
1/16
September 2005
STF2NK60Z - STQ2NK60ZR-AP
STP2NK60Z - STD2NK60Z-1
N-CHANNEL 600V - 7.2
- 1.4A TO-220/TO-220FP/TO-92/IPAK
Zener-Protected SuperMESHTM MOSFET
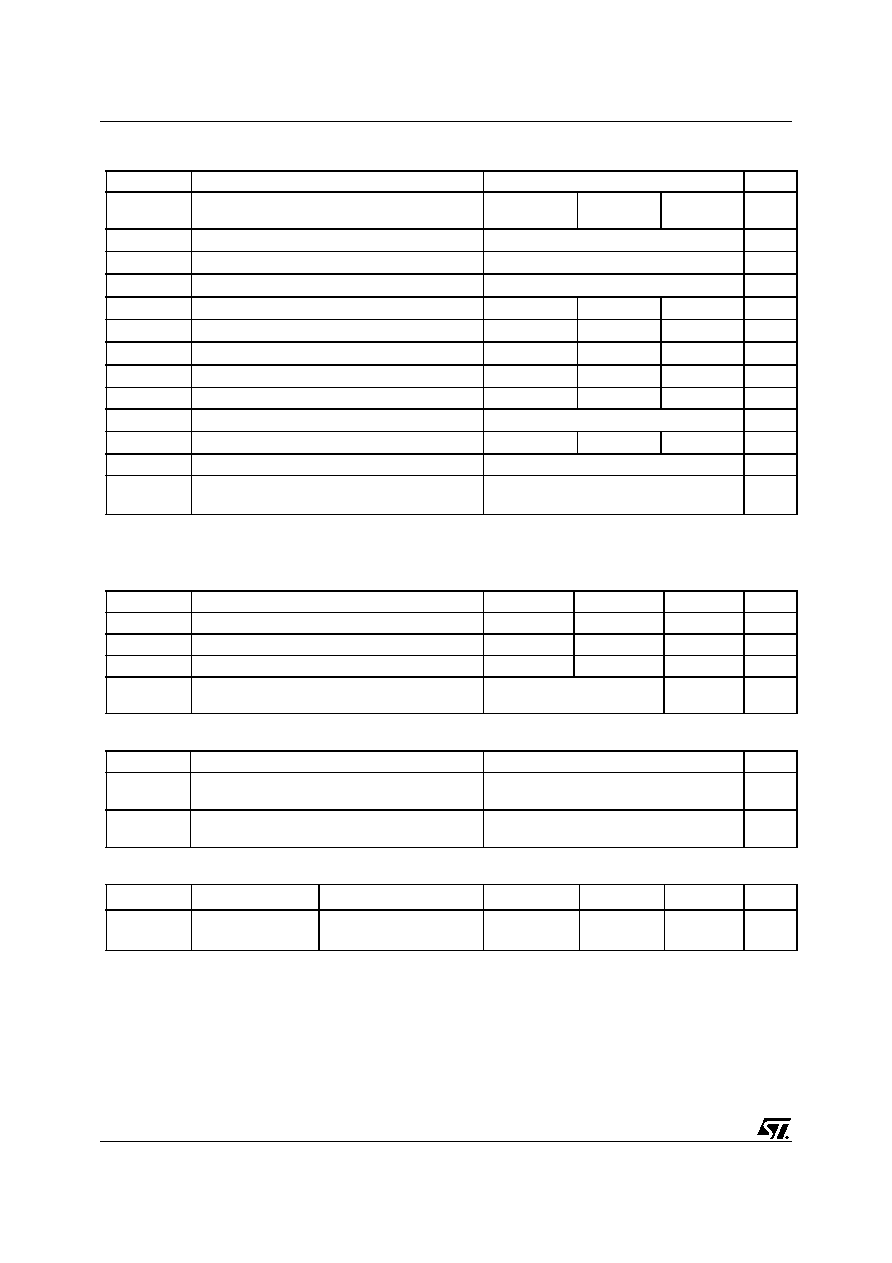
Table 1: General Features
s
TYPICAL R
DS
(on) = 7.2
s
EXTREMELY HIGH dv/dt CAPABILITY
s
ESD IMPROVED CAPABILITY
s
100% AVALANCHE TESTED
s
NEW HIGH VOLTAGE BENCHMARK
s
GATE CHARGE MINIMIZED
DESCRIPTION
The SuperMESHTM series is obtained through an
extreme optimization of ST's well established
strip-based PowerMESHTM layout. In addition to
pushing on-resistance significantly down, special
care is taken to ensure a very good dv/dt capability
for the most demanding applications. Such series
complements ST full range of high voltage MOS-
FETs including revolutionary MDmeshTM products.
APPLICATIONS
s
LOW POWER BATTERY CHARGERS
s
SWITH MODE LOW POWER
SUPPLIES(SMPS)
s
LOW POWER, BALLAST, CFL (COMPACT
FLUORESCENT LAMPS)
Table 2: Order Codes
Figure 1: Package
Figure 2: Internal Schematic Diagram
TYPE
V
DSS
R
DS(on)
I
D
Pw
STF2NK60Z
STQ2NK60ZR-AP
STP2NK60Z
STD2NK60Z-1
600 V
600 V
600 V
600 V
< 8
< 8
< 8
< 8
1.4 A
0.4 A
1.4 A
1.4 A
20
3 W
45 W
45 W
1
2
3
3
2
1
TO-92 (Ammopack)
TO-220
IPAK
1
2
3
TO-220FP
Part Number
Marking
Package
Packaging
STQ2NK60ZR-AP
Q2NK60ZR
TO-92
AMMOPAK
STP2NK60Z
P2NK60Z
TO-220
TUBE
STD2NK60Z-1
D2NK60Z
IPAK
TUBE
STF2NK60Z
F2NK60Z
TO-220FP
TUBE
Rev. 5
STQ2NK60ZR-AP - STP2NK60Z - STF2NK60Z - STD2NK60Z-1
2/16
Table 3: Absolute Maximum ratings
( ) Pulse width limited by safe operating area
(1) I
SD
1.4A, di/dt
200A/µs, V
DD
V
(BR)DSS
, T
j
T
JMAX.
(*) Limited only by maximum temperature allowed
Table 4: Thermal Data
Table 5: Avalanche Characteristics
Table 6: Gate-Source Zener Diode
PROTECTION FEATURES OF GATE-TO-SOURCE ZENER DIODES
The built-in back-to-back Zener diodes have specifically been designed to enhance not only the device's
ESD capability, but also to make them safely absorb possible voltage transients that may occasionally be
applied from gate to source. In this respect the Zener voltage is appropriate to achieve an efficient and
cost-effective intervention to protect the device's integrity. These integrated Zener diodes thus avoid the
usage of external components.
Symbol
Parameter
Value
Unit
TO-220 /
IPAK
TO-92
TO-220FP
V
DS
Drain-source Voltage (V
GS
= 0)
600
V
V
DGR
Drain-gate Voltage (R
GS
= 20 k
)
600
V
V
GS
Gate- source Voltage
± 30
V
I
D
Drain Current (continuous) at T
C
= 25∞C
1.4
0.4
1.4 (*)
A
I
D
Drain Current (continuous) at T
C
= 100∞C
0.77
0.25
0.77 (*)
A
I
DM
( )
Drain Current (pulsed)
5.6
1.6
5.6 (*)
A
P
TOT
Total Dissipation at T
C
= 25∞C
45
3
20
W
Derating Factor
0.36
0.025
0.16
W/∞C
V
ESD(G-S)
Gate source ESD (HBM-C= 100pF, R=1.5k
)
1500
V
V
ISO
Insulation Withstand Voltage (DC)
2500
V
dv/dt (1)
Peak Diode Recovery voltage slope
4.5
V/ns
T
j
T
stg
Operating Junction Temperature
Storage Temperature
-55 to 150
∞C
TO-220/IPAK
TO-220FP
TO-92
Unit
Rthj-case
Thermal Resistance Junction-case Max
2.77
6.25
--
∞C/W
Rthj-amb
Thermal Resistance Junction-ambient Max
100
100
120
∞C/W
Rthj-lead
Thermal Resistance Junction-lead Max
--
--
40
∞C/W
T
l
Maximum Lead Temperature For Soldering
Purpose
300
260
∞C
Symbol
Parameter
Max Value
Unit
I
AR
Avalanche Current, Repetitive or Not-Repetitive
(pulse width limited by T
j
max)
1.4
A
E
AS
Single Pulse Avalanche Energy
(starting T
j
= 25 ∞C, I
D
= I
AR
, V
DD
= 50 V)
90
mJ
Symbol
Parameter
Test Conditions
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
BV
GSO
Gate source
Breakdown Voltage
I
gs
= ± 1 mA
(Open Drain)
30
V

3/16
STQ2NK60ZR-AP - STP2NK60Z - STF2NK60Z - STD2NK60Z-1
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (T
CASE
=25∞C UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED)
Table 7: On/Off
Table 8: Dynamic
Table 9: Source Drain Diode
(1) Pulsed: Pulse duration = 300 µs, duty cycle 1.5 %.
(2) Pulse width limited by safe operating area.
(3) C
oss eq.
is defined as a constant equivalent capacitance giving the same charging time as Coss when VDS increases from 0 to 80% VDSS
Symbol
Parameter
Test Conditions
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
V
(BR)DSS
Drain-source
Breakdown Voltage
I
D
= 1mA, V
GS
= 0
600
V
I
DSS
Zero Gate Voltage
Drain Current (V
GS
= 0)
V
DS
= Max Rating
V
DS
= Max Rating, T
C
= 125 ∞C
1
50
µA
µA
I
GSS
Gate-body Leakage
Current (V
DS
= 0)
V
GS
= ± 20V
±10
µA
V
GS(th)
Gate Threshold Voltage
V
DS
= V
GS
, I
D
= 50 µA
3
3.75
4.5
V
R
DS(on)
Static Drain-source On
Resistance
V
GS
= 10V, I
D
= 0.7 A
7.2
8
Symbol
Parameter
Test Conditions
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
g
fs
(1)
Forward Transconductance
V
DS
= 15 V
,
I
D
= 0.7 A
1
S
C
iss
C
oss
C
rss
Input Capacitance
Output Capacitance
Reverse Transfer Capacitance
V
DS
= 25V, f = 1 MHz, V
GS
= 0
170
27
5
pF
pF
pF
C
oss eq.
(3)
Equivalent Output Capacitance V
GS
= 0V, V
DS
= 0V to 480V
30
pF
t
d(on)
t
r
t
d(off)
t
r
Turn-on Delay Time
Rise Time
Turn-off Delay Time
Fall Time
V
DD
= 300 V, I
D
= 0.65 A,
R
G
= 4.7
,
V
GS
= 10 V
(Resistive Load see, Figure
22)
8
30
22
55
ns
ns
ns
ns
Q
g
Q
gs
Q
gd
Total Gate Charge
Gate-Source Charge
Gate-Drain Charge
V
DD
= 480V, I
D
= 1.5 A,
V
GS
= 10V
(see, Figure 24)
7.7
1.7
4
10
nC
nC
nC
Symbol
Parameter
Test Conditions
Min.
Typ.
Max.
Unit
I
SD
I
SDM
(2)
Source-drain Current
Source-drain Current (pulsed)
1.5
6
A
A
V
SD
(1)
Forward On Voltage
I
SD
= 1.5 A, V
GS
= 0
1.6
V
t
rr
Q
rr
I
RRM
Reverse Recovery Time
Reverse Recovery Charge
Reverse Recovery Current
I
SD
= 1.3 A, di/dt = 100 A/µs
V
DD
= 25V, T
j
= 25∞C
(see test circuit, Figure 23)
250
550
4.4
ns
µC
A
t
rr
Q
rr
I
RRM
Reverse Recovery Time
Reverse Recovery Charge
Reverse Recovery Current
I
SD
= 1.3 A, di/dt = 100 A/µs
V
DD
= 25V, T
j
= 150∞C
(see test circuit, Figure 23)
300
690
4.6
ns
µC
A

STQ2NK60ZR-AP - STP2NK60Z - STF2NK60Z - STD2NK60Z-1
4/16
Figure 3:
.
Safe Operating Area For TO-220
Figure 4: Safe Operating Area For IPAK
Figure 5: Safe Operating Area For TO-92
Figure 6: Thermal Impedance For TO-220
Figure 7: Thermal Impedance For IPAK
Figure 8: Thermal Impedance For TO-92

5/16
STQ2NK60ZR-AP - STP2NK60Z - STF2NK60Z - STD2NK60Z-1
Figure 9: Safe Operating Area For TO-220FP
Figure 10: Output Characteristics
Figure 11: Transconductance
Figure 12: Thermal Impedance For TO-220FP
Figure 13: Transfer Characteristics
Figure 14: Gate Charge vs Gate-source Voltage




