input)
Data out
I/O
(Output)
t
SKEW
t
SKEW
High impedance
High impedance
t
RC1
t
BA
t
BA
t
RC1
t
RC
/OE
(Input)
t
ACS
t
OE
t
OE
Data out
t
OLZ
t
BLZ
t
OLZ
t
BLZ
t
OHZ
t
BHZ
t
OHZ
t
BHZ
Note
Note
Caution If the address is changed using a value that is either lower than the minimum value or higher than
the maximum value for the read cycle time (t
RC
), none of the data can be guaranteed.
Note To perform a continuous read toggling /OE, /UB, and /LB with /CS low level at an identical address, make
settings so that the sum (t
RC
) of the identical address read cycle times (t
RC1
) is 10
µ
s or less.
Remark In read cycle, /WE should be fixed to High.
Data Sheet M15085EJ5V0DS
15
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112
5
5
5
5
Write Cycle (BC version)
Parameter
Symbol
µ
PD4616112-BC80
µ
PD4616112-BC90
Unit
Notes
MIN.
MAX.
MIN.
MAX.
Write cycle time
t
WC
80
10,000
90
10,000
ns
1
Identical address write cycle time
t
WC1
80
10,000
90
10,000
ns
2
Address skew time
t
SKEW
10
20
ns
3
/CS to end of write
t
CW
40
50
ns
4
/LB, /UB to end of write
t
BW
30
35
ns
Address valid to end of write
t
AW
35
45
ns
Write pulse width
t
WP
30
35
ns
Write recovery time
t
WR
20
20
ns
5
/CS pulse width
t
CP
10
10
ns
Address setup time
t
AS
0
0
ns
Byte write hold time
t
BWH
20
20
ns
Data valid to end of write
t
DW
20
25
ns
Data hold time
t
DH
0
0
ns
/OE to output in low impedance
t
OLZ
5
5
ns
/WE to output in high impedance
t
WHZ
25
25
ns
/OE to output in high impedance
t
OHZ
25
25
ns
Output active from end of write
t
OW
5
5
ns
Notes 1. One write cycle (t
WC
) must satisfy the minimum value (t
WC(MIN.)
) and the maximum value (t
WC(MAX.)
= 10
µ
s).
t
WC
indicates the time from the /CS low level input point or address change start point, whichever is after,
to the /CS high level input point or the next address change start point, whichever is earlier. As a result,
there are the following four conditions for t
WC
.
1) Time from address change start point to /CS high level input point
2) Time from address change start point to next address change start point
3) Time from /CS low level input point to next address change start point
4) Time from /CS low level input point to /CS high level input point
2. The identical address read cycle time (t
WC1
) is the cycle time of one write cycle when performing continuous
write operations with the address fixed and /CS low level, changing /LB and /UB at the same time, and
toggling /WE, as well as when performing a continuous write toggling /LB and /UB. Make settings so that
the sum (t
WC
) of the identical address write cycle times (t
WC1
) is 10
µ
s or less.
3. t
SKEW
indicates the following three types of time depending on the condition.
1) When switching /CS from high level to low level, t
SKEW
is the time from the /CS low level input point until
the next address is determined.
2) When switching /CS from low level to high level, t
SKEW
is the time from the address change start point to
the /CS high level input point.
3) When /CS is fixed to low level, t
SKEW
is the time from the address change start point until the next address
is determined.
Since specs are defined for t
SKEW
only when /CS is active, t
SKEW
is not subject to limitations when /CS is
switched from high level to low level following address determination, or when the address is changed after
/CS is switched from low level to high level.

Data Sheet M15085EJ5V0DS
16
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112
4. Definition of write start and write end
/CS
/WE
/LB, /UB
Status
Write start pattern 1
H to L
L
L
If /WE, /LB, /UB are low level, time when /CS
changes from high level to low level
Write start pattern 2
L
H to L
L
If /CS, /LB, /UB are low level, time when /WE
changes from high level to low level
Write start pattern 3
L
L
H to L
If /CS, /WE are low level, time when /LB or
/UB changes from high level to low level
Write end pattern 1
L
L to H
L
If /CS, /WE, /LB, /UB are low level, time when
/WE changes from low level to high level
Write end pattern 2
L
L
L to H
When /CS, /WE, /LB, /UB are low level, time
when /LB or /UB changes from low level to
high level
5. Definition of write end recovery time (t
WR
)
1) Time from write end to address change start point, or from write end to /CS high level input point
2) When /CS, /LB, /UB are low level and continuously written to the identical address, time from /WE high
level input point to /WE low level input point
3) When /CS, /WE are low level and continuously written to the identical address, time from /LB or /UB
high level input point, whichever is later, to /LB or /UB low level input point, whichever is earlier.
4) When /CS is low level and continuously written to the identical address, time from write end to point at
which /WE , /LB, or /UB starts to change from high level to low level, whichever is earliest.

Data Sheet M15085EJ5V0DS
17
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112
5
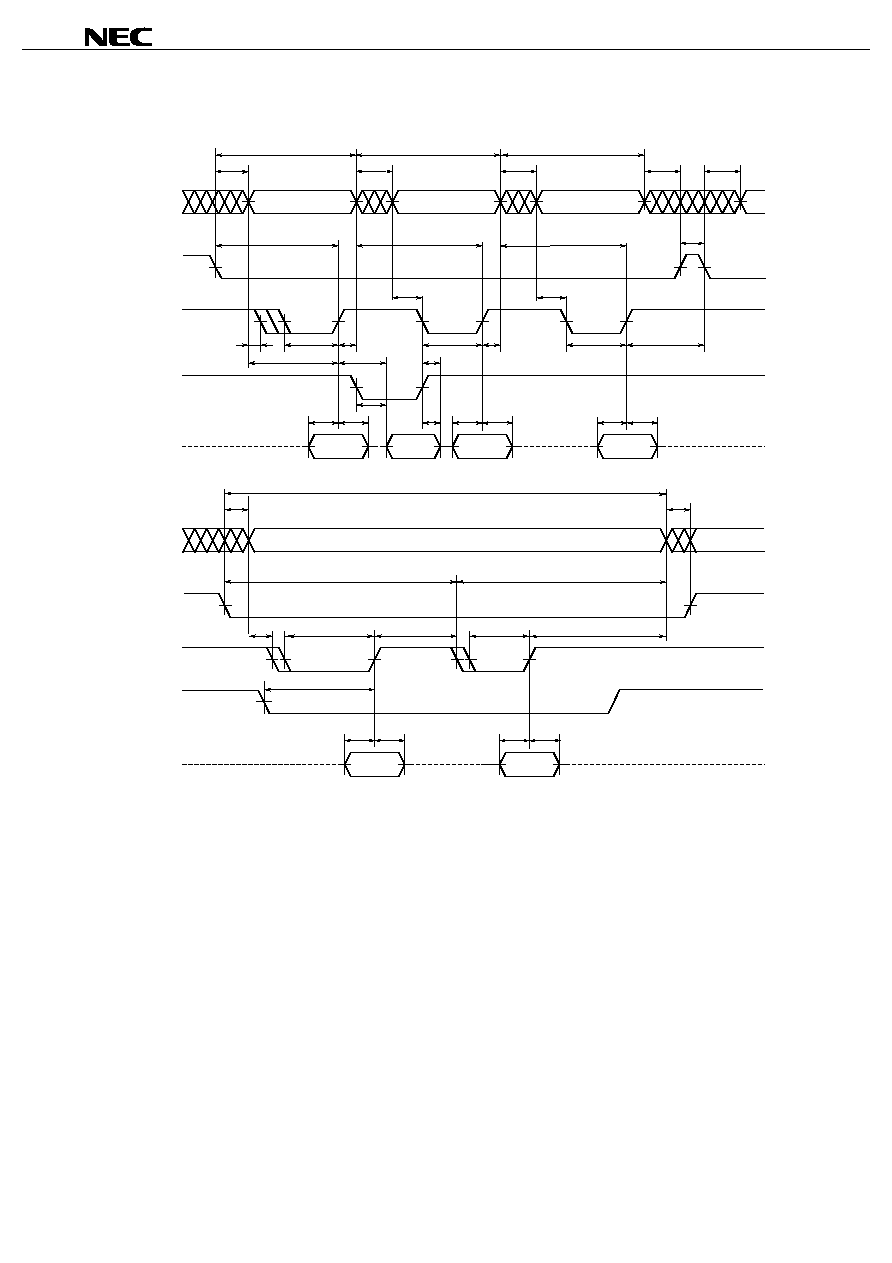
Write Cycle Timing Chart 1
t
BW
t
DW
t
DH
High impedance
Address (Input)
/LB, /UB
(Input)
I/O
(Input)
/CS
(Input)
t
WP
t
WR
/WE
(Input)
t
SKEW
t
CP
High impedance
t
WC
t
CW
t
SKEW
t
DW
t
DH
t
AS
t
WP
t
WR
t
AS
t
BW
t
WC
t
CW
t
BW
t
DW
t
DH
High impedance
Address (Input)
/LB, /UB
(Input)
I/O
(Input)
/CS
(Input)
t
WP
t
WR
/WE
(Input)
t
SKEW
t
CP
High impedance
t
WC
t
SKEW
t
DW
t
DH
t
WP
t
WR
t
BW
t
WC
t
CW
t
CW
t
SKEW
Data in
Data in
Data in
Data in
Cautions 1. During address transition, at least one of pins /CS, /WE should be inactivated.
2. Do not input data to the I/O pins while they are in the output state.
3. If the address is changed using a value that is either lower than the minimum value or higher
than the maximum value for the write cycle time (t
WC
), none of the data can be guaranteed.
Remark
Write operation is done during the overlap time of a Low /CS, /WE, /LB and/or /UB.
Data Sheet M15085EJ5V0DS
18
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112
5
Write Cycle Timing Chart 2 (/WE Controlled)
t
CW
t
AW
/CS (Input)
Address (Input)
t
AS
t
WP
/WE (Input)
t
SKEW
t
SKEW
t
AW
t
DW
t
DH
I/O (Input / Output)
t
WR
t
OW
t
AW
t
SKEW
t
CP
t
WHZ
High impedance
High impedance
High impedance
/OE (Input)
t
OHZ
t
OLZ
t
WP
t
AS
t
AS
t
WC
t
WC
t
WC
t
WP
t
WR
t
WR
t
DW
t
DH
t
DW
t
DH
t
SKEW
/CS (Input)
Address (Input)
/WE (Input)
t
DW
t
DH
I/O (Input)
t
SKEW
t
SKEW
High impedance
High impedance
High impedance
t
WC1
t
AS
t
WP
t
WP
t
WR
t
DW
t
DH
t
WC1
/LB, /UB (Input)
t
BW
t
SKEW
t
WC
t
WR
Data in
Data in
Data in
Data in
Data in
High
impedance
High
impedance
Indefinite
data out
Note
Note
Cautions 1. During address transition, at least one of pins /CS, /WE should be inactivated.
2. Do not input data to the I/O pins while they are in the output state.
3. If the address is changed using a value that is either lower than the minimum value or higher
than the maximum value for the write cycle time (t
WC
), none of the data can be guaranteed.
Note If /LB and /UB are changed at the same time with /CS low level and a continuous write operation toggling /WE
is performed, make settings so that the sum (t
WC
) of the identical address write cycle time (t
WC1
) is 10
µ
s or
less.
Remarks 1. Write operation is done during the overlap time of a Low /CS, /WE, /LB and/or /UB.
2. When /WE is at Low, the I/O pins are always high impedance. When /WE is at High, read operation is
executed. Therefore /OE should be at High to make the I/O pins high impedance.

Data Sheet M15085EJ5V0DS
19
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112
5
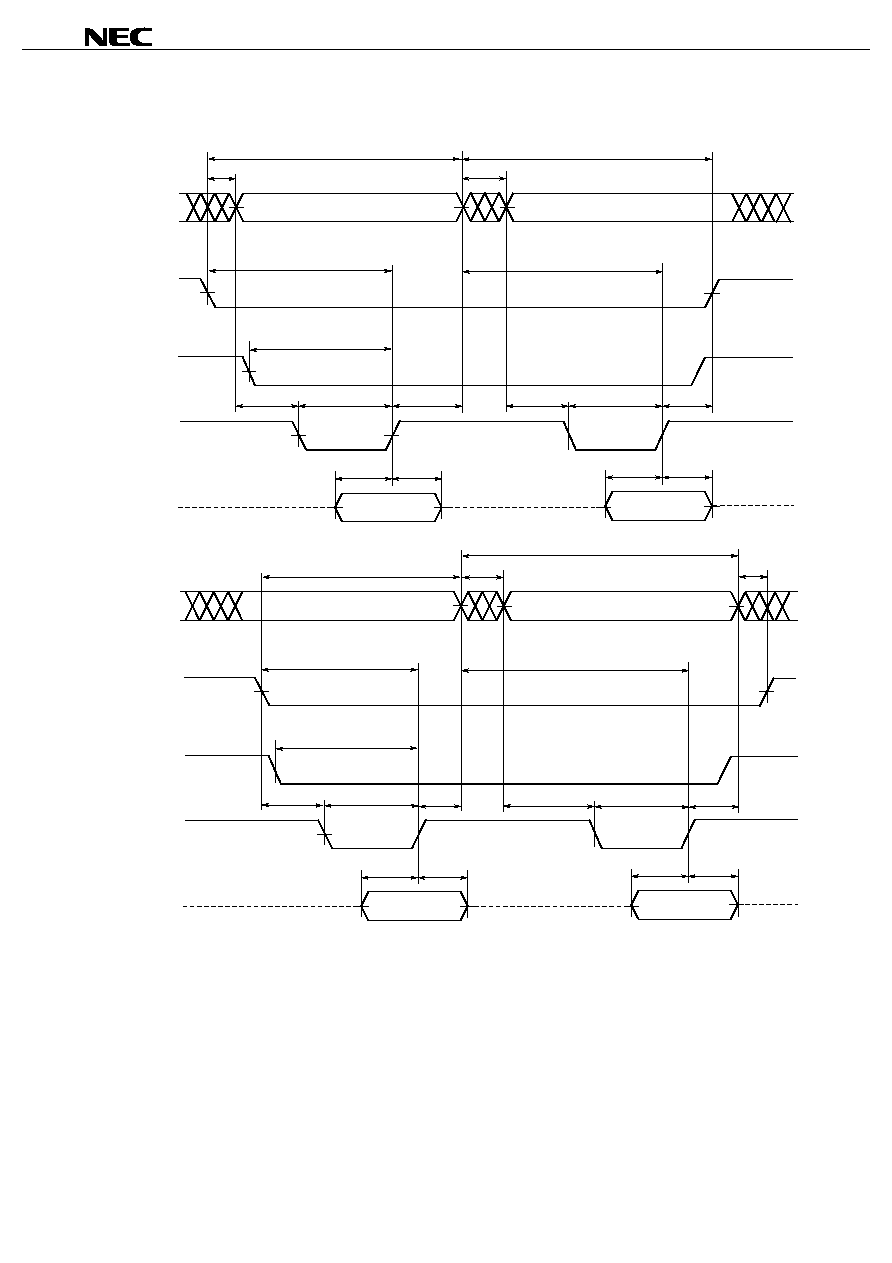
Write Cycle Timing Chart 3 (/CS Controlled)
t
AS
t
CW
I/O (Input)
t
WR
t
WC
/WE (Input)
/CS (Input)
Address (Input)
/LB, /UB (Input)
t
DW
t
DH
High impedance
High impedance
High impedance
t
WC
t
DW
t
DH
t
CW
t
WR
t
AS
t
AS
t
CW
I/O (Input)
t
WR
t
WC
/WE (Input)
/CS (Input)
Address (Input)
/LB, /UB (Input)
t
DW
t
DH
High impedance
High impedance
High impedance
t
WC
t
DW
t
DH
t
CW
t
WR
t
AS
Data in
Data in
Data in
Data in
Cautions 1. During address transition, at least one of pins /CS, /WE should be inactivated.
2. Do not input data to the I/O pins while they are in the output state.
3. If the address is changed using a value that is either lower than the minimum value or higher
than the maximum value for the write cycle time (t
WC
), none of the data can be guaranteed.
Remark Write operation is done during the overlap time of a Low /CS, /WE, /LB and/or /UB.
Data Sheet M15085EJ5V0DS
20
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112
5
Write Cycle Timing Chart 4 (/LB, /UB Controlled 1)
t
BW
t
DW
t
DH
High impedance
Address (Input)
/LB, /UB (Input)
I/O (Input)
/CS (Input)
t
WP
/WE (Input)
t
SKEW
High impedance
t
WC
t
CW
t
SKEW
t
DW
t
DH
t
WR
t
AS
t
BW
t
AS
t
WC
t
AW
t
WR
t
BW
t
DW
t
DH
High impedance
Address (Input)
/LB, /UB (Input)
I/O (Input)
/CS (Input)
t
WP
t
WR
/WE (Input)
t
SKEW
High impedance
t
WC
t
CW
t
SKEW
t
DW
t
DH
t
AS
t
WC
t
BW
t
AS
t
WR
t
AW
Data in
Data in
Data in
Data in
Cautions 1. During address transition, at least one of pins /CS, /WE should be inactivated.
2. Do not input data to the I/O pins while they are in the output state.
3. If the address is changed using a value that is either lower than the minimum value or higher
than the maximum value for the write cycle time (t
WC
), none of the data can be guaranteed.
Remark Write operation is done during the overlap time of a Low /CS, /WE, /LB and/or /UB.

Data Sheet M15085EJ5V0DS
21
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112
5
Write Cycle Timing Chart 5 (/LB, /UB Controlled 2)
/CS (Input)
Address (Input)
/LB, /UB (Input)
t
DW
t
DH
I/O (Input)
t
SKEW
t
SKEW
High impedance
High impedance
High impedance
t
WC1
t
AS
t
BW
t
BW
t
WR
t
DW
t
DH
t
WC1
t
WR
t
WC
/WE (Input)
t
WP
Data in
Data in
Note
Note
Cautions 1. During address transition, at least one of pins /CS, /WE should be inactivated.
2. Do not input data to the I/O pins while they are in the output state.
3. If the address is changed using a value that is either lower than the minimum value or higher
than the maximum value for the write cycle time (t
WC
), none of the data can be guaranteed.
Note If /LB and /UB are changed at the same time with /CS low level and a continuous write operation toggling /WE
is performed, make settings so that the sum (t
WC
) of the identical address write cycle time (t
WC1
) is 10
µ
s or
less.
Remark Write operation is done during the overlap time of a Low /CS, /WE, /LB and/or /UB.

Data Sheet M15085EJ5V0DS
22
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112
5
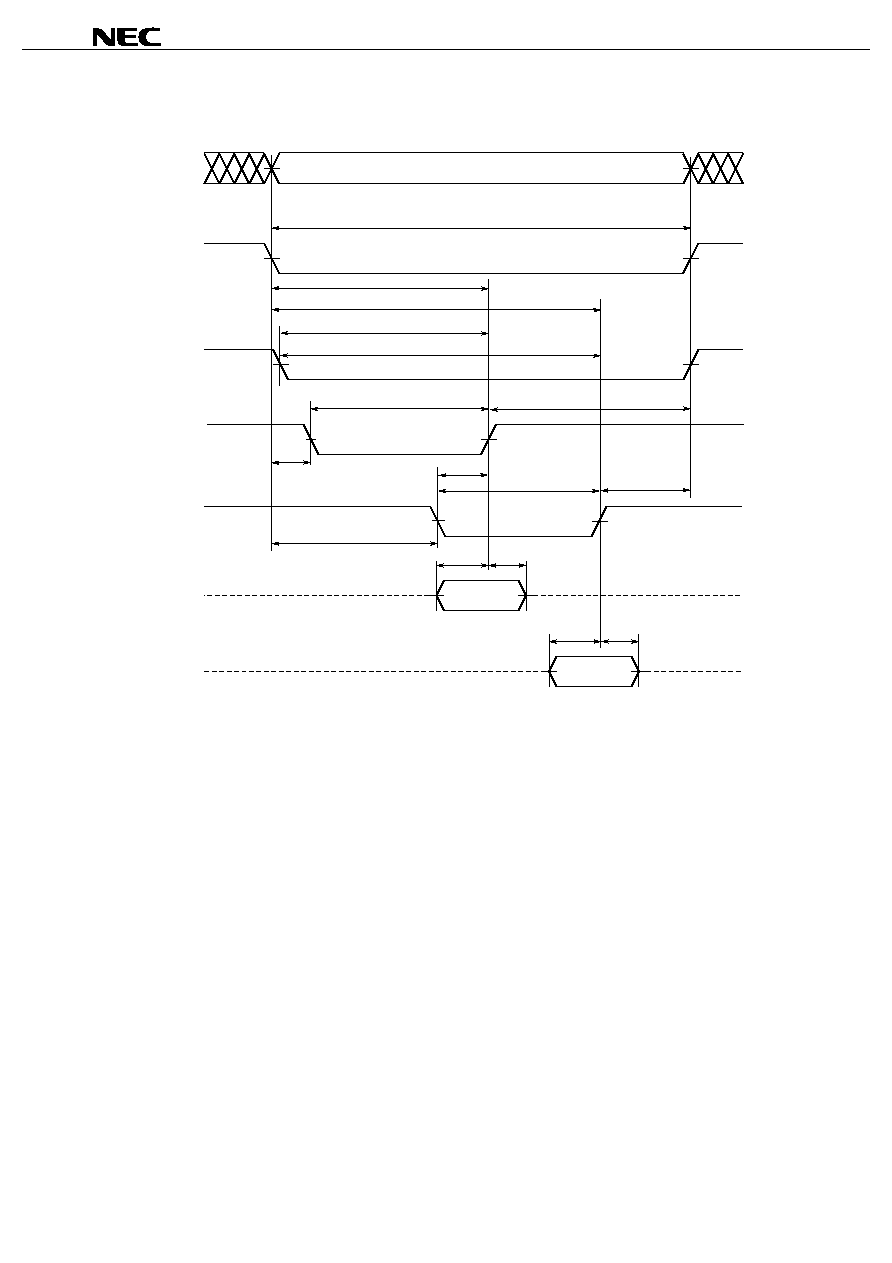
Write Cycle Timing Chart 6 (/LB, /UB Independent Controlled 1)
t
WP
t
AS
t
CW
I/O0 - 7 (Input)
t
WR
t
WC1
/WE (Input)
/CS (Input)
Address (Input)
/LB (Input)
t
BW
High impedance
High impedance
/UB (Input)
t
BW
t
WC1
t
DW
t
DH
t
WR
I/O8 - 15 (Input)
High impedance
High impedance
t
DW
t
DH
t
WC
Data in
Data in
Note
Note
Cautions 1. During address transition, at least one of pins /CS, /WE should be inactivated.
2. Do not input data to the I/O pins while they are in the output state.
3. If the address is changed using a value that is either lower than the minimum value or higher
than the maximum value for the write cycle time (t
WC
), none of the data can be guaranteed.
Note If /LB and /UB are changed at the same time with /CS low level and a continuous write operation toggling /WE
is performed, make settings so that the sum (t
WC
) of the identical address write cycle time (t
WC1
) is 10
µ
s or
less.
Remark Write operation is done during the overlap time of a Low /CS, /WE, /LB and/or /UB.
Data Sheet M15085EJ5V0DS
23
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112
5
Write Cycle Timing Chart 7 (/LB, /UB Independent Controlled 2)
t
WP
t
AS
t
CW
I/O0 - 7 (Input)
t
WC
/WE (Input)
/CS (Input)
Address (Input)
/LB (Input)
t
BW
High impedance
High impedance
/UB (Input)
t
BW
t
DW
t
DH
I/O8 - 15 (Input)
High impedance
High impedance
t
DW
t
DH
t
WR
t
WR
t
AS
t
BWH
t
CW
t
WP
Data in
Data in
Cautions 1. During address transition, at least one of pins /CS, /WE should be inactivated.
2. Do not input data to the I/O pins while they are in the output state.
3. If the address is changed using a value that is either lower than the minimum value or higher
than the maximum value for the write cycle time (t
WC
), none of the data can be guaranteed.
Remark Write operation is done during the overlap time of a Low /CS, /WE, /LB and/or /UB.

Data Sheet M15085EJ5V0DS
24
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112
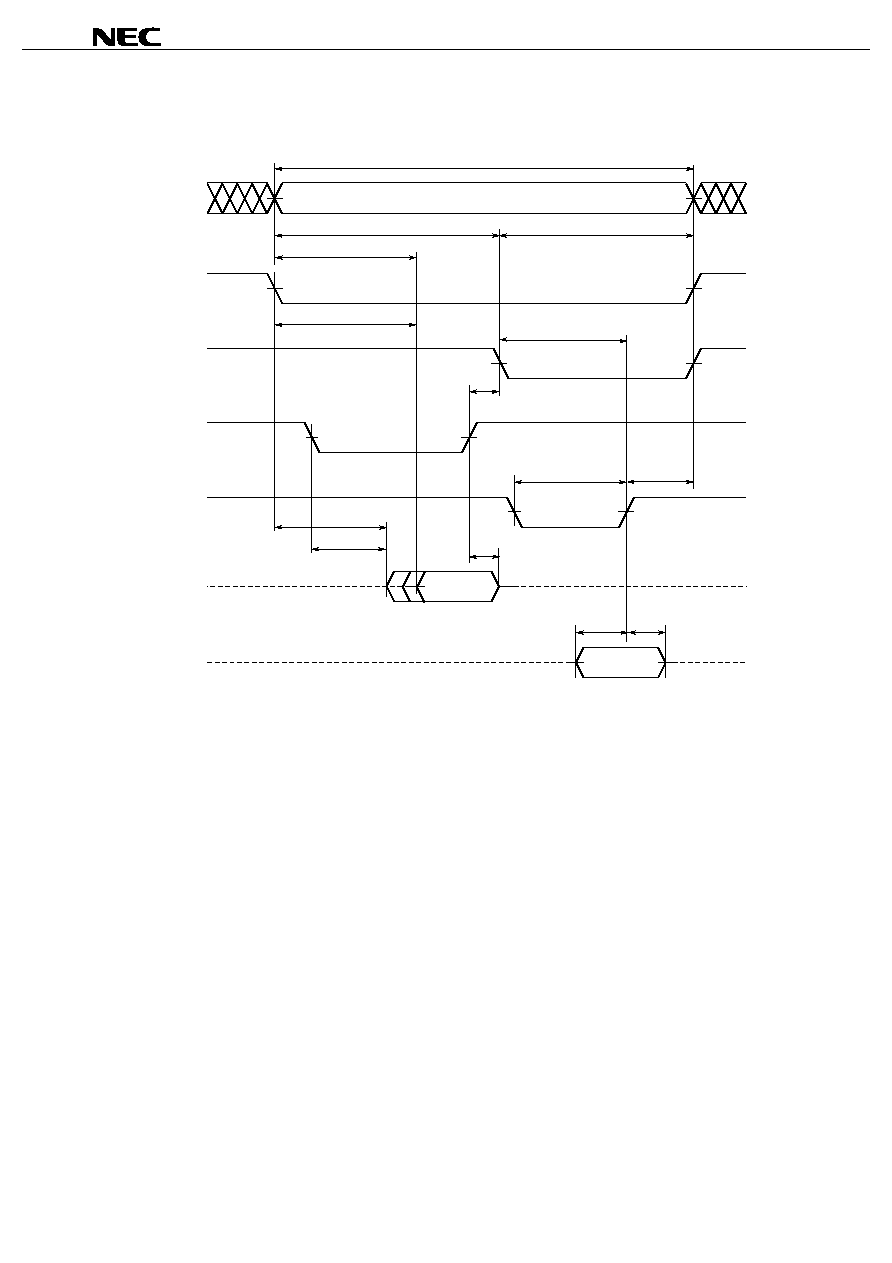
Read Write Cycle (BC version)
Parameter
Symbol
MIN.
MAX.
Unit
Notes
Read write cycle time
t
RWC
10,000
ns
1, 2
Byte write setup time
t
BWS
20
ns
Byte read setup time
t
BRS
20
ns
Notes 1. Make settings so that the sum (t
RWC
) of the identical address read cycle time (t
RC1
) and the identical address
write cycle time (t
WC1
) is 10
µ
s or less when a write is performed at the identical address using /UB following
a read using /LB with /CS low level, or when a write is performed using /LB following a read using /UB.
2. Make settings so that the sum (t
RWC
) of the identical address read cycle time (t
RC1
) and the identical address
write cycle time (t
WC1
) is 10
µ
s or less when a read is performed at the identical address using /UB following
a write using /LB with /CS low level, or when a read is performed using /LB following a write using /UB.
Data Sheet M15085EJ5V0DS
25
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112
5
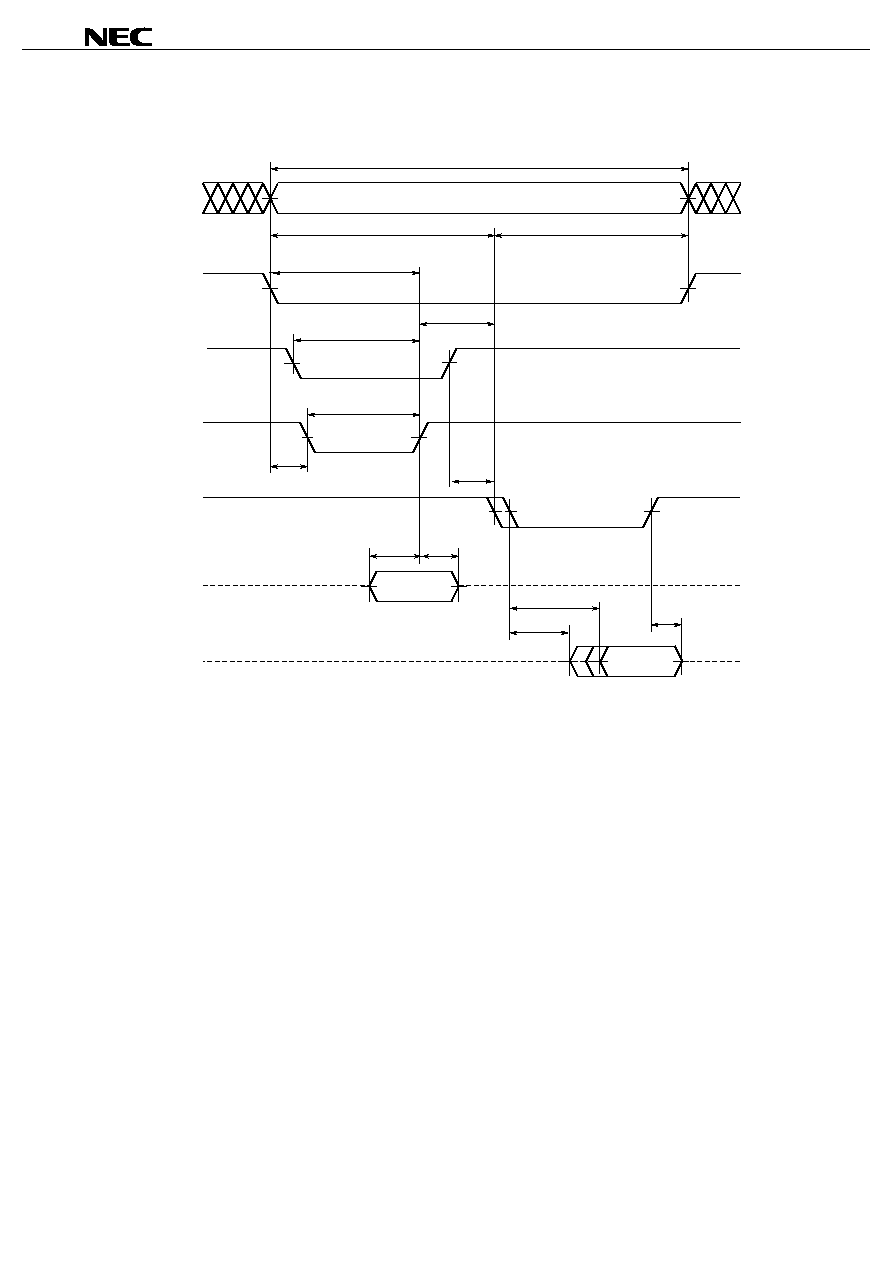
Read Write Cycle Timing Chart 1 (/LB, /UB Independent Controlled 1)
t
WP
I/O0 - 7 (Output)
t
BWS
t
RC1
/WE (Input)
/CS (Input)
Address (Input)
/LB (Input)
High impedance
High impedance
/UB (Input)
t
BW
t
WC1
t
WR
I/O8 - 15 (Input)
High impedance
High impedance
t
DW
t
DH
t
RWC
t
CLZ
t
BLZ
t
BHZ
t
ACS
t
AA
Data in
Data out
Note
Note
Cautions 1. During address transition, at least one of pins /CS, /WE should be inactivated.
2. Do not input data to the I/O pins while they are in the output state.
3. If the address is changed using a value that is either lower than the minimum value or higher
than the maximum value for the identical address read cycle time (t
RC1
) and the identical address
write cycle time (t
WC1
), none of the data can be guaranteed.
Note Make settings so that the sum (t
RWC
) of the identical address read cycle time (t
RC1
) and the identical address
write cycle time (t
WC1
) is 10
µ
s or less when a write is performed at the identical address using /UB following a
read using /LB with /CS low level, or when a write is performed using /LB following a read using /UB.
Remark Write operation is done during the overlap time of a Low /CS, /WE, /LB and/or /UB.
Data Sheet M15085EJ5V0DS
26
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112
5
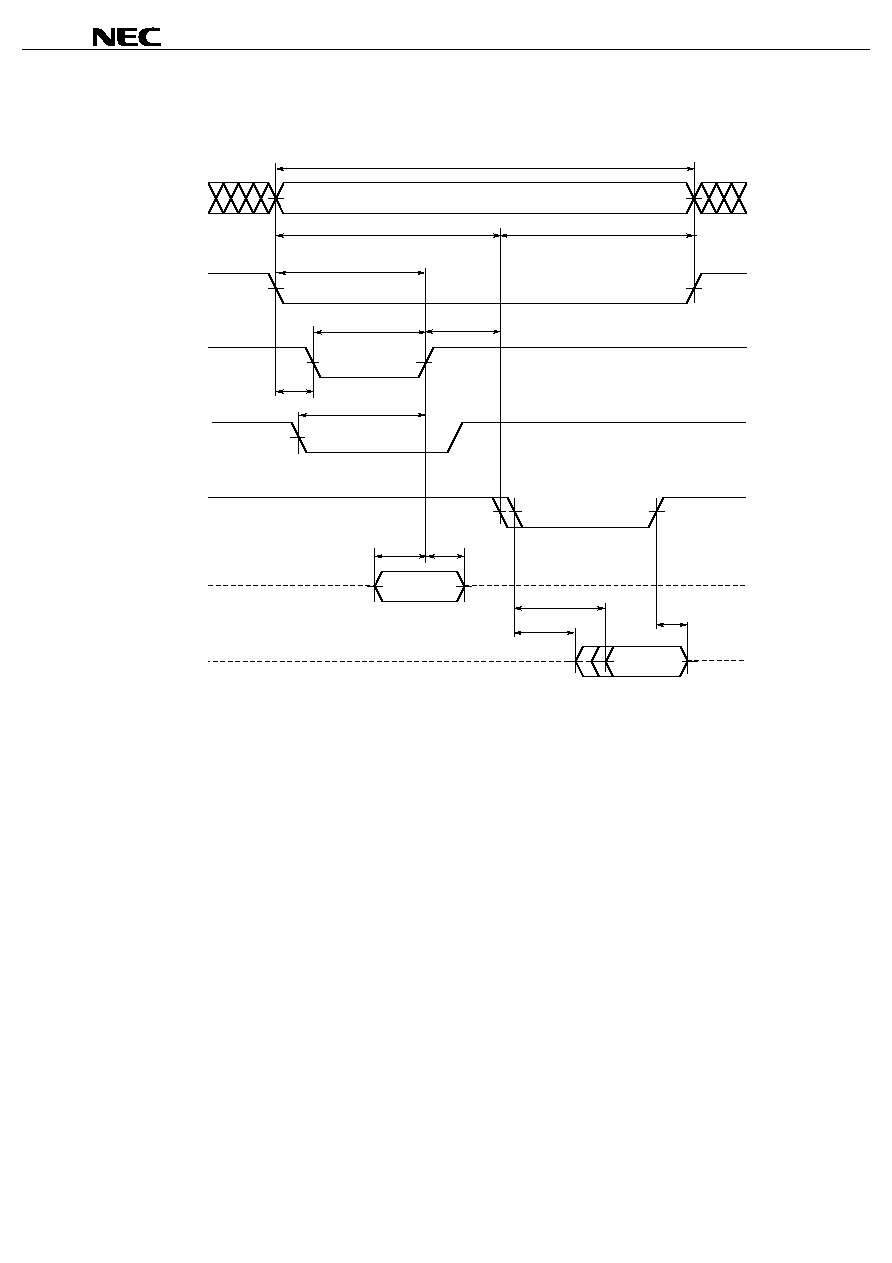
Read Write Cycle Timing Chart 2 (/LB, /UB Independent Controlled 2)
t
WP
I/O0 - 7 (Input)
t
RC1
/WE (Input)
/CS (Input)
Address (Input)
/LB (Input)
High impedance
High impedance
/UB (Input)
t
BW
t
WC1
t
WR
I/O8 - 15 (Output)
High impedance
High impedance
t
DW
t
DH
t
RWC
t
BLZ
t
BHZ
t
BRS
t
BA
t
CW
t
AS
Data in
Data out
Note
Note
Cautions 1. During address transition, at least one of pins /CS, /WE should be inactivated.
2. Do not input data to the I/O pins while they are in the output state.
3. If the address is changed using a value that is either lower than the minimum value or higher
than the maximum value for the identical address read cycle time (t
RC1
) and the identical address
write cycle time (t
WC1
), none of the data can be guaranteed.
Note Make settings so that the sum (t
RWC
) of the identical address read cycle time (t
RC1
) and the identical address
write cycle time (t
WC1
) is 10
µ
s or less when a write is performed at the identical address using /UB following a
read using /LB with /CS low level, or when a write is performed using /LB following a read using /UB.
Remark Write operation is done during the overlap time of a Low /CS, /WE, /LB and/or /UB.
Data Sheet M15085EJ5V0DS
27
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112
5
Read Write Cycle Timing Chart 3 (/LB, /UB Independent Controlled 3)
t
BW
I/O0 - 7 (Input)
t
RC1
/WE (Input)
/CS (Input)
Address (Input)
/LB (Input)
High impedance
High impedance
/UB (Input)
t
WP
t
WC1
t
WR
I/O8 - 15 (Output)
High impedance
High impedance
t
DW
t
DH
t
RWC
t
BLZ
t
BHZ
t
BA
t
CW
t
AS
Data in
Data out
Note
Note
Cautions 1. During address transition, at least one of pins /CS, /WE should be inactivated.
2. Do not input data to the I/O pins while they are in the output state.
3. If the address is changed using a value that is either lower than the minimum value or higher
than the maximum value for the identical address read cycle time (t
RC1
) and the identical address
write cycle time (t
WC1
), none of the data can be guaranteed.
Note Make settings so that the sum (t
RWC
) of the identical address read cycle time (t
RC1
) and the identical address
write cycle time (t
WC1
) is 10
µ
s or less when a write is performed at the identical address using /UB following a
read using /LB with /CS low level, or when a write is performed using /LB following a read using /UB.
Remark Write operation is done during the overlap time of a Low /CS, /WE, /LB and/or /UB.

Data Sheet M15085EJ5V0DS
28
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112
5
Standby Mode 2 entry and recovery Timing Chart
Address (Input)
/CS (Input)
MODE (Input)
t
CM
t
RC
t
CP
200 s
Wait Time
Read Operation 3 times
Normal
Operation
µ
Standby
Mode 2
(Data invalid)
Parameter
Symbol
MIN.
MAX.
Unit
Note
/CS High to MODE Low
t
CM
0
ns
Cautions 1. Make MODE and /CS high level during the wait time.
2. Make MODE high level during the wait time and three read operations.
3. The read operation must satisfy the specs described on page 10 (Read Cycle (BC Version)).
4. The read operation address can be either V
IH
or V
IL
.
5. Perform reading by toggling /CS.
6. To prevent bus contention, it is recommended to set /OE to high level.
7. Do not input data to the I/O pins if /OE is low level during a read operation.

Data Sheet M15085EJ5V0DS
29
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112
5
Package Drawing
S
w
B
S
w
A
6
5
4
3
2
1
A
B
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
S
y
S
y1
M
S
b
x
A B
S
48-PIN TAPE FBGA (8x6)
ITEM
MILLIMETERS
D
E
8.0
±
0.1
6.0
±
0.1
w
A
0.2
0.94
±
0.10
b
x
0.08
y
0.1
e
0.75
A1
0.24
±
0.05
A2
0.70
0.40
±
0.05
INDEX MARK
INDEX MARK
A
A2
A1
ZE
ZD
y1
0.2
ZD
1.125
ZE
1.375
P48F9-75-BC2
e
E
D

Data Sheet M15085EJ5V0DS
30
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112
Recommended Soldering Conditions
Please consult with our sales offices for soldering conditions of the
µ
PD4616112.
Type of Surface Mount Device
µ
PD4616112F9-BCxx-BC2: 48-pin TAPE FBGA (8 x 6)

Data Sheet M15085EJ5V0DS
31
µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112
NOTES FOR CMOS DEVICES
1
PRECAUTION AGAINST ESD FOR SEMICONDUCTORS
Note:
Strong electric field, when exposed to a MOS device, can cause destruction of the gate oxide and
ultimately degrade the device operation. Steps must be taken to stop generation of static electricity
as much as possible, and quickly dissipate it once, when it has occurred. Environmental control
must be adequate. When it is dry, humidifier should be used. It is recommended to avoid using
insulators that easily build static electricity. Semiconductor devices must be stored and transported
in an anti-static container, static shielding bag or conductive material. All test and measurement
tools including work bench and floor should be grounded. The operator should be grounded using
wrist strap. Semiconductor devices must not be touched with bare hands. Similar precautions need
to be taken for PW boards with semiconductor devices on it.
2
HANDLING OF UNUSED INPUT PINS FOR CMOS
Note:
No connection for CMOS device inputs can be cause of malfunction. If no connection is provided
to the input pins, it is possible that an internal input level may be generated due to noise, etc., hence
causing malfunction. CMOS devices behave differently than Bipolar or NMOS devices. Input levels
of CMOS devices must be fixed high or low by using a pull-up or pull-down circuitry. Each unused
pin should be connected to V
DD
or GND with a resistor, if it is considered to have a possibility of
being an output pin. All handling related to the unused pins must be judged device by device and
related specifications governing the devices.
3
STATUS BEFORE INITIALIZATION OF MOS DEVICES
Note:
Power-on does not necessarily define initial status of MOS device. Production process of MOS
does not define the initial operation status of the device. Immediately after the power source is
turned ON, the devices with reset function have not yet been initialized. Hence, power-on does
not guarantee out-pin levels, I/O settings or contents of registers. Device is not initialized until the
reset signal is received. Reset operation must be executed immediately after power-on for devices
having reset function.

µ
µ
µ
µ
PD4616112
M8E 00. 4
The information in this document is current as of October, 2001. The information is subject to
change without notice. For actual design-in, refer to the latest publications of NEC's data sheets or
data books, etc., for the most up-to-date specifications of NEC semiconductor products. Not all
products and/or types are available in every country. Please check with an NEC sales representative
for availability and additional information.
No part of this document may be copied or reproduced in any form or by any means without prior
written consent of NEC. NEC assumes no responsibility for any errors that may appear in this document.
NEC does not assume any liability for infringement of patents, copyrights or other intellectual property rights of
third parties by or arising from the use of NEC semiconductor products listed in this document or any other
liability arising from the use of such products. No license, express, implied or otherwise, is granted under any
patents, copyrights or other intellectual property rights of NEC or others.
Descriptions of circuits, software and other related information in this document are provided for illustrative
purposes in semiconductor product operation and application examples. The incorporation of these
circuits, software and information in the design of customer's equipment shall be done under the full
responsibility of customer. NEC assumes no responsibility for any losses incurred by customers or third
parties arising from the use of these circuits, software and information.
While NEC endeavours to enhance the quality, reliability and safety of NEC semiconductor products, customers
agree and acknowledge that the possibility of defects thereof cannot be eliminated entirely. To minimize
risks of damage to property or injury (including death) to persons arising from defects in NEC
semiconductor products, customers must incorporate sufficient safety measures in their design, such as
redundancy, fire-containment, and anti-failure features.
NEC semiconductor products are classified into the following three quality grades:
"Standard", "Special" and "Specific". The "Specific" quality grade applies only to semiconductor products
developed based on a customer-designated "quality assurance program" for a specific application. The
recommended applications of a semiconductor product depend on its quality grade, as indicated below.
Customers must check the quality grade of each semiconductor product before using it in a particular
application.
"Standard": Computers, office equipment, communications equipment, test and measurement equipment, audio
and visual equipment, home electronic appliances, machine tools, personal electronic equipment
and industrial robots
"Special":
Transportation equipment (automobiles, trains, ships, etc.), traffic control systems, anti-disaster
systems, anti-crime systems, safety equipment and medical equipment (not specifically designed
for life support)
"Specific": Aircraft, aerospace equipment, submersible repeaters, nuclear reactor control systems, life
support systems and medical equipment for life support, etc.
The quality grade of NEC semiconductor products is "Standard" unless otherwise expressly specified in NEC's
data sheets or data books, etc. If customers wish to use NEC semiconductor products in applications not
intended by NEC, they must contact an NEC sales representative in advance to determine NEC's willingness
to support a given application.
(Note)
(1) "NEC" as used in this statement means NEC Corporation and also includes its majority-owned subsidiaries.
(2) "NEC semiconductor products" means any semiconductor product developed or manufactured by or for
NEC (as defined above).
∑
∑
∑
∑
∑
∑































