 | ÐлекÑÑоннÑй компоненÑ: SP7650 | СкаÑаÑÑ:  PDF PDF  ZIP ZIP |
Äîêóìåíòàöèÿ è îïèñàíèÿ www.docs.chipfind.ru
1
Date: 08/24/04
SP7650 Wide Input Voltage Range 3A, 300kHz, Buck Regulator © Copyright 2004 Sipex Corporation
SP7650
FEATURES
2.5V to 28V Step Down Achieved Using Dual Input
Output Voltage down to 0.8V
3A Output Capability
Built in Low R
DSON
Power Switches (40 m typ)
Highly Integrated Design, Minimal Components
300 kHz Fixed Frequency Operation
UVLO Detects Both V
CC
and V
IN
Over Temperature Protection
Short Circuit Protection with Auto-Restart
Wide BW Amp Allows Type II or III Compensation
Programmable Soft Start
Fast Transient Response
High Efficiency: Greater than
95%
Possible
Asynchronous Start-Up into a Pre-Charged Output
Small 7mm x 4mm DFN Package
Wide Input Voltage Range 3A, 300kHz, Buck Regulator
The SP7650 is a synchronous step-down switching regulator optimized for high efficiency. The part is designed to be
especially attractive for dual supply, 12V or 24V distributed power systems step down with 5V used to power the
controller. This lower V
CC
voltage minimizes power dissipation in the part and is used to drive the top switch. The SP7650
is designed to provide a fully integrated buck regulator solution using a fixed 300kHz frequency, PWM voltage mode
architecture. Protection features include UVLO, thermal shutdown and output short circuit protection. The SP7650 is
available in the space saving DFN package
.
®
Advanced
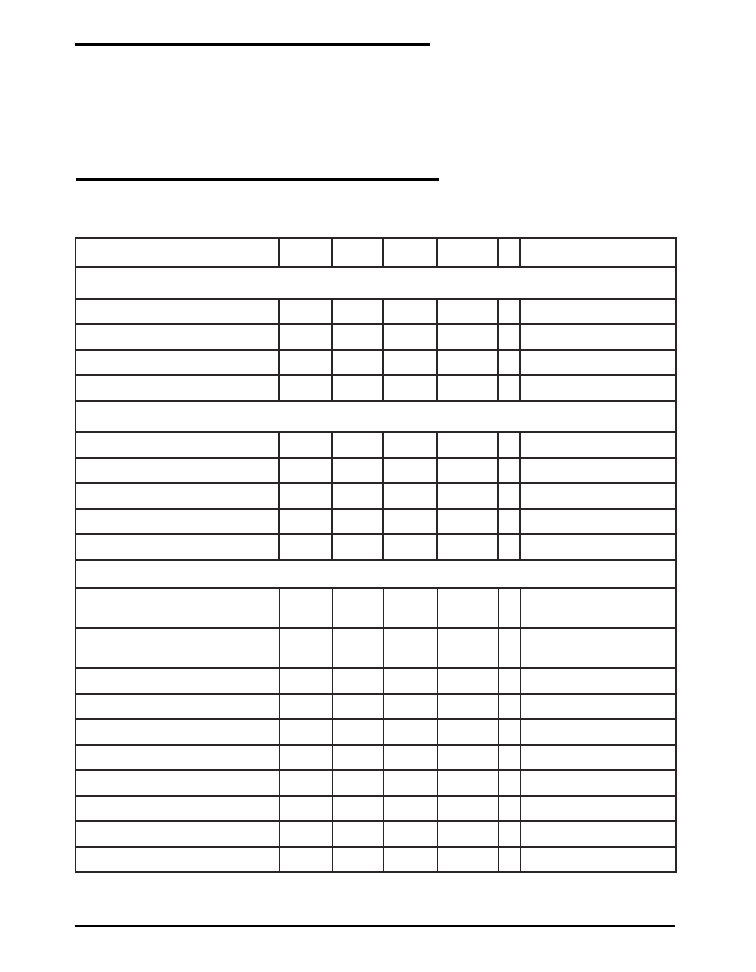
TYPICAL APPLICATION CIRCUIT
Now Available in Lead Free Packaging
DESCRIPTION
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
2 2
23
24
25
26
TOP VIEW
Heatsink Pad 1
Connect to Lx
Heatsink pad 2
Connect to GND
Heatsink pad 3
Connect to V
IN
P
GND
P
GND
GND
V
FB
COMP
UVIN
GND
SS
V
IN
LX
LX
LX
LX
V
CC
GND
GND
GND
BST
NC
LX
LX
LX
DFN PACKAGE
7mm x 4mm
SP7650
P
GND
V
IN
V
IN
V
IN
CBST
6800pF
L1
2.2uH, Irate=4.78A
C1
22uF
CVCC
2.2uF
U1
SP7650
PGND
1
PGND
2
PGND
3
GND
4
VFB
5
COMP
6
UVIN
7
GND
8
SS
9
VIN
10
VIN
11
VIN
12
VIN
13
LX
14
LX
15
LX
16
NC
17
BST
18
GND
19
GND
20
GND
21
VCC
22
LX
23
LX
24
LX
25
LX
26
DBST
CSS
47nF
CP1
22pF
3.3V
0-3A
RSET
21.5k,1%
GND
C3
47uF
N o t e s :
1 2 V
VIN
1. U1 Bottom-Side Layout should
has three contacts isolated from
one another Vin SWNODE and GND
SD101AWS
VOUT
RZ3
7.15k,1%
CZ3
150pF
CZ2
1,000pF
R1
68.1k,1%
RZ2
15k,1%
CF1
100pF
fs=300Khz
+5V VCC
ENABLE
2. RSET=54.48/(Vout-0.8V) (KOhm)
1 6 V
6.3V
(note 2)
2
Date: 08/24/04
SP7650 Wide Input Voltage Range 3A, 300kHz, Buck Regulator © Copyright 2004 Sipex Corporation
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Unless otherwise specified: -40°C < T
AMB
< 85°C, -40°C<Tj<125°C, 4.5V < V
CC
< 5.5V, 3V<Vin<28V, BST=LX
+ 5V, LX =
GND = 0V, UVIN = 3.0V, CV
CC
= 1µF, C
COMP
= 0.1µF, C
SS
= 50nF, Typical measured at V
CC
= 5V.
The denotes the specifications which apply over the full temperature range, unless otherwise specified.
These are stress ratings only and functional operation of the device at
these ratings or any other above those indicated in the operation sections
of the specifications below is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum
rating conditions for extended periods of time may affect reliability.
V
CC
.................................................................................................. 7V
V
IN ...........................................................................................................................................
30V
I
LX ...............................................................................................................................................
5A
BST ............................................................................................... 35V
BST-SWN ......................................................................... -0.3V to 7V
SWN ................................................................................... -1V to 30V
GH ......................................................................... -0.3V to BST+0.3V
GH-SWN ......................................................................................... 7V
All other pins .......................................................... -0.3V to V
CC
+0.3V
Storage Temperature .................................................. -65°C to 150°C
Power Dissipation ...................................... Internally Limited via OTP
Lead Temperature (Soldering, 10 sec) ...................................... 300°C
ESD Rating .......................................................................... 2kV HBM
Thermal Resistance
JC ....................................................................................
5°C/W
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
R
E
T
E
M
A
R
A
P
.
N
I
M
.
P
Y
T
.
X
A
M
S
T
I
N
U
S
N
O
I
T
I
D
N
O
C
T
N
E
R
R
U
C
T
N
E
C
S
E
I
U
Q
V
C
C
)
g
n
i
h
c
t
i
w
s
o
N
(
t
n
e
r
r
u
C
y
l
p
p
u
S
5
.
1
3
A
m
V
B
F
V
9
.
0
=
V
C
C
)
g
n
i
h
c
t
i
w
s
(
t
n
e
r
r
u
C
y
l
p
p
u
S
8
D
B
T
A
m
)
g
n
i
h
c
t
i
w
s
o
N
(
t
n
e
r
r
u
C
y
l
p
p
u
S
T
S
B
2
.
0
4
.
0
A
m
V
B
F
V
9
.
0
=
)
g
n
i
h
c
t
i
w
s
(
t
n
e
r
r
u
C
y
l
p
p
u
S
T
S
B
0
.
4
D
B
T
A
m
O
L
V
U
:
N
O
I
T
C
E
T
O
R
P
V
C
C
d
l
o
h
s
e
r
h
T
t
r
a
t
S
O
L
V
U
0
0
.
4
5
2
.
4
5
.
4
V
V
C
C
s
i
s
e
r
e
t
s
y
H
O
L
V
U
0
0
1
0
0
2
0
0
3
V
m
d
l
o
h
s
e
r
h
T
t
r
a
t
S
N
I
V
U
3
.
2
5
.
2
5
6
.
2
V
s
i
s
e
r
e
t
s
y
H
N
I
V
U
0
0
2
0
0
3
0
0
4
V
m
t
n
e
r
r
u
C
t
u
p
n
I
N
I
V
U
1
A
µ
V
0
.
3
=
N
I
V
U
E
C
N
E
R
E
F
E
R
R
E
I
F
I
L
P
M
A
R
O
R
R
E
e
c
n
e
r
e
f
e
R
r
e
i
f
il
p
m
A
r
o
r
r
E
2
9
7
.
0
0
0
8
.
0
8
0
8
.
0
V
e
r
u
s
a
e
M
,
.
g
i
f
n
o
C
n
i
a
G
X
2
V
B
F
V
;
C
C
C
º
5
2
=
T
,
V
5
=
e
c
n
e
r
e
f
e
R
r
e
i
f
il
p
m
A
r
o
r
r
E
e
r
u
t
a
r
e
p
m
e
T
d
n
a
e
n
i
L
r
e
v
O
8
8
7
.
0
0
0
8
.
0
2
1
8
.
0
V
e
c
n
a
t
c
u
d
n
o
c
s
n
a
r
T
r
e
i
f
il
p
m
A
r
o
r
r
E
6
V
/
A
m
n
i
a
G
r
e
i
f
il
p
m
A
r
o
r
r
E
0
6
B
d
d
a
o
L
o
N
t
n
e
r
r
u
C
k
n
i
S
P
M
O
C
0
5
1
A
µ
V
B
F
V
9
.
0
=
P
M
O
C
,
V
9
.
0
=
t
n
e
r
r
u
C
e
c
r
u
o
S
P
M
O
C
0
5
1
A
µ
V
B
F
V
2
.
2
=
P
M
O
C
,
V
7
.
0
=
V
B
F
t
n
e
r
r
u
C
s
a
i
B
t
u
p
n
I
0
5
0
0
2
A
n
V
B
F
V
8
.
0
=
e
l
o
P
l
a
n
r
e
t
n
I
4
z
H
M
p
m
a
l
C
P
M
O
C
5
.
2
V
V
B
F
C
º
5
2
=
A
T
,
V
7
.
0
=
t
n
e
i
c
i
f
f
e
o
C
.
p
m
e
T
p
m
a
l
C
P
M
O
C
2
-
C
º
/
V
m
3
Date: 08/24/04
SP7650 Wide Input Voltage Range 3A, 300kHz, Buck Regulator © Copyright 2004 Sipex Corporation
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Unless otherwise specified: -40°C < T
AMB
< 85°C, -40°C<Tj<125°C, 4.5V < V
CC
< 5.5V, 3V<Vin<28V, BST=LX
+ 5V, LX =
GND = 0V, UVIN = 3.0V, CV
CC
= 1µF, C
COMP
= 0.1µF, C
SS
= 50nF, Typical measured at V
CC
= 5V.
The denotes the specifications which apply over the full temperature range, unless otherwise specified.
R
E
T
E
M
A
R
A
P
.
N
I
M
.
P
Y
T
.
X
A
M
S
T
I
N
U
S
N
O
I
T
I
D
N
O
C
H
T
A
P
Y
A
L
E
D
P
O
O
L
&
P
M
A
R
,
R
O
T
A
R
A
P
M
O
C
M
W
P
:
P
O
O
L
L
O
R
T
N
O
C
e
d
u
t
il
p
m
A
p
m
a
R
2
9
.
0
1
.
1
8
2
.
1
V
t
e
s
f
f
O
P
M
A
R
1
.
1
V
T
A
P
M
O
C
P
M
A
R
,
C
º
5
2
=
g
n
i
h
c
t
i
w
S
s
t
r
a
t
s
H
G
li
t
n
u
t
n
e
i
c
i
f
f
e
o
C
.
p
m
e
T
t
e
s
f
f
o
P
M
A
R
2
-
C
º
/
V
m
h
t
d
i
W
e
s
l
u
P
m
u
m
i
n
i
M
H
G
0
9
0
8
1
s
n
o
i
t
a
R
y
t
u
D
e
l
b
a
ll
o
r
t
n
o
C
m
u
m
i
x
a
M
2
9
7
9
%
o
i
t
a
R
y
t
u
D
m
u
m
i
x
a
M
e
r
o
f
e
b
t
s
u
j
d
e
r
u
s
a
e
M
s
n
i
g
e
b
g
n
i
s
l
u
p
o
i
t
a
R
y
t
u
D
m
u
m
i
x
a
M
0
0
1
%
s
e
l
c
y
c
0
2
r
o
f
d
il
a
V
o
i
t
a
R
r
o
t
a
ll
i
c
s
O
l
a
n
r
e
t
n
I
0
4
2
0
0
3
0
6
3
z
H
k
T
R
A
T
S
T
F
O
S
:
S
R
E
M
I
T
:
t
n
e
r
r
u
C
e
g
r
a
h
C
S
S
0
1
A
µ
:
t
n
e
r
r
u
C
e
g
r
a
h
c
s
i
D
S
S
1
A
m
V
2
.
0
=
S
S
,
t
n
e
s
e
r
P
t
l
u
a
F
l
a
m
r
e
h
T
&
t
i
u
c
r
i
C
t
r
o
h
S
:
N
O
I
T
C
E
T
O
R
P
e
g
a
t
l
o
V
d
l
o
h
s
e
r
h
T
t
i
u
c
r
i
C
t
r
o
h
S
2
.
0
5
2
.
0
3
.
0
V
V
d
e
r
u
s
a
e
M
F
E
R
-
)
V
8
.
0
(
V
B
F
t
u
o
e
m
i
T
p
u
c
c
i
H
0
0
2
s
m
V
B
F
V
5
.
0
=
s
e
l
c
y
C
k
c
o
l
C
e
l
b
a
w
o
ll
A
f
o
r
e
b
m
u
N
e
l
c
y
C
y
t
u
D
%
0
0
1
t
a
0
2
s
e
l
c
y
C
s
e
l
c
y
C
0
2
r
e
t
f
A
e
s
l
u
P
L
G
m
u
m
i
n
i
M
5
.
0
s
e
l
c
y
C
V
B
F
V
7
.
0
=
e
r
u
t
a
r
e
p
m
e
T
n
w
o
d
t
u
h
S
l
a
m
r
e
h
T
5
4
1
C
º
V
B
F
V
7
.
0
=
e
r
u
t
a
r
e
p
m
e
T
y
r
e
v
o
c
e
R
l
a
m
r
e
h
T
5
3
1
C
º
s
i
s
e
r
e
t
s
y
H
l
a
m
r
e
h
T
0
1
C
º
E
G
A
T
S
R
E
W
O
P
:
T
U
P
T
U
O
R
h
c
t
i
w
S
e
d
i
S
h
g
i
H
N
O
S
D
0
4
m
V
C
C
I
;
V
5
=
T
U
O
A
3
=
T
B
M
A
C
º
5
2
=
R
h
c
t
i
w
S
e
d
i
s
w
o
L
s
u
o
r
h
c
n
y
S
N
O
S
D
0
4
m
V
C
C
I
;
V
5
=
T
U
O
A
3
=
T
B
M
A
C
º
5
2
=
t
n
e
r
r
u
C
t
u
p
t
u
O
m
u
m
i
x
a
M
3
A
4
Date: 08/24/04
SP7650 Wide Input Voltage Range 3A, 300kHz, Buck Regulator © Copyright 2004 Sipex Corporation
General Overview
The SP7650 is a fixed frequency, voltage mode,
synchronous PWM regulator optimized for high
efficiency. The part has been designed to be
especially attractive for high voltage applica-
tions utilizing 5V to power the controller and
2.5V to 28V for step down conversion.
The heart of the SP7650 is a wide bandwidth
transconductance amplifier designed to accom-
modate Type II and Type III compensation
schemes. A precision 0.8V reference, present on
the positive terminal of the error amplifier per-
mits the programming of the output voltage
down to 0.8V via the V
FB
pin. The output of the
error amplifier, COMP, compared to a 1.1V
peak-to-peak ramp is responsible for trailing
edge PWM control. This voltage ramp, and
PWM control logic are governed by the internal
oscillator that accurately sets the PWM fre-
quency to 300kHz.
THEORY OF OPERATION
The SP7650 contains two unique control fea-
tures that are very powerful in distributed appli-
cations. First, asynchronous driver control is
enabled during start up, to prohibit the low side
switch from pulling down the output until the
high side switch has attempted to turn on. Sec-
ond, a 100% duty cycle timeout ensures that the
low side switch is periodically enhanced during
extended periods at 100% duty cycle. This guar-
antees the synchronized refreshing of the BST
capacitor during very large duty ratios.
The SP7650 also contains a number of valuable
protection features. Programmable V
IN
UVLO
allows the user to set the exact value at which the
conversion voltage can safely begin down con-
version, and an internal V
CC
UVLO which en-
sures that the controller itself has enough volt-
age to properly operate. Other protection fea-
PIN DESCRIPTION
#
n
i
P
e
m
a
N
n
i
P
n
o
i
t
p
i
r
c
s
e
D
3
-
1
P
D
N
G
r
e
i
f
i
t
c
e
r
s
u
o
n
o
r
h
c
n
y
s
e
h
t
r
o
f
n
o
i
t
c
e
n
n
o
c
d
n
u
o
r
G
1
2
-
9
1
,
8
,
4
D
N
G
e
r
a
r
e
v
i
r
d
r
e
w
o
p
r
e
w
o
l
d
n
a
C
I
e
h
t
f
o
y
r
t
i
u
c
r
i
c
l
o
r
t
n
o
c
e
h
T
.
n
i
P
d
n
u
o
r
G
)
-
(
e
h
t
o
t
s
e
c
a
r
t
d
n
u
o
r
g
r
e
h
t
o
m
o
r
f
y
l
e
t
a
r
a
p
e
s
n
r
u
t
e
R
.
n
i
p
s
i
h
t
o
t
d
e
c
n
e
r
e
f
e
r
.
t
u
o
C
f
o
l
a
n
i
m
r
e
t
5
V
B
F
t
u
p
n
i
g
n
i
t
r
e
v
n
i
e
h
t
s
i
t
I
.
n
i
p
n
o
i
t
c
e
t
e
D
t
i
u
c
r
i
C
t
r
o
h
S
d
n
a
e
g
a
t
l
o
V
k
c
a
b
d
e
e
F
r
o
f
t
n
i
o
p
k
c
a
b
d
e
e
f
e
g
a
t
l
o
v
t
u
p
t
u
o
e
h
t
s
a
s
e
v
r
e
s
d
n
a
r
e
i
f
il
p
m
A
r
o
r
r
E
e
h
t
f
o
d
e
t
s
u
j
d
a
e
b
n
a
c
d
n
a
d
e
s
n
e
s
s
i
e
g
a
t
l
o
v
t
u
p
t
u
o
e
h
T
.
r
e
t
r
e
v
n
o
C
k
c
u
B
e
h
t
V
r
e
v
e
n
e
h
W
.
r
e
d
i
v
i
d
r
o
t
s
i
s
e
r
l
a
n
r
e
t
x
e
n
a
h
g
u
o
r
h
t
B
F
e
h
t
w
o
l
e
b
V
5
2
.
0
s
p
o
r
d
p
u
c
c
i
h
s
r
e
t
n
e
C
I
e
h
t
d
n
a
d
e
t
c
e
t
e
d
s
i
t
l
u
a
f
t
i
u
c
r
i
c
t
r
o
h
s
a
,
e
c
n
e
r
e
f
e
r
e
v
i
t
i
s
o
p
.
e
d
o
m
6
P
M
O
C
t
u
p
n
i
g
n
i
t
r
e
v
n
i
e
h
t
o
t
d
e
t
c
e
n
n
o
c
y
ll
a
n
r
e
t
n
i
s
i
t
I
.
r
e
i
f
il
p
m
A
r
o
r
r
E
e
h
t
f
o
t
u
p
t
u
O
d
n
a
n
e
s
o
h
c
s
i
n
o
i
t
a
n
i
b
m
o
c
r
e
t
li
f
l
a
m
i
t
p
o
n
A
.
r
o
t
a
r
a
p
m
o
c
M
W
P
e
h
t
f
o
V
r
o
d
n
u
o
r
g
r
e
h
t
i
e
d
n
a
n
i
p
s
i
h
t
o
t
d
e
t
c
e
n
n
o
c
B
F
e
g
a
t
l
o
v
e
h
t
e
z
il
i
b
a
t
s
o
t
.
p
o
o
l
e
d
o
m
7
N
I
V
U
V
n
e
e
w
t
e
b
r
e
d
i
v
i
d
r
o
t
s
i
s
e
r
a
t
c
e
n
n
o
C
.
e
g
a
t
l
o
v
n
i
V
r
o
f
t
u
p
n
i
O
L
V
U
N
I
d
n
a
V
U
N
I
e
g
a
t
l
o
v
g
n
i
t
a
r
e
p
o
m
u
m
i
n
i
m
t
e
s
o
t
9
S
S
e
h
t
t
e
s
o
t
D
N
G
d
n
a
S
S
n
e
e
w
t
e
b
r
o
t
i
c
a
p
a
c
l
a
n
r
e
t
x
e
n
a
t
c
e
n
n
o
C
.
t
r
a
t
S
t
f
o
S
w
o
l
d
l
e
h
s
i
n
i
p
S
S
e
h
T
.
t
n
e
r
r
u
c
e
c
r
u
o
s
A
µ
0
1
e
h
t
n
o
d
e
s
a
b
e
t
a
r
t
r
a
t
s
t
f
o
s
.
s
n
o
i
t
i
d
n
o
c
t
l
u
a
f
ll
a
g
n
i
r
u
d
t
n
e
r
r
u
c
)
n
i
m
(
A
m
1
a
a
i
v
3
1
-
0
1
V
N
I
g
n
il
p
u
o
c
e
d
a
e
c
a
l
P
.
T
E
F
S
O
M
l
e
n
n
a
h
c
-
N
e
d
i
s
h
g
i
h
e
h
t
o
t
n
o
i
t
c
e
n
n
o
c
t
u
p
n
I
.
D
N
G
P
d
n
a
n
i
p
s
i
h
t
n
e
e
w
t
e
b
r
o
t
i
c
a
p
a
c
6
2
-
3
2
,
6
1
-
4
1
X
L
V
d
n
a
n
i
p
s
i
h
t
n
e
e
w
t
e
b
r
o
t
c
u
d
n
i
n
a
t
c
e
n
n
o
C
T
U
O
2
2
V
C
C
y
l
p
p
u
s
s
a
i
b
V
5
l
a
n
r
e
t
x
e
r
o
f
t
u
p
n
I
7
1
C
N
t
c
e
n
n
o
C
o
N

5
Date: 08/24/04
SP7650 Wide Input Voltage Range 3A, 300kHz, Buck Regulator © Copyright 2004 Sipex Corporation
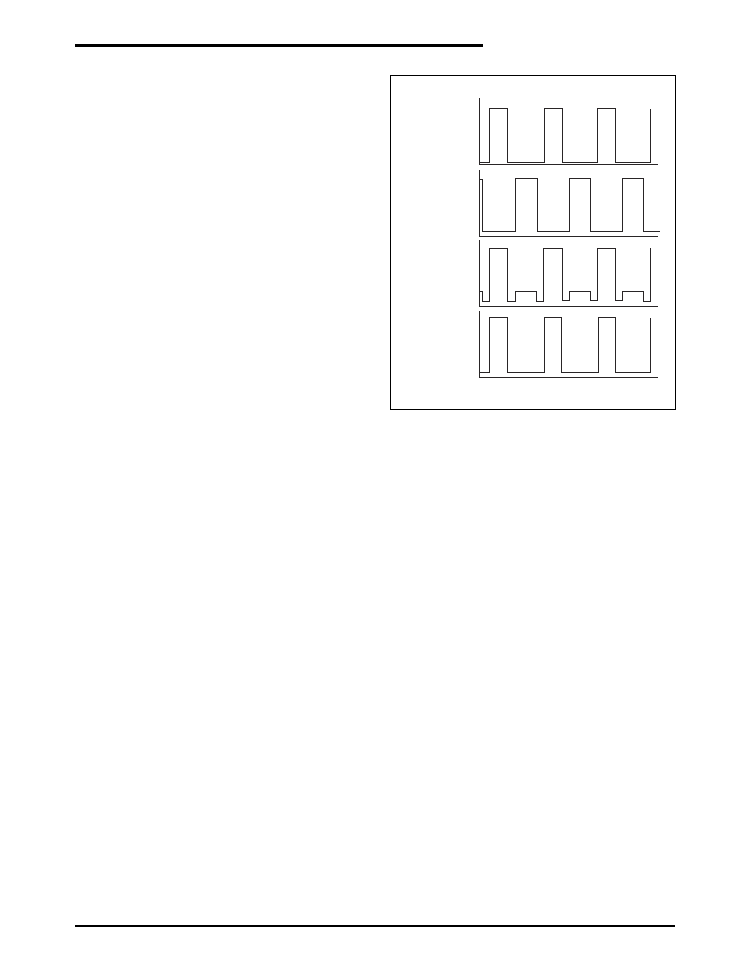
tures include thermal shutdown and short-cir-
cuit detection. In the event that either a thermal,
short-circuit, or UVLO fault is detected, the
SP7650 is forced into an idle state where the
output drivers are held off for a finite period
before a restart is attempted.
Soft Start
"Soft Start" is achieved when a power converter
ramps up the output voltage while controlling
the magnitude of the input supply source cur-
rent. In a modern step down converter, ramping
up the positive terminal of the error amplifier
controls soft start. As a result, excess source
current can be defined as the current required to
charge the output capacitor.
I
VIN
= C
OUT
* (DV
OUT
/ DT
SOFT-START
)
The SP7650 provides the user with the option to
program the soft start rate by tying a capacitor
from the SS pin to GND. The selection of this
capacitor is based on the 10uA pull up current
present at the SS pin and the 0.8V reference
voltage. Therefore, the excess source can be
redefined as:
IV
IN
= C
OUT
* (DV
OUT
*10
µA / (C
SS
* 0.8V)
Under Voltage Lock Out (UVLO)
The SP7650 contains two separate UVLO com-
parators to monitor the bias (V
CC
) and conver-
sion (V
IN
) voltages independently. The V
CC
UVLO threshold is internally set to 4.25V,
whereas the V
IN
UVLO threshold is program-
mable through the UVIN pin. When the UVIN
pin is greater than 2.5V, the SP7650 is permitted
to start up pending the removal of all other
faults. Both the V
CC
and V
IN
UVLO compara-
tors have been designed with hysteresis to pre-
vent noise from resetting a fault.
Thermal and Short-Circuit
Protection
Because the SP7650 is designed to drive large
output current, there is a chance that the power
converter will become too hot. Therefore, an
internal thermal shutdown (145
°C) has been
included to prevent the IC from malfunctioning
at extreme temperatures.
A short-circuit detection comparator has also
been included in the SP7650 to protect against
an accidental short at the output of the power
converter. This comparator constantly monitors
the positive and negative terminals of the error
amplifier, and if the V
FB
pin falls more than
250mV (typical) below the positive reference, a
short-circuit fault is set. Because the SS pin
overrides the internal 0.8V reference during soft
start, the SP7650 is capable of detecting short-
circuit faults throughout the duration of soft
start as well as in regular operation.
Handling of Faults:
Upon the detection of power (UVLO), thermal,
or short-circuit faults, the SP7650 is forced into
an idle state where the SS and COMP pins are
pulled low and both switches are held off. In the
event of UVLO fault, the SP7650 remains in this
idle state until the UVLO fault is removed.
Upon the detection of a thermal or short-circuit
fault, an internal 200ms timer is activated. In the
event of a short-circuit fault, a re-start is at-
tempted immediately after the 200ms timeout
expires. Whereas, when a thermal fault is de-
tected the 200ms delay continuously recycles
and a re-start cannot be attempted until the
thermal fault is removed and the timer expires.
Error Amplifier and Voltage Loop
Since the heart of the SP7650 voltage error loop
is a high performance, wide bandwidth
transconductance amplifier. Because of the
amplifier's current limited (+/-150
µA)
transconductance, there are many ways to com-
pensate the voltage loop or to control the COMP
pin externally. If a simple, single pole, single
THEORY OF OPERATION
6
Date: 08/24/04
SP7650 Wide Input Voltage Range 3A, 300kHz, Buck Regulator © Copyright 2004 Sipex Corporation
THEORY OF OPERATION
zero response is desired, then compensation can
be as simple as an RC to ground. If a more
complex compensation is required, then the
amplifier has enough bandwidth (45
° at 4 MHz)
and enough gain (60dB) to run Type III compen-
sation schemes with adequate gain and phase
margins at cross over frequencies greater than
50kHz.
The common mode output of the error amplifier
is 0.9V to 2.2V. Therefore, the PWM voltage
ramp has been set between 1.1V and 2.2V to
ensure proper 0% to 100% duty cycle capability.
The voltage loop also includes two other very
important features. One is an asynchronous start
up mode. Basically, the synchronous rectifier
can not turn on unless the high side switch has
attempted to turn on or the SS pin has exceeded
1.7V. This feature prevents the controller from
"dragging down" the output voltage during
startup or in fault modes. The second feature is
a 100% duty cycle timeout that ensures synchro-
nized refreshing of the BST capacitor at very
high duty ratios. In the event that the high side
NFET is on for 20 continuous clock cycles, a
reset is given to the PWM flip flop half way
through the 21st cycle. This forces GL to rise for
the cycle, in turn refreshing the BST capacitor.
The boost capacitor is used to generate a high
voltage drive supply for the high side switch,
which is 5V above V
IN
.
Power MOSFETs
The SP7650 contains a pair of integrated low
resistance N-channel switches designed to drive
up to 3A of output current. Care should be taken
to de-rate the output current based on the ther-
mal conditions in the system such as ambient
temperature, airflow and heat sinking. Maxi-
mum output current could be limited by thermal
limitations of a particular application by taking
advantage of the integrated over temperature
protective scheme employed in the SP7650.
The SP7650 incorporates a built-in over-tem-
perature protection to prevent internal overheat-
ing.
GH
Voltage
GL
Voltage
V(VIN)
0V
-0V
-V(Diode) V
V(VIN)+V(VCC)
BST
Voltage
V(VCC)
TIME
SWN
Voltage
VBST
VSWN
V(VCC)
The SP7650 can be set to different output
voltages. The relationship in the following
formula is based on a voltage divider from the
output to the feedback pin VFB, which is set
to an internal reference voltage of 0.80V.
Standard 1% metal film resistors of surface
mount size 0603 are recommended.
Vout = 0.80V ( R1 / R2 + 1 ) => R2 = R1 / [ (
Vout / 0.80V ) 1 ]
Where R1 = 68.1K
and for Vout = 0.80V
setting, simply remove R2 from the board.
Furthermore, one could select the value of R1
and R2 combination to meet the exact output
voltage setting by restricting R1 resistance
range such that 50K
< R1 < 100K for
overall system loop stability.
Setting Output Voltages

7
Date: 08/24/04
SP7650 Wide Input Voltage Range 3A, 300kHz, Buck Regulator © Copyright 2004 Sipex Corporation
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
Inductor Selection
There are many factors to consider in selecting
the inductor including core material, inductance
vs. frequency, current handling capability, effi-
ciency, size and EMI. In a typical SP7650 cir-
cuit, the inductor is chosen primarily for value,
saturation current and DC resistance. Increasing
the inductor value will decrease output voltage
ripple, but degrade transient response. Low in-
ductor values provide the smallest size, but
cause large ripple currents, poor efficiency and
more output capacitance to smooth out the larger
ripple current. The inductor must be able to
handle the peak current at the switching fre-
quency without saturating, and the copper resis-
tance in the winding should be kept as low as
possible to minimize resistive power loss. A
good compromise between size, loss and cost is
to set the inductor ripple current to be within
20% to 40% of the maximum output current.
The switching frequency and the inductor oper-
ating point determine the inductor value as fol-
lows:
( max)
(max )
(max)
)
(
OUT
r
S
IN
OUT
IN
OUT
I
K
F
V
V
V
V
L
-
=
where:
f
S
= switching frequency
Kr = ratio of the AC inductor ripple current to
the maximum output current
The peak to peak inductor ripple current is:
L
F
V
V
V
V
I
S
I N
OUT
IN
OUT
PP
(max)
(max)
)
(
-
=
Once the required inductor value is selected, the
proper selection of core material is based on
peak inductor current and efficiency require-
ments. The core must be large enough not to
saturate at the peak inductor current
2
(max)
P P
OUT
PEAK
I
I
I
+
=
and provide low core loss at the high switching
frequency. Low cost powdered iron cores have
a gradual saturation characteristic but can intro-
duce considerable AC core loss, especially when
the inductor value is relatively low and the
ripple current is high. Ferrite materials, although
more expensive, and have an abrupt saturation
characteristic with the inductance dropping
sharply when the peak design current is ex-
ceeded. Nevertheless, they are preferred at high
switching frequencies because they present very
low core loss while the designer is only required
to prevent saturation. In general, ferrite or
molypermalloy materials are a better choice for
all but the most cost sensitive applications.
Optimizing Efficiency
The power dissipated in the inductor is equal to
the sum of the core and copper losses. To mini-
mize copper losses, the winding resistance needs
to be minimized, but this usually comes at the
expense of a larger inductor. Core losses have a
more significant contribution at low output cur-
rent where the copper losses are at a minimum,
and can typically be neglected at higher output
currents where the copper losses dominate. Core
loss information is usually available from the
magnetic vendor. Proper inductor selection can
affect the resulting power supply efficiency by
more than 15%!
The copper loss in the inductor can be calculated
using the following equation:
WINDING
RMS
L
Cu
L
R
I
P
2
)
(
)
(
=
where I
L(RMS)
is the RMS inductor current that
can be calculated as follows:
I
L(RMS)
= I
OUT(max)
1 + 1
(
I
PP
)
2
3 I
OUT(max)

8
Date: 08/24/04
SP7650 Wide Input Voltage Range 3A, 300kHz, Buck Regulator © Copyright 2004 Sipex Corporation
Output Capacitor Selection
The required ESR (Equivalent Series Resis-
tance) and capacitance drive the selection of the
type and quantity of the output capacitors. The
ESR must be small enough that both the resis-
tive voltage deviation due to a step change in the
load current and the output ripple voltage do not
exceed the tolerance limits expected on the
output voltage. During an output load transient,
the output capacitor must supply all the addi-
tional current demanded by the load until the
SP7650 adjusts the inductor current to the new
value.
In order to maintain V
OUT
,the capacitance must
be large enough so that the output voltage is
helped up while the inductor current ramps to
the value corresponding to the new load current.
Additionally, the ESR in the output capacitor
causes a step in the output voltage equal to the
current. Because of the fast transient response
and inherent 100%/0% duty cycle capability
provided by the SP7650 when exposed to output
load transient, the output capacitor is typically
chosen for ESR, not for capacitance value.
The output capacitor's ESR, combined with the
inductor ripple current, is typically the main
contributor to output voltage ripple. The maxi-
mum allowable ESR required to maintain a
specified output voltage ripple can be calculated
by:
R
ESR
V
OUT
I
PK-PK
where:
V
OUT
= Peak to Peak Output Voltage Ripple
I
PK-PK
= Peak to Peak Inductor Ripple Current
The total output ripple is a combination of the
ESR and the output capacitance value and can
be calculated as follows:
V
OUT
=
(
I
PP
(1 D)
)
2
+ (I
PP
R
ESR
)
2
C
OUT
F
S
F
S
= Switching Frequency
D = Duty Cycle
C
OUT
= Output Capacitance Value
Input Capacitor Selection
The input capacitor should be selected for ripple
current rating, capacitance and voltage rating.
The input capacitor must meet the ripple current
requirement imposed by the switching current.
In continuous conduction mode, the source cur-
rent of the high-side MOSFET is approximately
a square wave of duty cycle V
OUT
/V
IN
. More
accurately the current wave form is trapezoidal,
given a finite turn-on and turn-off, switch tran-
sition slope. Most of this current is supplied by
the input bypass capacitors. The RMS current
handling capability of the input capacitors is
determined at maximum output current and
under the assumption that the peak
to peak inductor ripple current is low, it is given
by:
I
CIN(RMS)
= I
OUT(max)
D(1 - D)
The worse case occurs when the duty cycle D is
50% and gives an RMS current value equal to
I
OUT
/2.
Select input capacitors with adequate ripple
current rating to ensure reliable operation.
The power dissipated in the input capacitor is:
)
(
2
)
(
CIN
ESR
rms
CIN
CIN
R
I
P
=
This can become a significant part of power
losses in a converter and hurt the overall energy
transfer efficiency. The input voltage ripple
primarily depends on the input capacitor ESR
and capacitance. Ignoring the inductor ripple
current, the input voltage ripple can be deter-
mined by:
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
9
Date: 08/24/04
SP7650 Wide Input Voltage Range 3A, 300kHz, Buck Regulator © Copyright 2004 Sipex Corporation
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
2
)
(
)
(
(max)
)
(
IN
IN
S
OUT
I N
OUT
MAX
OUT
CIN
E SR
out
IN
V
C
F
V
V
V
I
R
I
V
-
+
=
The capacitor type suitable for the output capac-
itors can also be used for the input capacitors.
However, exercise extra caution when tantalum
capacitors are used. Tantalum capacitors are known
for catastrophic failure when exposed to surge
current, and input capacitors are prone to such
surge current when power supplies are connected
"live" to low impedance power sources. Although
tantalum capacitors have been successfully em-
ployed at the input, it is generally not recom-
mended.
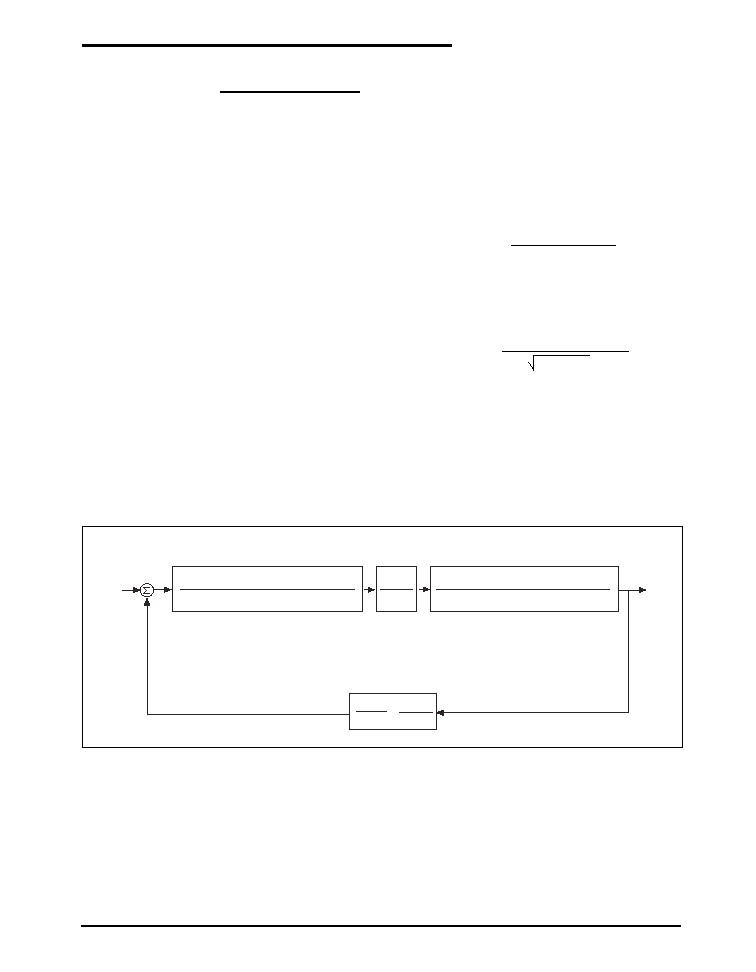
Loop Compensation Design
The open loop gain of the whole system can be
divided into the gain of the error amplifier,
PWM modulator, buck converter output stage,
and feedback resistor divider. In order to cross
over at the desired frequency cut-off (FCO), the
gain of the error amplifier has to compensate for
the attenuation caused by the rest of the loop at
this frequency. The goal of loop compensation
is to manipulate loop frequency response such
that its cross-over gain at 0db, results in a slope
of -20db/dec.
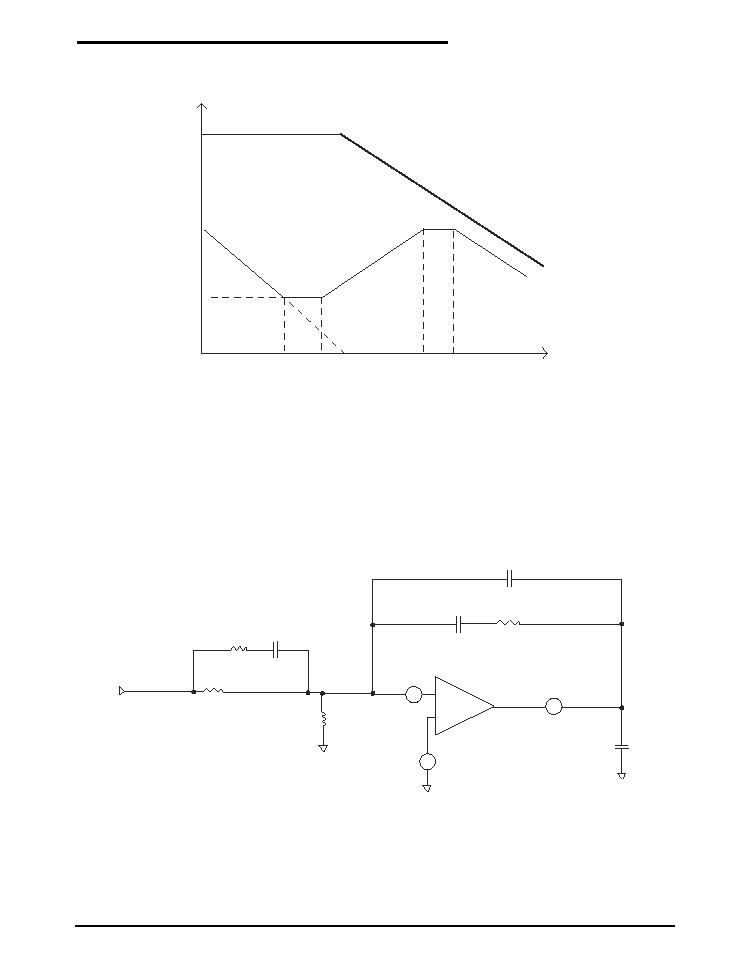
The first step of compensation design is to pick
the loop cross over frequency. High cross over
frequency is desirable for fast transient response,
but often jeopardizes the power supply stability.
Cross over frequency should be higher than the
ESR zero but less than 1/5 of the switching
frequency or 60kHz. The ESR zero is contrib-
uted by the ESR associated with the output
capacitors and can be determined by:
Z(ESR)
=
1
2
C
OUT
R
ESR
The next step is to calculate the complex conju-
gate poles contributed by the LC output filter,
P(LC)
=
1
2
L C
OUT
When the output capacitors are of a Ceramic
Type, the SP7650 Evaluation Board requires a
Type III compensation circuit to give a phase
boost of 180
° in order to counteract the effects of
an under damped resonance of the output filter
at the double pole frequency.
SP7650 Voltage Mode Control Loop with Loop Dynamic
(SRz2Cz2+1)(SR1Cz3+1)
(SR
ESR
C
OUT
+ 1)
[S^2LC
OUT
+S(R
ESR
+R
DC
) C
OUT
+1]
V
IN
SR1Cz2(SRz3Cz3+1)(SRz2Cp1+1)
V
RAMP_PP
V
OUT
(Volts)
+
_
V
REF
(Volts)
Notes: R
ESR
= Output Capacitor Equivalent Series Resistance.
R
DC
= Output Inductor DC Resistance.
V
RAMP_PP
= SP6132 Internal RAMP Amplitude Peak to Peak Voltage.
Condition: Cz2 >> Cp1 & R1 >> Rz3
Output Load Resistance >> R
ESR
& R
DC
R
2
V
REF
(R
1
+ R
2
)
or
V
OUT
V
FBK
(Volts)
Type III Voltage Loop
Compensation
G
AMP
(s) Gain Block
PWM Stage
G
PWM
Gain
Block
Output Stage
G
OUT
(s) Gain
Block
Voltage Feedback
G
FBK
Gain Block
Definitions:
R
ESR
= Output Capacitor Equivalent Series Resistance
R
DC
= Output Inductor DC Resistance
R
RAMP_PP
= SP7650 internal RAMP Amplitude Peak to Peak Voltage
Conditions:
C
Z
2 >> Cp1 and R1 >> Rz3
Output Load Resistance >>
R
ESR
and
R
DC
10
Date: 08/24/04
SP7650 Wide Input Voltage Range 3A, 300kHz, Buck Regulator © Copyright 2004 Sipex Corporation
Bode Plot of Type III Error Amplifier Compensation.
CP1
RZ2
CZ2
-
+
6
5
VFB
COMP
+
- 0.8V
CF1
VOUT
R1
68.1k, 1%
R
SET
CZ3
RZ3
R
SET
=54.48/ (VOUT -0.8) (k)
Type III Error Amplifier Compensation Circuit
APPLICATIONS INFORMATION
Frequency
(Hz)
Error Amplifier Gain
Bandwidth Product
Condition:
C22 >> CP1, R1 >> RZ3
20 Log (RZ2/R1)
Gain
(dB)
1/6.28(R22) (CZ2)
1/6.28 (R1) (CZ3)
1/6.28 (R1) (CZ2)
1/6.28 (RZ2) (CP1)
1/6.28 (RZ3) (CZ3)
11
Date: 08/24/04
SP7650 Wide Input Voltage Range 3A, 300kHz, Buck Regulator © Copyright 2004 Sipex Corporation
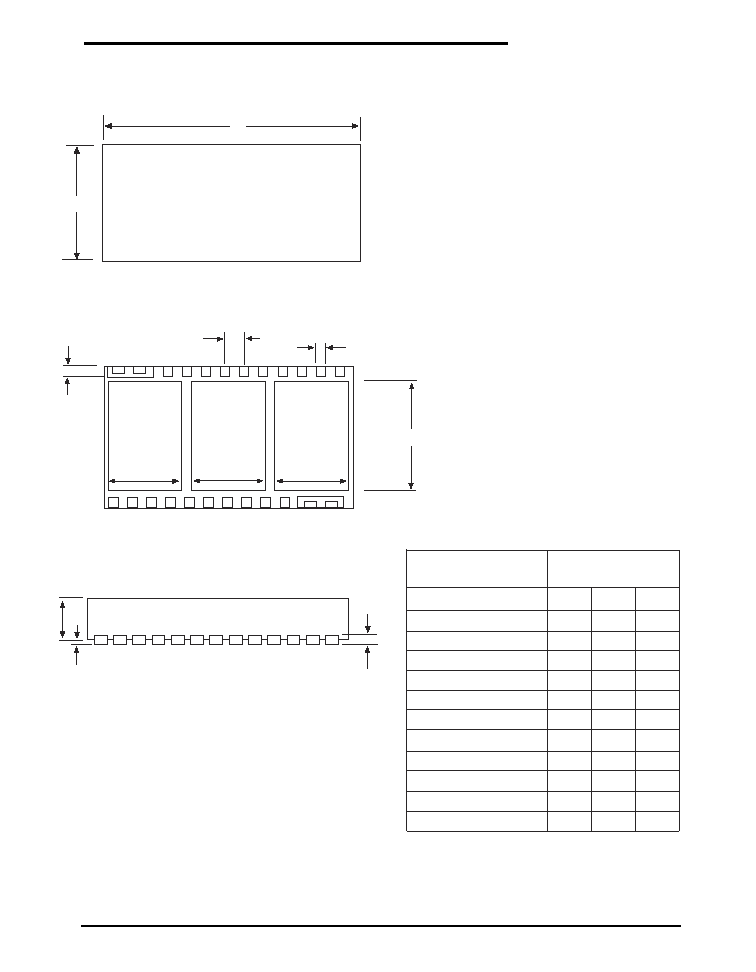
PACKAGE: 26 PIN DFN
26 Pin DFN
DIMENSIONS in
(mm)
26 Pin DFN
A
A1
A3
b
D
E2
E
e
D2
L
0.800 0.850 0.900
2.00
2.730 2.780 2.830
0.350
0.450
0.17
0.22
0.27
SYMBOL
MIN NOM MAX
0.050
3.95
4.05
6.95
7.05
7.00
2.05
2.10
0.178 0.203 0.228
0.400
1.78 1.83 1.88
D3
4.00
0.45 0.50 0.55
0.000
Side View
Top View
b
A3
A
A1
D
E
(7 x 4 mm)
e
L
E2
Bottom View
D2
D3
D2
-

12
Date: 08/24/04
SP7650 Wide Input Voltage Range 3A, 300kHz, Buck Regulator © Copyright 2004 Sipex Corporation
Corporation
ANALOG EXCELLENCE
Sipex Corporation reserves the right to make changes to any products described herein. Sipex does not assume any liability arising out of the
application or use of any product or circuit described herein; neither does it convey any license under its patent rights nor the rights of others.
Sipex Corporation
Headquarters and
Sales Office
233 South Hillview Drive
Milpitas, CA 95035
TEL: (408) 934-7500
FAX: (408) 935-7600
ORDERING INFORMATION
Part Number
Temperature
Package
SP7650ER/TR ......................................... -40°C to +85°C ................................. 26 Pin 7 X 4 DFN
SP7650ER-L/TR ..................................... -40°C to +85°C ............. (Lead Free) 26 Pin 7 X 4 DFN
/TR = Tape and Reel
Pack quantity is 3000 DFN.











