 | ÐлекÑÑоннÑй компоненÑ: HEF4067BT | СкаÑаÑÑ:  PDF PDF  ZIP ZIP |
Äîêóìåíòàöèÿ è îïèñàíèÿ www.docs.chipfind.ru
DATA SHEET
Product specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC04
January 1995
INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
HEF4067B
MSI
16-channel analogue
multiplexer/demultiplexer
For a complete data sheet, please also download:
·
The IC04 LOCMOS HE4000B Logic
Family Specifications HEF, HEC
·
The IC04 LOCMOS HE4000B Logic
Package Outlines/Information HEF, HEC
January 1995
2
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
16-channel analogue
multiplexer/demultiplexer
HEF4067B
MSI
DESCRIPTION
The HEF4067B is a 16-channel analogue
multiplexer/demultiplexer with four address inputs (A
0
to
A
3
), an active LOW enable input (E), sixteen independent
inputs/outputs (Y
0
to Y
15
) and a common input/output (Z).
The device contains sixteen bidirectional analogue
switches, each with one side connected to an independent
input/output (Y
0
to Y
15
) and the other side connected to
the common input/output (Z).
With E LOW, one of the sixteen switches is selected (low
impedance ON-state) by A
0
to A
3
. All unselected switches
are in the high impedance OFF-state. With E HIGH all
switches are in the high impedance OFF-state,
independent of A
0
to A
3
.
The analogue inputs/outputs (Y
0
to Y
15
and Z) can swing
between V
DD
as a positive limit and V
SS
as a negative
limit. V
DD
to V
SS
may not exceed 15 V.
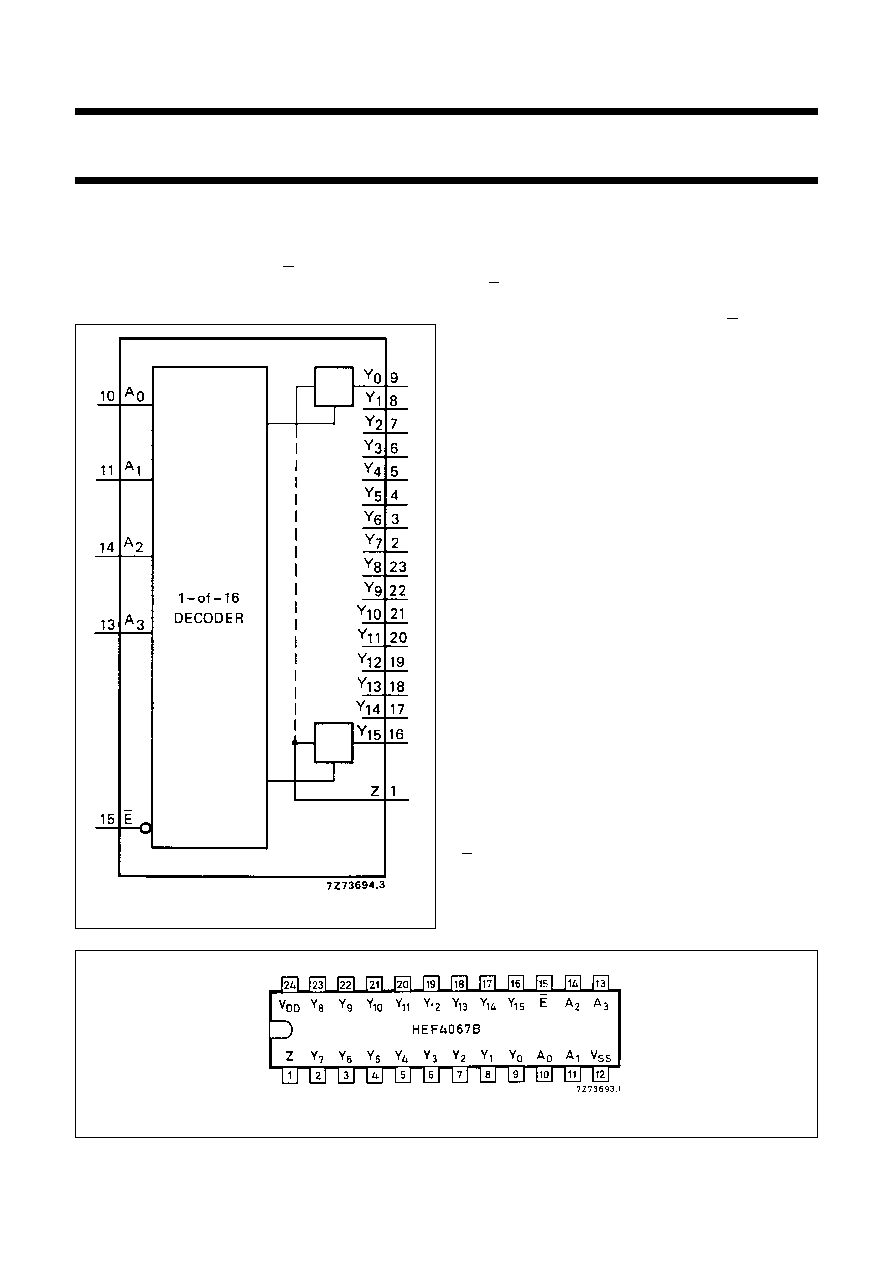
Fig.1 Functional diagram.
FAMILY DATA, I
DD
LIMITS category MSI
See Family Specifications
PINNING
HEF4067BP(N):
24-lead DIL; plastic
(SOT101-1)
HEF4067BD(F):
24-lead DIL; ceramic (cerdip)
(SOT94)
HEF4067BT(D):
24-lead SO; plastic
(SOT137-1)
( ): Package Designator North America
Y
0
to Y
15
independent inputs/outputs
A
0
to A
3
address inputs
E
enable input (active LOW)
Z
common input/output
Fig.2 Pinning diagram.
January 1995
3
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
16-channel analogue
multiplexer/demultiplexer
HEF4067B
MSI
FUNCTION TABLE
Note
1. H = HIGH state (the more positive voltage)
L = LOW state (the less positive voltage)
X = state is immaterial
INPUTS
CHANNEL
E
A
3
A
2
A
1
A
0
ON
L
L
L
L
L
Y
0
-
Z
L
L
L
L
H
Y
1
-
Z
L
L
L
H
L
Y
2
-
Z
L
L
L
H
H
Y
3
-
Z
L
L
H
L
L
Y
4
-
Z
L
L
H
L
H
Y
5
-
Z
L
L
H
H
L
Y
6
-
Z
L
L
H
H
H
Y
7
-
Z
L
H
L
L
L
Y
8
-
Z
L
H
L
L
H
Y
9
-
Z
L
H
L
H
L
Y
10
-
Z
L
H
L
H
H
Y
11
-
Z
L
H
H
L
L
Y
12
-
Z
L
H
H
L
H
Y
13
-
Z
L
H
H
H
L
Y
14
-
Z
L
H
H
H
H
Y
15
-
Z
H
X
X
X
X
none
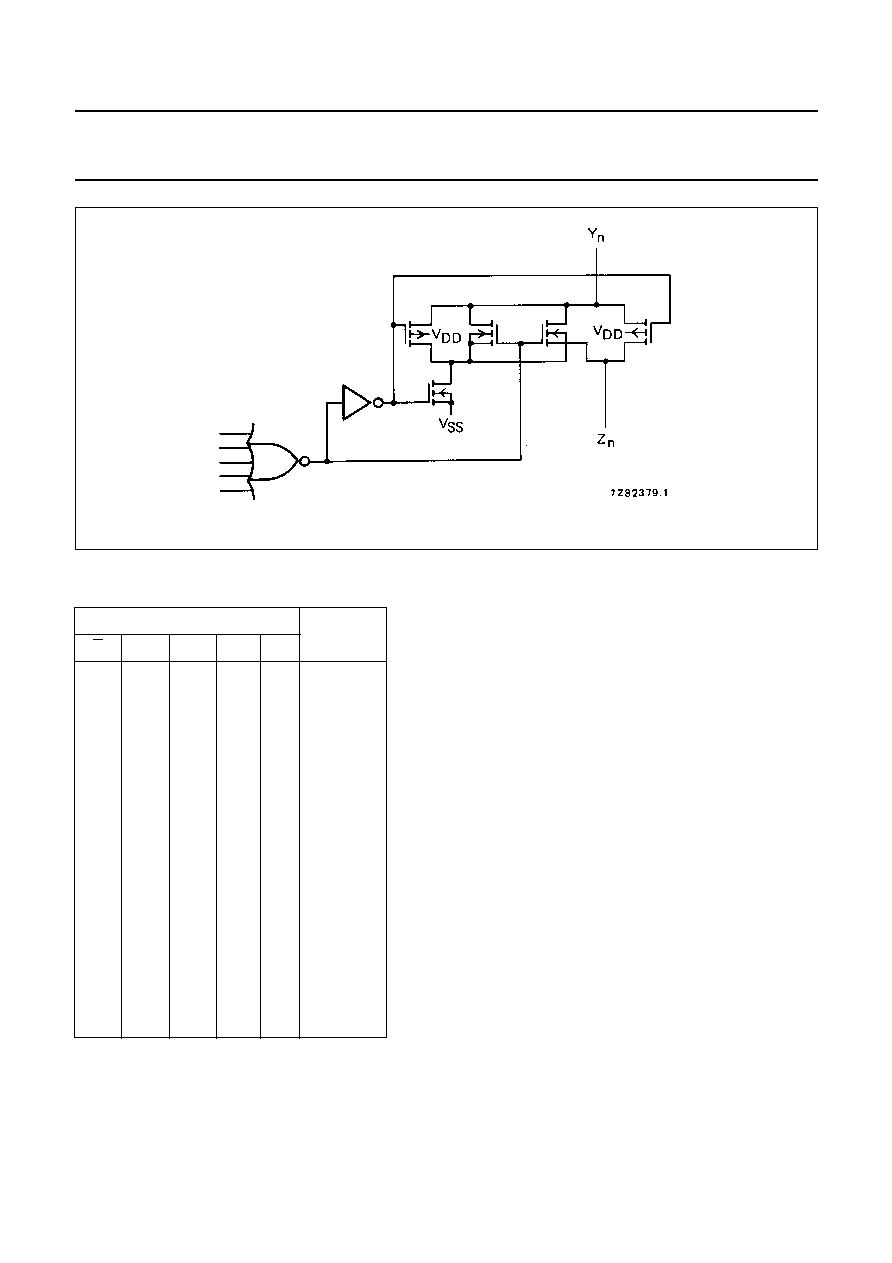
Fig.3 Schematic diagram (one switch).
January 1995
4
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
16-channel analogue
multiplexer/demultiplexer
HEF4067B
MSI
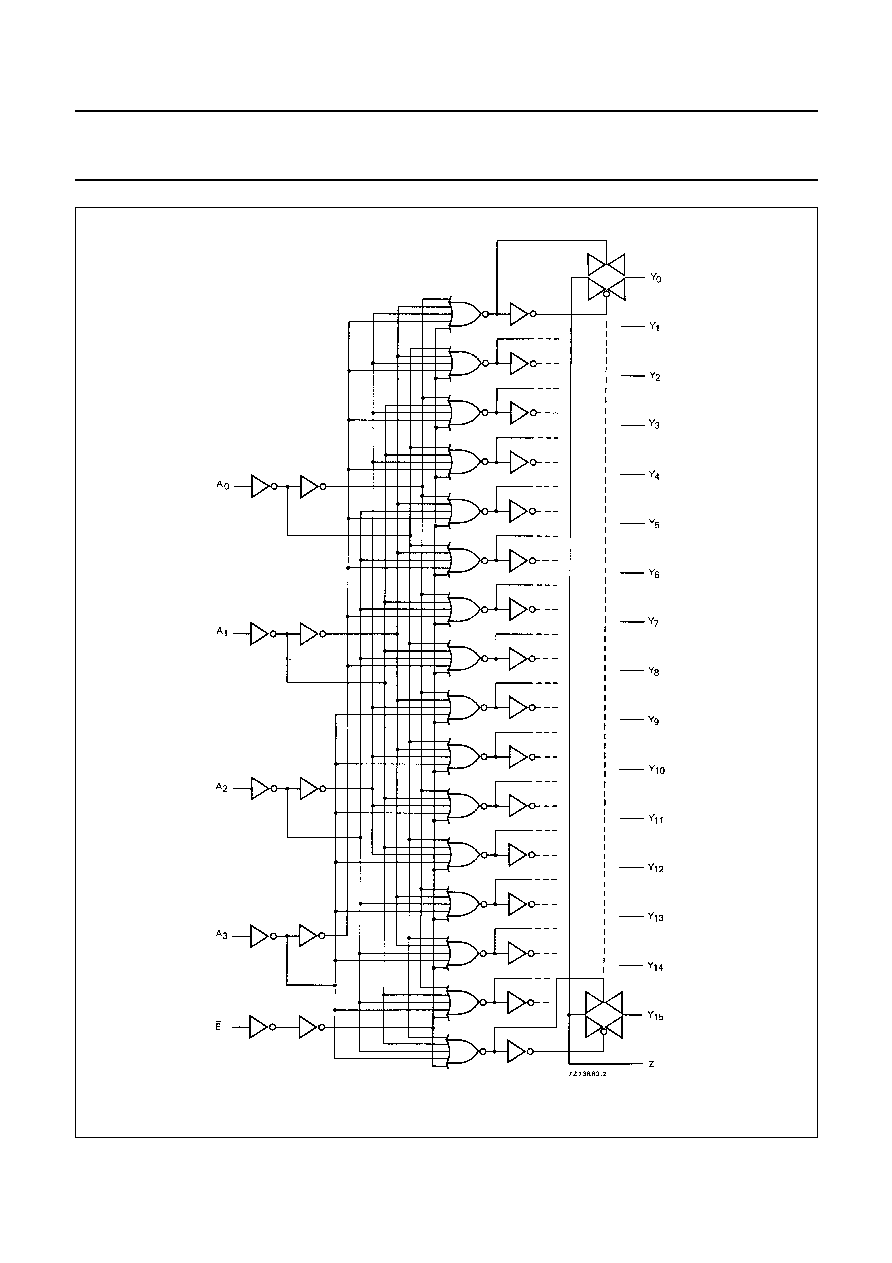
Fig.4 Logic diagram.
January 1995
5
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
16-channel analogue
multiplexer/demultiplexer
HEF4067B
MSI
DC CHARACTERISTICS
T
amb
= 25
°
C
V
DD
V
SYMBOL
TYP.
MAX.
CONDITIONS
5
350
2500
V
is
= V
SS
to V
DD
see Fig.5
ON resistance
10
R
ON
80
245
15
60
175
5
115
340
V
is
= V
SS
see Fig.5
ON resistance
10
R
ON
50
160
15
40
115
5
120
365
V
is
= V
DD
see Fig.5
ON resistance
10
R
ON
65
200
15
50
155
`
' ON resistance
5
25
-
V
is
= V
SS
to V
DD
see Fig.5
between any two
10
R
ON
10
-
channels
15
5
-
OFF-state leakage
5
-
-
nA
E at V
DD
current, all
10
I
OZZ
-
-
nA
channels OFF
15
-
1000
nA
OFF-state leakage
5
-
-
nA
E at V
SS
current, any
10
I
OZY
-
-
nA
channel
15
-
200
nA
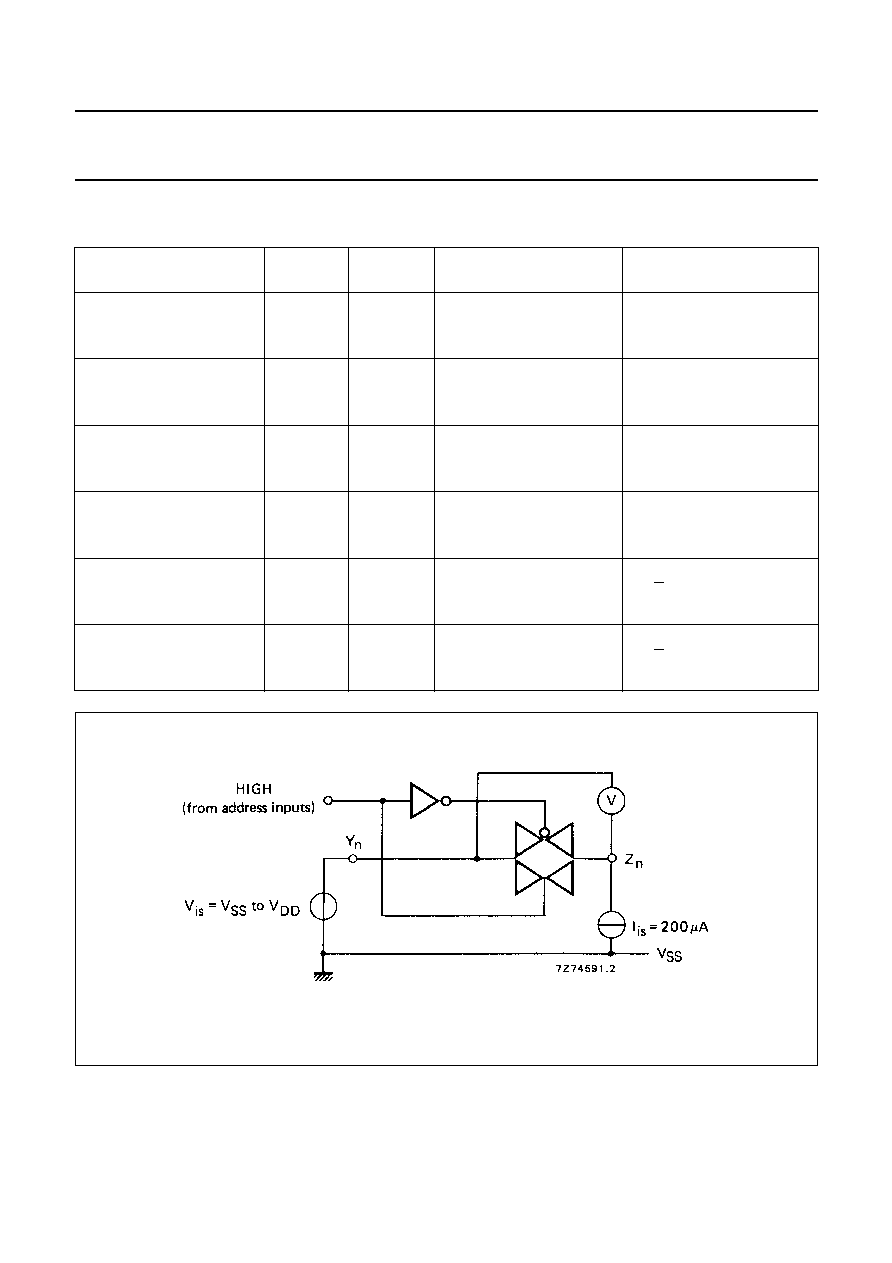
Fig.5 Test set-up for measuring R
ON
.
January 1995
6
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
16-channel analogue
multiplexer/demultiplexer
HEF4067B
MSI
NOTE
To avoid drawing V
DD
current out of terminal Z, when switch current flows into terminals Y, the voltage drop across the
bidirectional switch must not exceed 0,4 V. If the switch current flows into terminal Z, no V
DD
current will flow out of
terminals Y, in this case there is no limit for the voltage drop across the switch, but the voltages at Y and Z may not
exceed V
DD
or V
SS
.
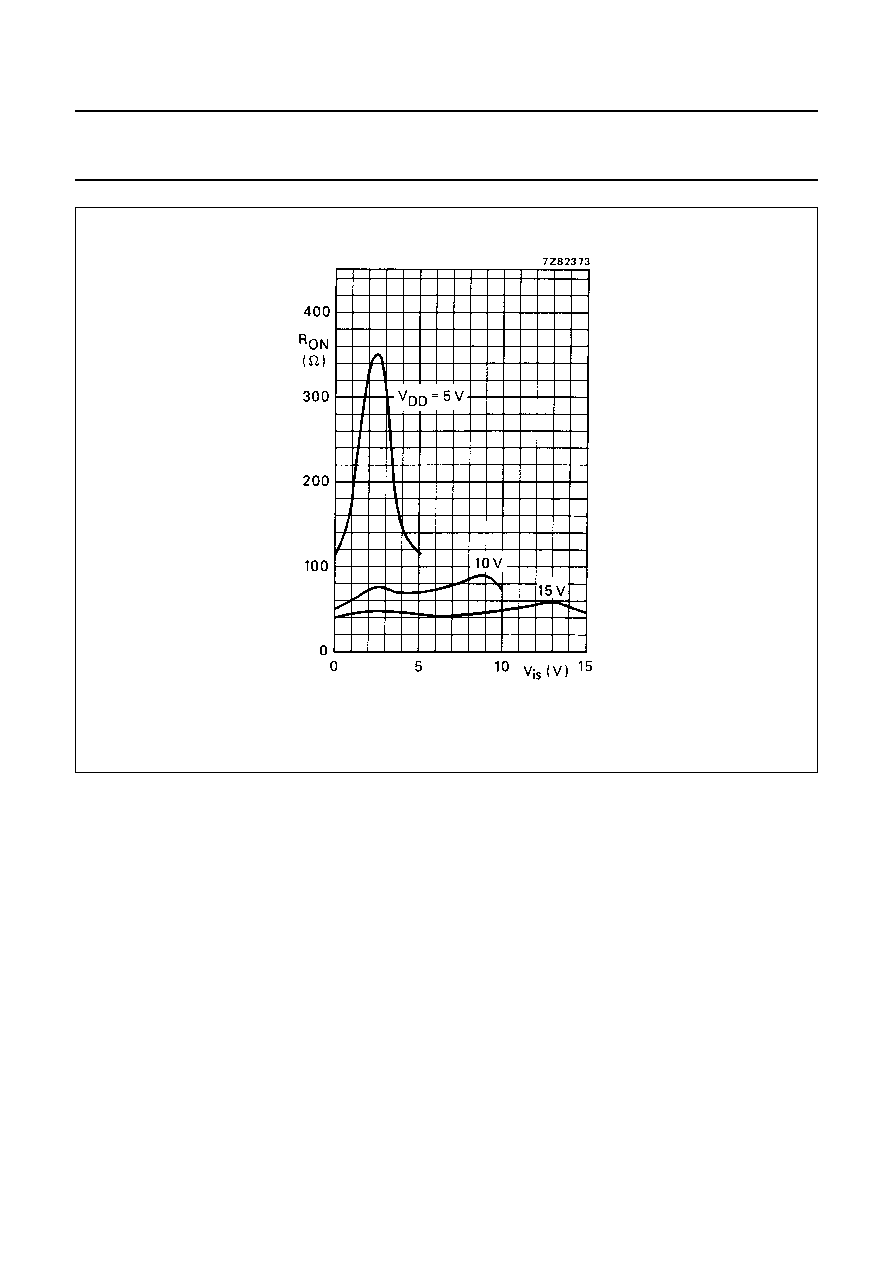
Fig.6 Typical R
ON
as a function of input voltage.
I
is
= 200
µ
A
V
SS
= 0 V
January 1995
7
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
16-channel analogue
multiplexer/demultiplexer
HEF4067B
MSI
AC CHARACTERISTICS
V
SS
= 0 V; T
amb
= 25
°
C; input transition times
20 ns
AC CHARACTERISTICS
(1)
,
(2)
V
SS
= 0 V; T
amb
= 25
°
C; input transition times
20 ns
V
DD
V
TYPICAL FORMULA FOR P (
µ
W)
Dynamic power
5
1 100 f
i
+
(f
o
C
L
)
×
V
DD
2
where
dissipation per
10
5 000 f
i
+
(f
o
C
L
)
×
V
DD
2
f
i
= input freq. (MHz)
package (P)
15
13 300 f
i
+
(f
o
C
L
)
×
V
DD
2
f
o
= output freq. (MHz)
C
L
= load capacitance (pF)
(f
o
C
L
) = sum of outputs
V
DD
= supply voltage (V)
V
DD
V
SYMBOL
TYP.
MAX.
Propagation delays
V
is
V
os
5
30
60
ns
note 3
HIGH to LOW
10
t
PHL
15
25
ns
15
10
20
ns
5
25
50
ns
note 3
LOW to HIGH
10
t
PLH
10
20
ns
15
10
20
ns
A
n
V
os
5
190
380
ns
note 4
HIGH to LOW
10
t
PHL
70
145
ns
15
50
100
ns
5
175
345
ns
note 4
LOW to HIGH
10
t
PLH
70
140
ns
15
50
100
ns
Output disable times
E
V
os
5
195
385
ns
note 5
HIGH
10
t
PHZ
140
280
ns
15
130
260
ns
5
215
435
ns
note 5
LOW
10
t
PLZ
180
355
ns
15
170
340
ns
Output enable times
E
V
os
5
155
315
ns
note 5
HIGH
10
t
PZH
70
135
ns
15
50
100
ns
5
170
340
ns
note 5
LOW
10
t
PZL
70
140
ns
15
50
100
ns
January 1995
8
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
16-channel analogue
multiplexer/demultiplexer
HEF4067B
MSI
AC CHARACTERISTICS
V
SS
= 0 V; T
amb
= 25
°
C; input transition times
20 ns
Notes
1. V
is
is the input voltage at a Y or Z terminal, whichever is assigned as input.
2. V
os
is the output voltage at a Y or Z terminal, whichever is assigned as output.
3. R
L
= 10 k
to V
SS
; C
L
= 50 pF to V
SS
; E = V
SS
; V
is
= V
DD
(square-wave); see Fig.7.
4. R
L
= 10 k
; C
L
= 50 pF to V
SS
; E = V
SS
; A
n
= V
DD
(square-wave); V
is
= V
DD
and R
L
to V
SS
for t
PLH
; V
is
= V
SS
and
R
L
to V
DD
for t
PHL
; see Fig.7.
5. R
L
= 10 k
; C
L
= 50 pF to V
SS
; E = V
DD
(square-wave);
V
is
= V
DD
and R
L
to V
SS
for t
PHZ
and t
PZH
;
V
is
= V
SS
and R
L
to V
DD
for t
PLZ
and t
PZL
; see Fig.7.
6. R
L
= 10 k
; C
L
= 15 pF; channel ON; V
is
=
1
/
2
V
DD(p-p)
(sine-wave, symmetrical about
1
/
2
V
DD
);
f
is
= 1 kHz; see Fig.8.
7. R
L
= 1 k
; V
is
=
1
/
2
V
DD(p-p)
(sine-wave, symmetrical about
1
/
2
V
DD
);
8. R
L
= 10 k
to V
SS
; C
L
= 15 pF to V
SS
; E or A
n
= V
DD
(square-wave); crosstalk is
V
os
(peak value); see Fig.7.
9. R
L
= 1 k
; C
L
= 5 pF; channel OFF; V
is
=
1
/
2
V
DD(p-p)
(sine-wave, symmetrical about
1
/
2
V
DD
);
10. R
L
= 1 k
; C
L
= 5 pF; channel ON; V
is
=
1
/
2
V
DD(p-p)
(sine-wave, symmetrical about
1
/
2
V
DD
);
V
DD
V
SYMBOL
TYP.
MAX.
Distortion, sine-wave
5
0,25
%
note 6
response
10
0,04
%
15
0,04
%
Crosstalk between
5
-
MHz
note 7
any two channels
10
1
MHz
15
-
MHz
Crosstalk; enable
5
-
mV
note 8
or address input
10
50
mV
to output
15
-
mV
OFF-state
5
-
MHz
note 9
feed-through
10
1
MHz
15
-
MHz
ON-state frequency
5
13
MHz
note 10
response
10
40
MHz
15
70
MHz
20
V
os
V
is
---------
50 dB; see Fig.9.
=
log
20
V
os
V
is
---------
50 dB; see Fig.8.
=
log
20
V
os
V
is
---------
3 dB; see Fig.8.
=
log
January 1995
9
Philips Semiconductors
Product specification
16-channel analogue
multiplexer/demultiplexer
HEF4067B
MSI
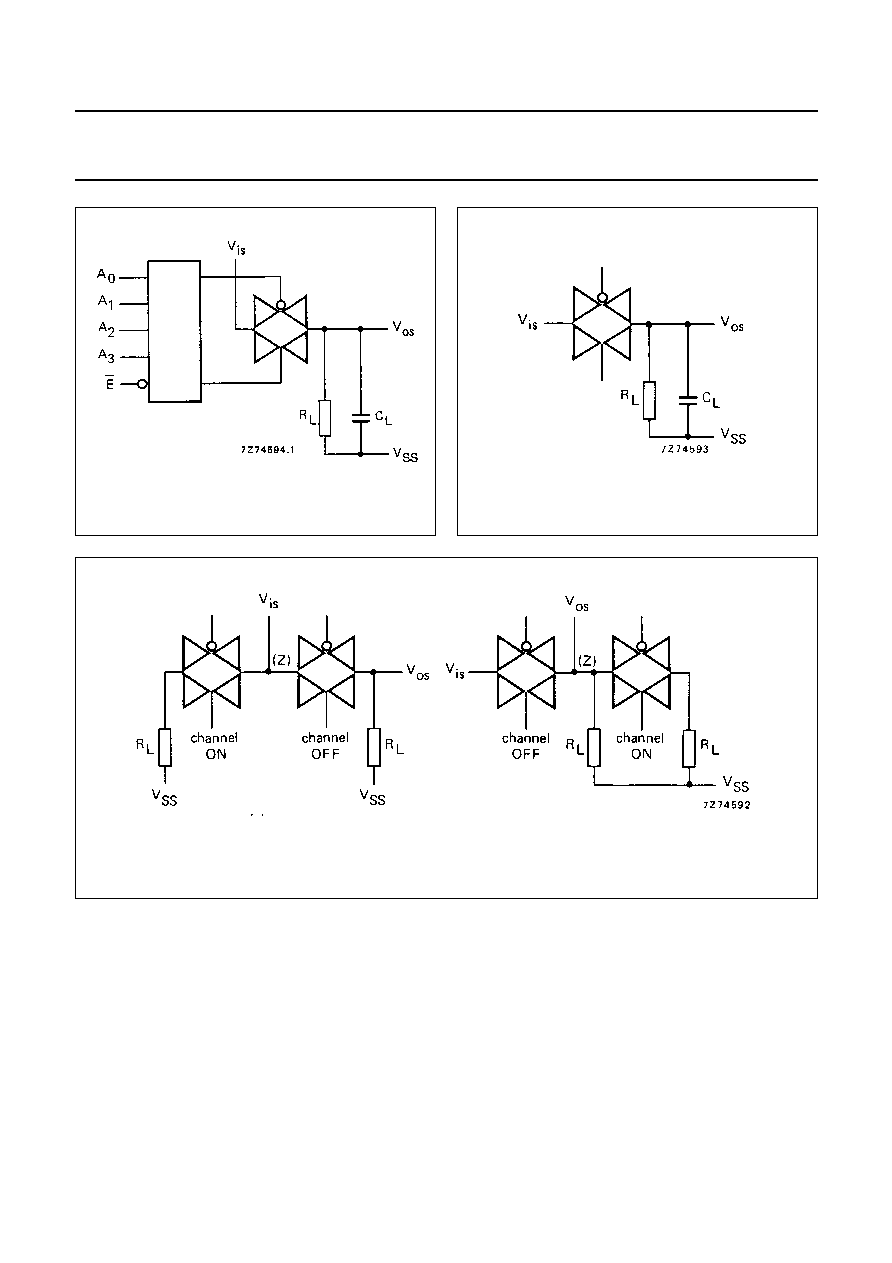
Fig.7
Fig.8
Fig.9
(a)
(b)
APPLICATION INFORMATION
Some examples of applications for the HEF4067B are:
·
Analogue multiplexing and demultiplexing.
·
Digital multiplexing and demultiplexing.
·
Signal gating.
NOTE
If break before make is needed, then it is necessary to use
the enable input.








