
1/19
° Semiconductor
MSM82C53-2RS/GS/JS
° Semiconductor
MSM82C53-2RS/GS/JS
CMOS PROGRAMMABLE INTERVAL TIMER
E2O0018-27-X2
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The MSM82C53-2RS/GS/JS is programmable universal timers designed for use in
microcomputer systems. Based on silicon gate CMOS technology, it requires a standby current
of only 100 mA (max.) when the chip is in the nonselected state. During timer operation, power
consumption is still very low only 8 mA (max.) at 8 MHz of current required.
The device consists of three independent counters, and can count up to a maximum of 8 MHz
(MSM82C53-2). The timer features six different counter modes, and binary count/BCD count
functions. Count values can be set in byte or word units, and all functions are freely
programmable.
FEATURES
∑ Maximum operating frequency of 8 MHz (MSM82C53-2)
∑ High speed and low power consumption achieved through silicon gate CMOS technology
∑ Completely static operation
∑ Three independent 16-bit down-counters
∑ 3 V to 6 V single power supply
∑ Six counter modes available for each counter
∑ Binary and decimal counting possible
∑ 24-pin Plastic DIP (DIP24-P-600-2.54): (Product name: MSM82C53-2RS)
∑ 28-pin Plastic QFJ (QFJ28-P-S450-1.27): (Product name: MSM82C53-2JS)
∑ 32-pin Plastic SSOP(SSOP32-P-430-1.00-K): (Product name: MSM82C53-2GS-K)
This version: Jan. 1998
Previous version: Aug. 1996
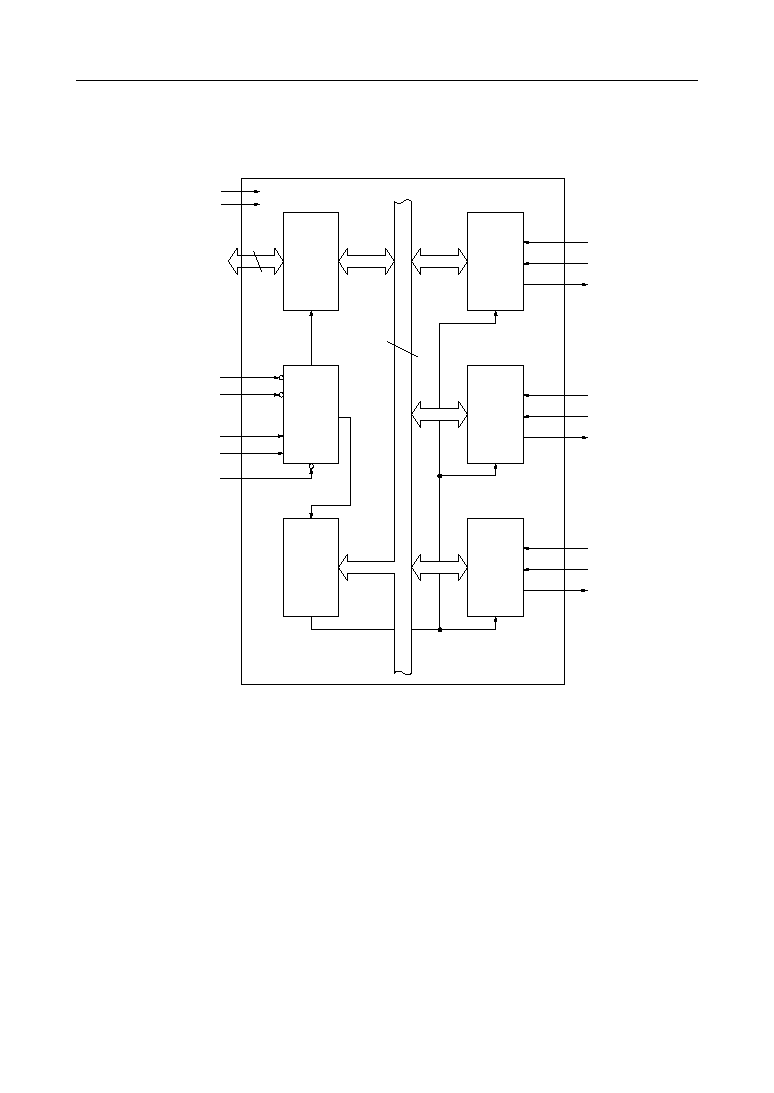
2/19
° Semiconductor
MSM82C53-2RS/GS/JS
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
Data
Bus
Buffer
8
D
7
- D
0
Counter
#0
CLK
0
GATE
0
OUT
0
Read/
Write
Logic
Counter
#1
CLK
1
GATE
1
OUT
1
V
CC
GND
WR
RD
A
0
A
1
CS
Control
Word
Register
Counter
#2
CLK
2
GATE
2
OUT
2
Internal Bus
8

3/19
° Semiconductor
MSM82C53-2RS/GS/JS
PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)
24 pin Plastic DIP
32 pin Plastic SSOP
16
15
14
13
NC
D
7
D
6
D
5
NC
D
4
D
3
D
2
D
1
D
0
CLK
0
NC
OUT
0
GATE
0
GND
NC
NC
Vcc
WR
RD
NC
CS
A
1
A
0
CLK
2
OUT
2
GATE
2
NC
CLK
1
GATE
1
OUT
1
NC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
29
30
31
32
28
27
26
25
17
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
13
Vcc
WR
RD
CS
A
1
A
0
CLK
2
OUT
2
GATE
2
CLK
1
GATE
1
OUT
1
D
7
D
6
D
5
D
4
D
3
D
2
D
1
D
0
CLK
0
OUT
0
GATE
0
GND
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
NC
CS
A
1
A
0
CLK
2
OUT
2
GATE
2
D
4
D
3
D
2
D
1
D
0
CLK
0
NC
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
OUT0
GATE0
GND
NC
OUT
1
GATE
1
CLK
1
4
3
2
1
28
27
26
D
5
D
6
D
7
NC
V
CC
WR
RD
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
28 pin Plastic QFJ
(NC denotes "not connected")

4/19
° Semiconductor
MSM82C53-2RS/GS/JS
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
≠55 to + 150
MSM82C53-2RS
Supply Voltage
V
CC
≠0.5 to + 7
V
Input Voltage
V
IN
≠0.5 to V
CC
+ 0.5
V
Output Voltage
V
OUT
≠0.5 to V
CC
+ 0.5
V
Storage Temperature
T
STG
∞C
Power Dissipation
P
D
0.7
W
Parameter
Units
Symbol
Respect
to GND
--
Ta = 25∞C
Condition
Rating
MSM82C53-2GS
MSM82C53-2JS
0.9
0.9
OPERATING RANGES
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
DC CHARACTERISTICS
Typ.
Max.
"L" Output Voltage
V
OL
--
0.45
V
"H" Output Voltage
V
OH
--
--
V
Parameter
Unit
Symbol
Min.
--
3.7
I
OL
= 4 mA
I
OH
= ≠1 mA
Condition
V
CC
= 4.5 V to 5.5 V
Ta
= ≠40∞C to +85∞C
Input Leak Current
I
LI
--
10
mA
Output Leak Current
I
LO
--
10
mA
≠10
≠10
0 £ V
IN
£ V
CC
0 £ V
OUT
£ V
CC
CS V
CC
- 0.2 V
V
IH
V
CC
- 0.2 V
V
IL
£
0.2 V
Standby Supply
Current
Operating Supply
Current
I
CCS
I
CC
--
100
mA
--
8
mA
--
--
t
CLK
= 125 ns
C
L
= 0 pF
Condition
Supply Voltage
V
CC
V
IL
= 0.2 V, V
IH
= V
CC
-0.2 V,
Operating Frequency 2.6 MHz
V
Operating Temperature
T
op
Range
3 to 6
≠40 to +85
∞C
Parameter
Unit
Symbol
Typ.
Supply Voltage
V
CC
5
V
T
op
+25
"L" Input Voltage
V
IL
--
"H" Input Voltage
V
IH
--
Min.
4.5
≠40
≠0.3
2.2
Max.
5.5
+85
+0.8
V
CC
+ 0.3
Parameter
Unit
Symbol
∞C
V
V
Operating Temperature

5/19
° Semiconductor
MSM82C53-2RS/GS/JS
AC CHARACTERISTICS
Note: Timing measured at V
L
= 0.8 V and V
H
= 2.2 V for both inputs and outputs.
Parameter
Symbol
Unit
Condition
Max.
Min.
MSM82C53-2
Address Set-up Time before Reading
(V
CC
= 4.5 V to 5.5 V, Ta = ≠40 to +85∞C)
t
AR
ns
Address Hold Time after Reading
t
RA
ns
Read
Cycle
30
--
0
--
Read Recovery Time
Read Pulse Width
t
RR
ns
150
--
Address Set-up Time before Writing
t
RVR
ns
200
--
Address Hold Time after Writing
t
AW
ns
0
--
Write Pulse Width
t
WA
t
WW
ns
20
--
Data Input Set-up Time before Writing
t
DW
ns
Write
Cycle
150
--
Data Input Hold Time after Writing
t
WD
ns
100
--
Write Recovery Time
t
RVW
ns
20
--
Clock Cycle Time
t
CLK
ns
200
--
Clock "H" Pulse Width
t
PWH
ns
125
D.C.
Clock "L" Pusle Width
t
PWL
ns
60
--
t
GW
ns
Clock
and
Gate
Timing
60
--
"H" Gate Pulse Width
C
L
= 150 pF
t
GL
ns
"L" Gate PUlse Width
t
GS
ns
50
--
50
--
Gate Input Hold Time after Clock
Gate Input Set-up Time before Clock
t
GH
ns
50
--
Output Delay Time after Reading
t
RD
ns
50
--
ns
--
120
Output Delay Time after Gate
t
ODG
Output Delay Time after Clock
t
OD
ns
--
120
Output Delay Time after Address
t
AD
ns
--
150
ns
--
180
Output Floating Delay Time after
Reading
t
DF
ns
Delay
Time
5
90

6/19
° Semiconductor
MSM82C53-2RS/GS/JS
TIMING CHART
WriteTiming
WR
A
0 - 1
CS
t
AW
t
WA
t
DW
t
WD
t
WW
D
0 - 7
CLK
t
CLK
t
PWH
t
PWL
t
GL
t
GS
t
GH
t
ODG
t
OD
t
GW
t
GH
t
GS
GATE
OUT
Clock & Gate Timing
Read Timing
RD
A
0 - 7
,
CS
t
AR
t
RA
D
0 - 7
t
AD
t
RR
t
DF
Valid
t
RD
High Impedance
High Impedance

7/19
° Semiconductor
MSM82C53-2RS/GS/JS
DESCRIPTION OF PIN FUNCTIONS
SYSTEM INTERFACING
16 bits
Address Bus
Control Bus
D
7
-
0
A
1
A
0
A
1
A
0
CS
8 bits
RD
WR
8 bits
Data Bus
MSM82C53-2
OUT GATE CLK
Counter #0
OUT GATE CLK
Counter #1
OUT GATE CLK
Counter #2
Pin Symbol
Function
Name
D
7
- D
0
Three-state 8-bit bidirectional data bus used when writing control words
and count values, and reading count values upon reception of WR and
RD signals from CPU.
Bidirectional
Data Bus
Input/Output
A
0
- A
1
One of the three internal counters or the control word register is selected
by A
0
/A
1
combination. These two pins are normally connected to the two
lower order bits of the address bus.
Address Input
Input
RD
Data can be transferred from MSM82C53-2 to CPU when this pin is at low
level.
Read Input
Input
WR
Data can be transferred from CPU to MSM82C53-2 when this pin is at low
level.
Write Input
Input
CLK
0
-
2
Supply of three clock signals to the three counters incorporated in
MSM82C53-2.
Clock Input
Input
GATE
0
-
2
Control of starting, interruption, and restarting of counting in the three
respective counters in accordance with the set control word contents.
Gate Input
Input
OUT
0
-
2
Output of counter output waveform in accordance with the set mode and
count value.
Counter Output
Output
CS
Data transfer with the CPU is enabled when this pin is at low level. When
at high level, the data bus (D
0
thru D
7
) is switched to high impedance
state where neither writing nor reading can be executed. Internal registers,
however, remain unchanged.
Chip Select
Input
Input
Input/Output
8/19
° Semiconductor
MSM82C53-2RS/GS/JS
DESCRIPTION OF BASIC OPERATIONS
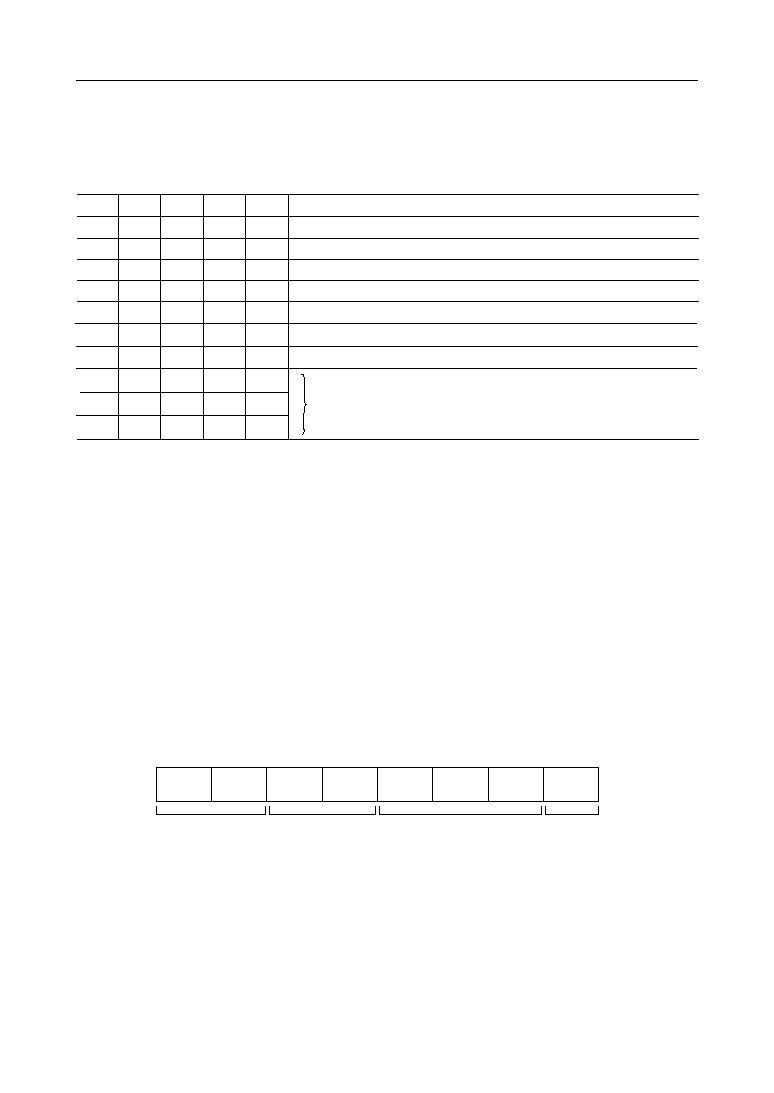
Data transfers between the internal registers and the external data bus is outlined in the
following table.
0
0
0
0
0
CS
Function
0
0
0
1
0
1
1
1
0
1
RD
0
0
0
•
1
0
0
0
1
0
WR
1
1
1
•
1
0
1
1
0
0
A
1
0
1
1
•
•
1
0
1
0
0
A
0
1
0
1
•
•
Data Bus to Counter #0 Writing
Data Bus to Counter #1 Writing
Data Bus to Counter #2 Writing
Data Bus to Control Word Register Writing
Data Bus from Counter #0 Reading
Data Bus from Counter #1 Reading
Data Bus from Counter #2 Reading
Data Bus High Impedance Status
• denotes "not specified".
DESCRIPTION OF OPERATION
MSM82C53-2 functions are selected by a control word from the CPU. In the required program
sequence, the control word setting is followed by the count value setting and execution of the
desired timer operation.
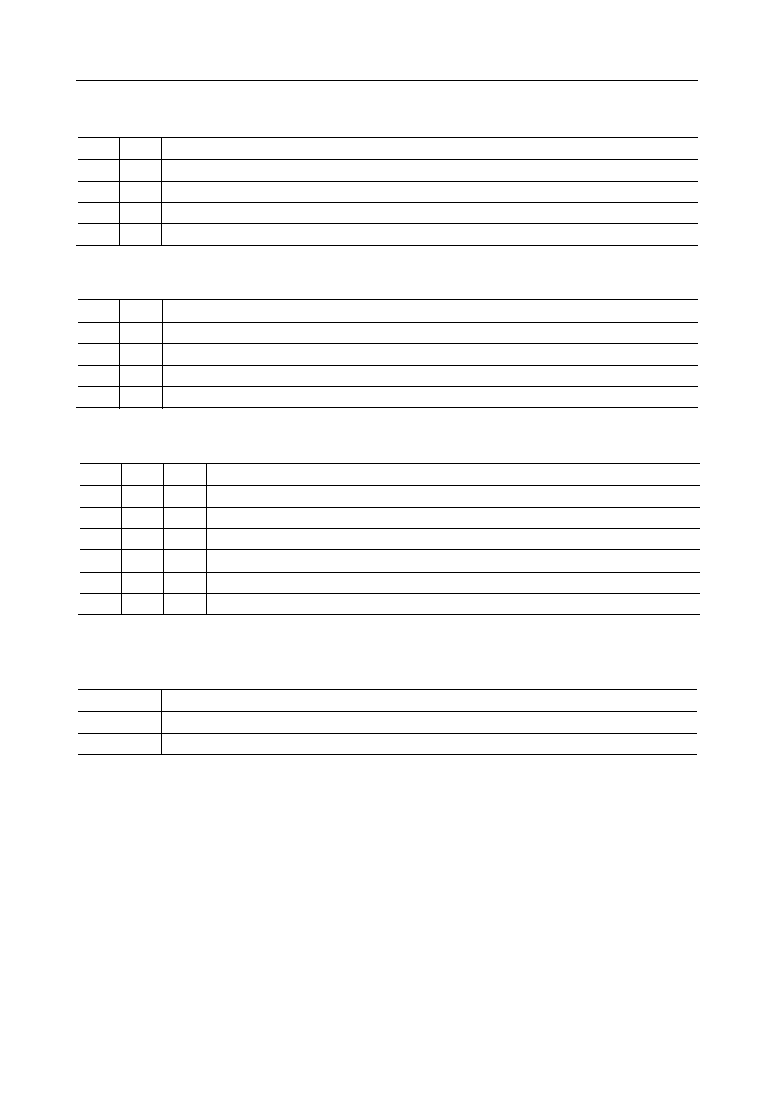
Control Word and Count Value Program
Each counter operation mode is set by control word programming. The control word format
is out-lined below.
SC1
D
7
SC0
D
6
RL1
D
5
RL0
D
4
M2
D
3
M1
D
2
M0
D
1
BCD
D
0
Select Counter
Read/Load
Mode
BCD
(CS=0, A
0
, A
1
=1, 1, RD=1, WR=0)
9/19
° Semiconductor
MSM82C53-2RS/GS/JS
∑ Select Counter (SC0, SC1):
Selection of set counter
∑ Read/Load (RL1, RL0):
Count value Reading/Loading format setting
∑ Mode (M2, M1, M0):
Operation waveform mode setting
0
•
•
0
M2
Set Contents
0
1
1
0
M1
1
0
1
0
M0
1
1
0
0
0
1
Mode 0 (Interrupt on Terminal Count)
Mode 1 (Programmable One-Shot)
Mode 2 (Rate Generator)
Mode 3 (Square Wave Generator)
Mode 4 (Software Triggered Strobe)
Mode 5 (Hardware Triggered Strobe)
• denotes "not specified".
∑ BCD:
Operation count mode setting
1
0
BCD
Binary Count (16-bit Binary)
BCD Count (4-decade Binary Coded Decimal)
Set Contents
After setting Read/Load, Mode, and BCD in each counter as outlined above, next set the desired
count value. (In some Modes, counting is started immediately after the count value has been
written). This count value setting must conform with the Read/Load format set in advance.
Note that the internal counters are reset to 0000H during control word setting. The counter
value (0000H) can't be read.
If the two bytes (LSB and MSB) are written at this stage (RL0 and RL1 = 1,1), take note of the
following precaution.
Although the count values may be set in the three counters in any sequence after the control
word has been set in each counter, count values must be set consecutively in the LSB - MSB order
in any one counter.
0
1
1
0
SC1
1
0
1
0
SC0
Counter #0 Selection
Counter #1 Selection
Counter #2 Selection
Illegal Combination
Set Contents
0
1
1
0
RL1
Set Contents
1
0
1
0
RL0
Counter Latch Operation
Reading/Loading of Least Significant Byte (LSB)
Reading/Loading of Most Significant Byte (MSB)
Reading/Loading of LSB Followed by MSB

10/19
° Semiconductor
MSM82C53-2RS/GS/JS
∑ Example of control word and count value setting
Counter #0: Read/Load LSB only, Mode 3, Binary count, count value 3H
Counter #1: Read/Load MSB only, Mode 5, Binary count, count value AA00H
Counter #2: Read/Load LSB and MSB, Mode 0, BCD count, count value 1234
MVI A, 1EH
OUT n3
Counter #0 control word setting
MVI A, 6AH
OUT n3
Counter #1 control word setting
MVI A, B1H
OUT n3
Counter #2 control word setting
MVI A, 03H
OUT n0
Counter #0 control value setting
MVI A, AAH
OUT n1
Counter #1 control value setting
MVI A, 34H
OUT n2
Counter #2 count value setting (LSB then MSB)
MVI A, 12H
OUT n2
Notes: n0: Counter #0 address
n1: Counter #1 address
n2: Counter #2 address
n3: Control word register address
1
2
3
0
Mode
Remarks
1
2
2
1
MIn.
0
0
1
0
Max,
4
5
1
1
0
0
0 executes 10000H count (ditto in other modes)
--
1 cannot be counted
1 executes 10001H count
--
--
∑ The minimum and maximum count values which can be counted in each mode are listed
below.

11/19
° Semiconductor
MSM82C53-2RS/GS/JS
Mode Definition
∑ Mode 0 (terminal count)
The counter output is set to "L" level by the mode setting. If the count value is then written
in the counter with the gate input at "H" level (that is, upon completion of writing the MSB
when there are two bytes), the clock input counting is started. When the terminal count is
reached, the output is switched to "H" level and is maintained in this status until the control
word and count value are set again.
Counting is interrupted if the gate input is switched to "L" level, and restarted when switched
back to "H" level.
When Count Values are written during counting, the operation is as follows:
1-byte Read/Load. ............ When the new count value is written, counting is stopped
immediately, and then restarted at the new count value by the next
clock.
2-byte Read/Load ............. When byte 1 (LSB) of the new count value is written, counting is
stopped immediately. Counting is restarted at the new count
value when byte 2 (MSB) is written.
∑ Mode 1 (programmable one-shot)
The counter output is switched to "H" level by the mode setting. Note that in this mode,
counting is not started if only the count value is written. Since counting has to be started in
this mode by using the leading edge of the gate input as a trigger, the counter output is
switched to "L" level by the next clock after the gate input trigger. This "L" level status is
maintained during the set count value, and is switched back to "H" level when the terminal
count is reached.
Once counting has been started, there is no interruption until the terminal count is reached,
even if the gate input is switched to "L" level in the meantime. And although counting
continues even if a new count value is written during the counting, counting is started at the
new count value if another trigger is applied by the gate input.
∑ Mode 2 (rate generator)
The counter output is switched to "H" level by the mode setting. When the gate input is at
"H" level, counting is started by the next clock after the count value has been written. And
if the gate input is at "L" level, counting is started by using the rising edge of the gate input
as a trigger after the count value has been set.
An "L" level output pulse appears at the counter output during a single clock duration once
every n clock inputs where n is the set count value. If a new count value is written during
while counting is in progress, counting is started at the new count value following output of
the pulse currently being counted. And if the gate input is switched to "L" level during
counting, the counter output is forced to switch to "H" level, the counting being restarted by
the rising edge of the gate input.
∑ Mode 3 (square waveform rate generator)
The counter output is switched to "H" level by the mode setting. Counting is started in the
same way as described for mode 2 above.
The repeated square wave output appearing at the counter output contains half the number
of counts as the set count value. If the set count value (n) is an odd number, the repeated square
wave output consists of only (n+1)/2 clock inputs at "H" level and (n-1)/2 clock inputs at "L"
level.
If a new count value is written during counting, the new count value is reflected immediately
after the change ("H" to "L" or "L" to "H") in the next counter output to be executed. The
counting operation at the gate input is done the same as in mode 2.

12/19
° Semiconductor
MSM82C53-2RS/GS/JS
∑ Mode 4 (software trigger strobe)
The counter output is switched to "H" level by the mode setting. Counting is started in the
same way as described for mode 0. A single "L" pulse equivalent to one clock width is
generated at the counter output when the terminal count is reached.
This mode differs from 2 in that the "L" level output appears one clock earlier in mode 2, and
that pulses are not repeated in mode 4. Counting is stopped when the gate input is switched
to "L" level, and restarted from the set count value when switched back to "H" level.
∑ Mode 5 (hardware trigger strobe)
The counter output is switched to "H" level by the mode setting. Counting is started, and the
gate input used, in the same way as in mode 1.
The counter output is identical to the mode 4 output.
The various roles of the gate input signals in the above modes are summarized in the following
table.
0
1
"H" Level
"L" Level Falling Edge
Rising Edge
Mode
Gate
Counting not possible
Counting possible
(1)
(2)
Start of counting
Retriggering
2
(1)
(2)
Counting not possible
Counter output forced to "H" level
Start of counting
Counting possible
3
(1)
(2)
Counting not possible
Counter output forced to "H" level
Start of counting
Counting possible
4
Counting not possible
Counting possible
5
(1)
(2)
Start of counting
Retriggering

13/19
° Semiconductor
MSM82C53-2RS/GS/JS
4
3
2
1
0
2
1
0
3
2
1
0
(n = 4)
(n = 2)
(GATE="H")
(n = 4)
CLK
WR
OUT
WR
GATE
OUT
Mode 0
Mode 1
4
3
2
1
0
4
3
2
4
3
2
1
0
(n = 4)
(n = 4)
CLK
WR
GATE
OUT
GATE
OUT
4
3
2
1
4
3
2
1
2
1
2
4
3
2
1
4
4
3
2
1
(n = 4)
(n = 2)
(GATE="H")
(n = 4)
Mode 2
CLK
WR
OUT
GATE
OUT
4
2
4
2
4
2
4
3
2
3
3
2
5
2
4
4
2
5
2
4
5
5
5
(n = 4)
(n = 3)
(GATE="H")
(n = 5)
Mode 3
CLK
WR
OUT
GATE
OUT
CLK
WR
OUT
GATE
OUT
Mode 4
(GATE="H")
4
3
2
1
0
4
3
2
1
0
CLK
GATE
OUT
GATE
OUT
Mode 5
4
3
2
1
0
4
3
2
1
4
3
2
1
0
(n = 4)
(n = 4)
2
Note: "n" is the value set in the counter.
Figures in these diagrams refer to counter values.
4
4
4
4
4

14/19
° Semiconductor
MSM82C53-2RS/GS/JS
Reading of Counter Values
All MSM82C53-2 counting is down-counting, the counting being in steps of 2 in mode 3.
Counter values can be read during counting by (1) direct reading, and (2) counter latching
("read on the fly").
∑ Direct reading
Counter values can be read by direct reading operations.
Since the counter value read according to the timing of the RD and CLK signals is not
guaranteed, it is necessary to stop the counting by a gate input signal, or to interrupt the clock
input temporarily by an external circuit to ensure that the counter value is correctly read.
∑ Counter latching
In this method, the counter value is latched by writing counter latch command, thereby
enabling a stable value to be read without effecting the counting in any way at all. An example
of a counter latching program is given below.
Counter latching executed for counter #1 (Read/Load 2-byte setting)
0 1 0 0 • • • •
MVI A
Dentotes counter latching
OUT n3
Write in control word address (n3)
IN n1
Reading of the LSB of the counter
value latched from counter #1
n1: Counter #1 address
MOV B, A
IN n1
MOV C, A
Reading of MSB from counter #1
The counter value at this point is latched.
MSM82C53-2
CLK
0
OUT
0
CLK
1
OUT
1
CLK
2
OUT
2
Use counter #1 and counter #2
Counter #1: mode 0, upper order 16-bit counter
value
Counter #2: mode 2, lower order 16-bit counter
value
This setting enables counting up to a maximum of 2
32
.
Example of Practical Application
∑ MSM82C53-2 used as a 32-bit counter.

15/19
° Semiconductor
MSM82C53-2RS/GS/JS
NOTICE ON REPLACING LOW-SPEED DEVICES WITH HIGH-SPEED DEVICES
The conventional low speed devices are replaced by high-speed devices as shown below.
When you want to replace your low speed devices with high-speed devices, read the replacement
notice given on the next pages.
High-speed device (New)
Low-speed device (Old)
Remarks
M80C85AH
M80C85A/M80C85A-2
8bit MPU
M80C86A-10
M80C86A/M80C86A-2
16bit MPU
M80C88A-10
M80C88A/M80C88A-2
8bit MPU
M82C84A-2
M82C84A/M82C84A-5
Clock generator
M81C55-5
M81C55
RAM.I/O, timer
M82C37B-5
M82C37A/M82C37A-5
DMA controller
M82C51A-2
M82C51A
USART
M82C53-2
M82C53-5
Timer
M82C55A-2
M82C55A-5
PPI

16/19
° Semiconductor
MSM82C53-2RS/GS/JS
Differences between MSM82C53-5 and MSM82C53-2
1) Manufacturing Process
These devices use a 3 m Si-Gate CMOS process technology and have the same chip size.
2) Function
These devices have the same logics except for changes in AC characteristics listed in (3-2).
3) Electrical Characteristics
3-1) DC Characteristics
As shown above, the characteristics of these devices are identical under the same test condition. The
MSM82C53-2 satisfies the characteristics of the MSM82C53-5.
3-2) AC Characteristics
As shown above, the MSM82C53-2 satisfies the characteristics of the MSM82C53-5.
Parameter
Symbol
MSM82C53-5
MSM82C53-2
Address Hold Time After Write
30 ns minimum
20 ns minimum
t
WA
Data Input Hold Time After Write
30 ns minimum
20 ns minimum
t
WD
Clock Cycle Time
200 ns minimum
125 ns minimum
t
CLK
Parameter
Symbol
MSM82C53-5
MSM82C53-2
Average Operating Current
5 mA maximum
(t
CLK
=200 ns)
8 mA maximum
(t
CLK
=125 ns)
I
CC

17/19
° Semiconductor
MSM82C53-2RS/GS/JS
(Unit : mm)
PACKAGE DIMENSIONS
Notes for Mounting the Surface Mount Type Package
The SOP, QFP, TSOP, SOJ, QFJ (PLCC), SHP and BGA are surface mount type packages, which
are very susceptible to heat in reflow mounting and humidity absorbed in storage.
Therefore, before you perform reflow mounting, contact Oki's responsible sales person for the
product name, package name, pin number, package code and desired mounting conditions
(reflow method, temperature and times).
DIP24-P-600-2.54
Package material
Lead frame material
Pin treatment
Solder plate thickness
Package weight (g)
Epoxy resin
42 alloy
Solder plating
5 mm or more
3.55 TYP.

18/19
° Semiconductor
MSM82C53-2RS/GS/JS
(Unit : mm)
Notes for Mounting the Surface Mount Type Package
The SOP, QFP, TSOP, SOJ, QFJ (PLCC), SHP and BGA are surface mount type packages, which
are very susceptible to heat in reflow mounting and humidity absorbed in storage.
Therefore, before you perform reflow mounting, contact Oki's responsible sales person for the
product name, package name, pin number, package code and desired mounting conditions
(reflow method, temperature and times).
QFJ28-P-S450-1.27
Package material
Lead frame material
Pin treatment
Solder plate thickness
Package weight (g)
Epoxy resin
Cu alloy
Solder plating
5 mm or more
1.00 TYP.
Spherical surface

19/19
° Semiconductor
MSM82C53-2RS/GS/JS
(Unit : mm)
Notes for Mounting the Surface Mount Type Package
The SOP, QFP, TSOP, SOJ, QFJ (PLCC), SHP and BGA are surface mount type packages, which
are very susceptible to heat in reflow mounting and humidity absorbed in storage.
Therefore, before you perform reflow mounting, contact Oki's responsible sales person for the
product name, package name, pin number, package code and desired mounting conditions
(reflow method, temperature and times).
SSOP32-P-430-1.00-K
Package material
Lead frame material
Pin treatment
Solder plate thickness
Package weight (g)
Epoxy resin
42 alloy
Solder plating
5 mm or more
0.60 TYP.
Mirror finish


















