 | –≠–ª–µ–∫—Ç—Ä–æ–Ω–Ω—ã–π –∫–æ–º–ø–æ–Ω–µ–Ω—Ç: STPS130U | –°–∫–∞—á–∞—Ç—å:  PDF PDF  ZIP ZIP |

Æ
1/7
Table 1: Main Product Characteristics
I
F(AV)
1 A
V
RRM
30 V
T
j
(max)
150∞C
V
F
(max)
0.46 V
STPS130
POWER SCHOTTKY RECTIFIER
REV. 5
Table 3: Absolute Ratings (limiting values)
Symbol
Parameter
Value
Unit
V
RRM
Repetitive peak reverse voltage
30
V
I
F(RMS)
RMS forward voltage
7
A
I
F(AV)
Average forward current
T
L
= 130∞C
= 0.5
1
A
I
FSM
Surge non repetitive forward current
tp = 10ms sinusoidal
45
A
I
RRM
Repetitive peak reverse current
tp = 2µs F = 1kHz square
1
A
I
RSM
Non repetitive peak reverse current
tp = 100µs square
1
A
P
ARM
Repetitive peak avalanche power
tp = 1µs Tj = 25∞C
1200
W
T
stg
Storage temperature range
-65 to + 150
∞C
T
j
Maximum operating junction temperature *
150
∞C
dV/dt
Critical rate of rise of reverse voltage
10000
V/µs
* :
thermal runaway condition for a diode on its own heatsink
dPt ot
dTj
---------------
1
Rth j
a
≠
(
)
--------------------------
>
SMA
(JEDEC DO-214AC)
STPS130A
SMB
(JEDEC DO-214AA)
STPS130U
August 2004
FEATURES AND BENEFITS
Very low forward voltage drop for less power
dissipation
Optimized conduction/reverse losses trade-off
which means the highest yield in the
applications
Surface mount miniature packages
Avalanche capability specified
DESCRIPTION
Single Schottky rectifier suited to Switched Mode
Power Supplies and high frequency DC to DC
converters.
Packaged in SMA and SMB, this device is
especially intended for use in parallel with
MOSFETs in synchronous rectification and low
voltage secondary rectification.
Table 2: Order Codes
Part Number
Marking
STPS130A
S130
STPS130U
G12
STPS130
2/7
Table 4: Thermal Resistance
Table 5: Static Electrical Characteristics
Pulse test:
* tp = 380 µs,
< 2%
** tp = 5 ms,
< 2%
To evaluate the conduction losses use the following equation: P = 0.37 x I
F(AV)
+ 0.090 I
F
2
(RMS)
Symbol
Parameter
Value
Unit
R
th(j-l)
Junction to lead
SMA
30
∞C/W
SMB
23
Symbol
Parameter
Tests conditions
Min.
Typ
Max.
Unit
I
R
*
Reverse leakage current
T
j
= 25∞C
V
R
= V
RRM
10
µA
T
j
= 125∞C
1.5
10
mA
V
F
**
Forward voltage drop
T
j
= 25∞C
I
F
= 1A
0.55
V
T
j
= 125∞C
0.37
0.46
T
j
= 25∞C
I
F
= 2A
0.63
T
j
= 125∞C
0.45
0.55
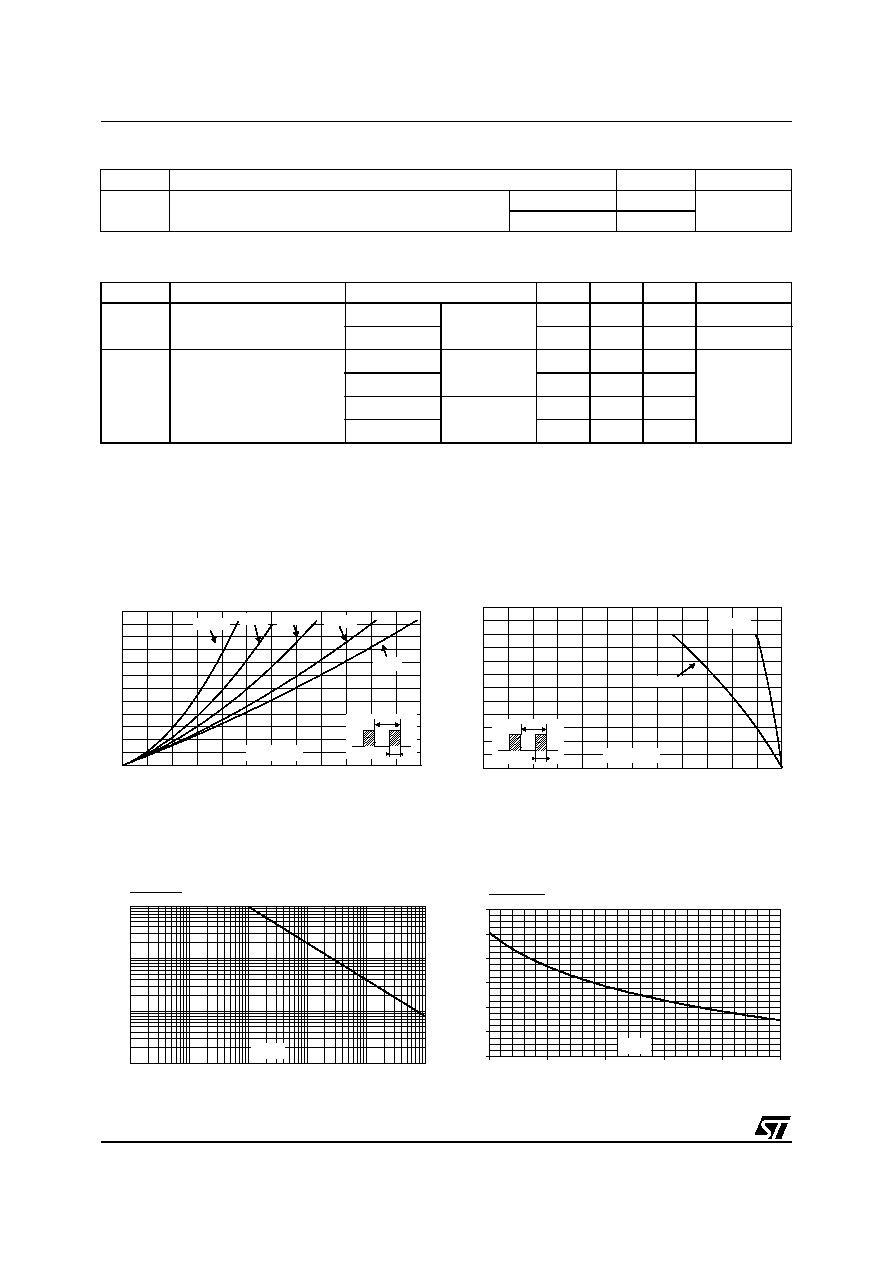
Figure 1: Average forward power dissipation
versus average forward current
Figure 2: Average forward current versus
ambient temperature (
= 0.5)
Figure 3: Normalized avalanche power
derating versus pulse duration
Figure 4: Normalized avalanche power
derating versus junction temperature
P
(W)
F(AV)
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
1.2
0.0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
T
=tp/T
tp
I
(A)
F(AV)
= 1
= 0.5
= 0.2
= 0.1
= 0.05
0
25
50
75
100
125
150
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
1.2
I
(A)
F(AV)
T
=tp/T
tp
R
=R
th(j-a)
th(j-I)
R
=100∞C/W
th(j-a)
T
(∞C)
amb
0.001
0.01
0.1
0.01
1
0.1
10
100
1000
1
t (µs)
p
P
(t )
P
(1µs)
ARM p
ARM
0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1
1.2
25
50
75
100
125
150
T (∞C)
j
P
(t )
P
(25∞C)
ARM p
ARM
STPS130
3/7
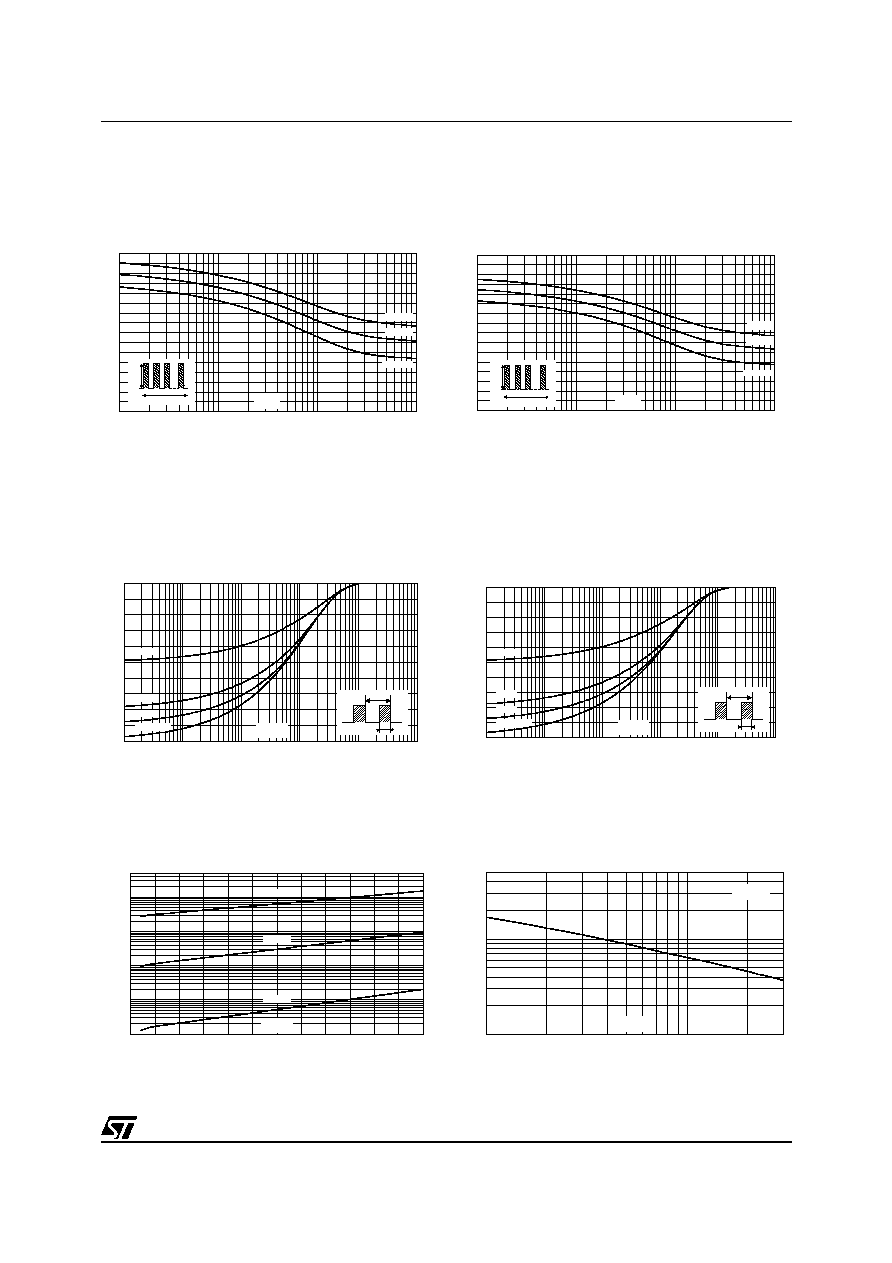
Figure 5: Non repetitive surge peak forward
current versus overload duration (maximum
values) (SMA)
Figure 6: Non repetitive surge peak forward
current versus overload duration (maximum
values) (SMB)
Figure 7: Relative variation of thermal
impedance junction to ambient versus pulse
duration (epoxy printed circuit board,
e(Cu)=35µm, recommended pad layout) (SMA)
Figure 8: Relative variation of thermal
impedance junction to ambient versus pulse
duration (epoxy printed circuit board,
e(Cu)=35µm, recommended pad layout) (SMB)
Figure 9: Reverse leakage current versus
reverse voltage applied (typical values)
Figure 10: Junction capacitance versus
reverse voltage applied (typical values)
I (A)
M
1.0E-3
1.0E-2
1.0E-1
1.0E+0
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
T =75∞C
a
T =50∞C
a
T =100∞C
a
I
M
t
=0.5
t(s)
1.0E-3
1.0E-2
1.0E-1
1.0E+0
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
I (A)
M
T =75∞C
a
T =50∞C
a
T =100∞C
a
I
M
t
=0.5
t(s)
1E-2
1E-1
1E+0
1E+1
1E+2
1E+3
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
Z
/R
th(j-c)
th(j-c)
T
=tp/T
tp
t (s)
p
= 0.5
= 0.2
= 0.1
Single pulse
1.0E-2
1.0E-1
1.0E+0
1.0E+1
1.0E+2
1.0E+3
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
Z
/R
th(j-c)
th(j-c)
T
=tp/T
tp
t (s)
p
= 0.5
= 0.2
= 0.1
Single pulse
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
1E-1
1E+0
1E+1
1E+2
1E+3
5E+3
I (µA)
R
V (V)
R
T =125∞C
j
T =70∞C
j
T =25∞C
j
1
2
5
10
20
30
10
20
50
100
200
500
C(pF)
V (V)
R
F=1MHz
T =25∞C
j

STPS130
4/7
Figure 11: Forward voltage drop versus
forward current (maximum values)
Figure 12: Thermal resistance junction to
ambient versus copper surface under each
lead (Epoxy printed circuit board FR4, copper
thickness: 35µm) (SMA)
Figure 13: Thermal resistance junction to
ambient versus copper surface under each
lead (Epoxy printed circuit board FR4, copper
thickness: 35µm) (SMB)
I
(A)
FM
0.0
0.2
0.4
0.6
0.8
1.0
1.2
0.01
0.10
1.00
10.00
V
(V)
FM
T =25∞C
j
T =75∞C
j
T =125∞C
j
0
1
2
3
4
5
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
S(Cu)(cm≤)
R
(∞C/W)
th(j-a)
P=1.5W
0
1
2
3
4
5
0
20
40
60
80
100
120
140
S(Cu)(cm≤)
R
(∞C/W)
th(j-a)
P=1.5W

STPS130
5/7
Figure 14: SMA Package Mechanical Data
Figure 15: SMA Foot Print Dimensions
(in millimeters)
E
C
L
E1
D
A1
A2
b
2.40
1.65
1.45
1.45
REF.
DIMENSIONS
Millimeters
Inches
Min.
Max.
Min.
Max.
A1
1.90
2.03
0.075
0.080
A2
0.05
0.20
0.002
0.008
b
1.25
1.65
0.049
0.065
c
0.15
0.41
0.006
0.016
E
4.80
5.60
0.189
0.220
E1
3.95
4.60
0.156
0.181
D
2.25
2.95
0.089
0.116
L
0.75
1.60
0.030
0.063




