Features
Æ Integrated SRAM, real-time
clock, CPU supervisor, crystal,
power-fail circuit, and battery
Æ Real-Time Clock counts hun-
dredths of seconds through years
in BCD format
Æ RAM-like clock access
Æ Compatible with industry-
standard 8K x 8 SRAMs
Æ Unlimited write cycles
Æ 10-year minimum data retention
and clock operation in the ab-
sence of power
Æ Automatic power-fail chip dese-
lect and write-protection
Æ Watchdog timer, power-on reset,
alarm/periodic interrupt, power-
fail and battery-low warning
Æ Automatic leap year adjustment
Æ Software clock calibration for
greater than
±
1 minute per
month accuracy
General Description
The bq4822Y RTC Module is a non-
volatile 65,536-bit SRAM organized
as 8192 words by 8 bits with an in-
tegral real-time clock and CPU su-
pervisor. The CPU supervisor pro-
vides a programmable watchdog
timer and a microprocessor reset.
Other features include an alarm,
power-fail and periodic interrupt,
and a battery low warning.
The device combines an internal
lithium battery, quartz crystal, clock
and power-fail chip, and a full
CMOS SRAM in a plastic 28-pin
DIP module.
The RTC Module di-
rectly replaces industry-standard
SRAMs and also fits into many
E P R O M a n d E E P R O M s o ck e t s
without any requirement for special
write timing or limitations on the
number of write cycles.
Registers for the real-time clock,
alarm and other special
func-
t i o n s a r e l o c a t e d i n r e g i s t e r s
1FF0h≠1FFFh of the memory array.
The clock and alarm registers are
dual-port read/write SRAM loca-
tions that are updated once per sec-
ond by a clock control circuit from
the internal clock counters.
The
dual-port registers allow clock up-
dates to occur without interrupting
normal access to the rest of the
SRAM array.
The bq4822Y also contains a power-
fail-detect circuit. The circuit dese-
lects the device whenever V
CC
falls
below tolerance, providing a high de-
gree of data security. The battery is
electrically isolated when shipped
from the factory to provide maxi-
mum battery capacity. The battery
remains disconnected until the first
application of V
CC
.
1
1
PN482201.eps
28-Pin DIP Module
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
9
10
20
19
11
12
18
17
13
14
16
15
VCC
WE
INT
A8
A9
A11
OE
A10
CE
DQ7
DQ6
DQ5
DQ4
DQ3
RST
A12
A7
A6
A5
A4
A3
A2
A1
A0
DQ0
DQ1
DQ2
VSS
May 1997
Pin Connections
bq4822Y
RTC Module With 8Kx8 NVSRAM
Pin Names
A
0
≠A
12
Address input
CE
Chip enable
RST
Microprocessor reset
WE
Write enable
OE
Output enable
DQ
0
≠DQ
7
Data in/data out
INT
Programmable interrupt
V
CC
+5 volts
V
SS
Ground
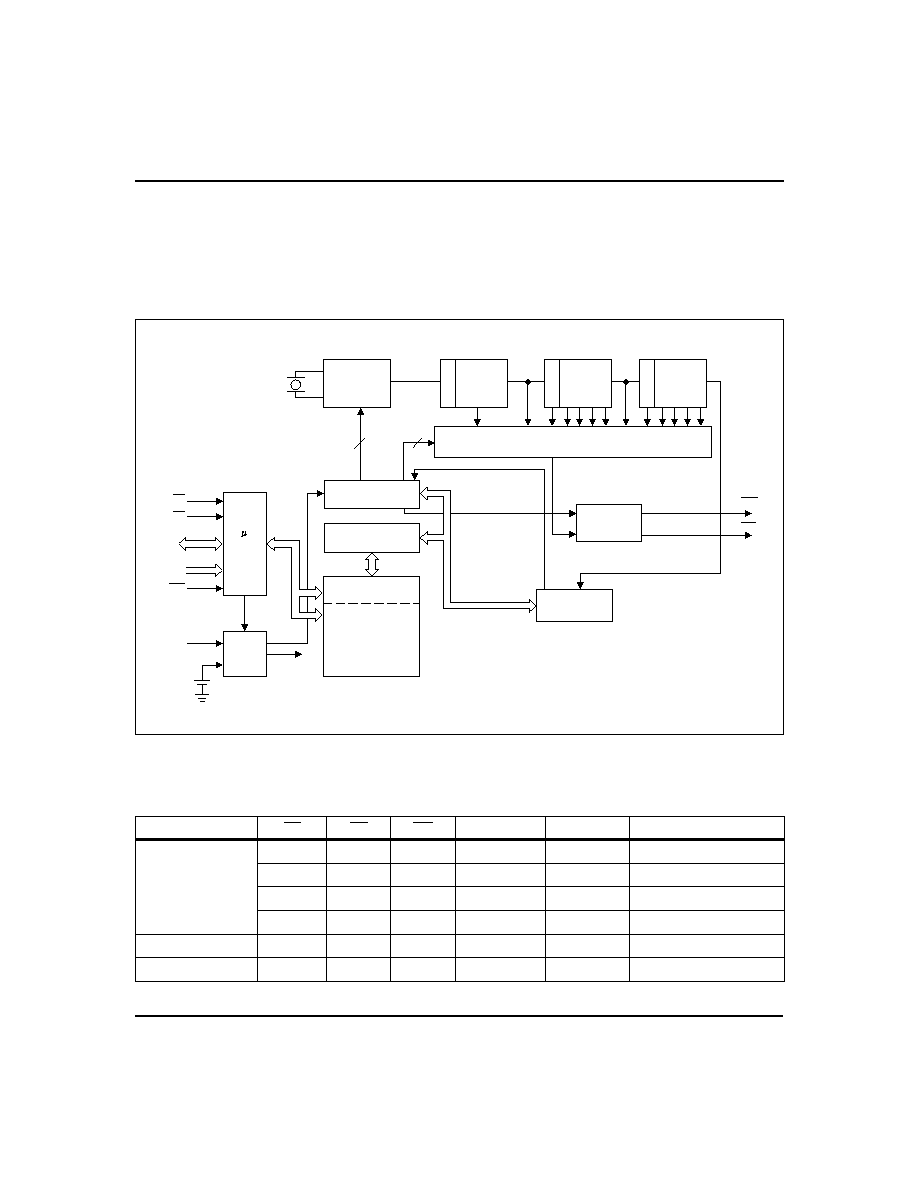
Functional Description
Figure 1 is a block diagram of the bq4822Y. The follow-
ing sections describe the bq4822Y functional operation,
including memory and clock interface, data-retention
modes, power-on reset timing, watchdog timer activa-
tion, and interrupt generation.
2
BD482201.eps
P
Bus
I/F
Power-
Fail
Control
Storage Registers
(8,176 Bytes)
Storage Registers
(16 Bytes)
Write
Protect
Clock/Calendar, Alarm
and Control Bytes
Time-
Base
Oscillator
Control/Status
Registers
˜ 8
˜ 64
˜ 64
16 1 MUX
:
Reset and
Interupt
Generator
Control/Calendar
Update
Internal
Battery
VCC
WE
AD0≠AD14
DQ0≠DQ7
OE
CE
RST
INT
Internal
Quartz
Crystal
Figure 1. Block Diagram
V
CC
CE
OE
WE
Mode
DQ
Power
< V
CC
(max.)
V
IH
X
X
Deselect
High Z
Standby
V
IL
X
V
IL
Write
D
IN
Active
> V
CC
(min.)
V
IL
V
IL
V
IH
Read
D
OUT
Active
V
IL
V
IH
V
IH
Read
High Z
Active
< V
PFD
(min.) > V
SO
X
X
X
Deselect
High Z
CMOS standby
V
SO
X
X
X
Deselect
High Z
Battery-backup mode
Truth Table
May 1997
bq4822Y
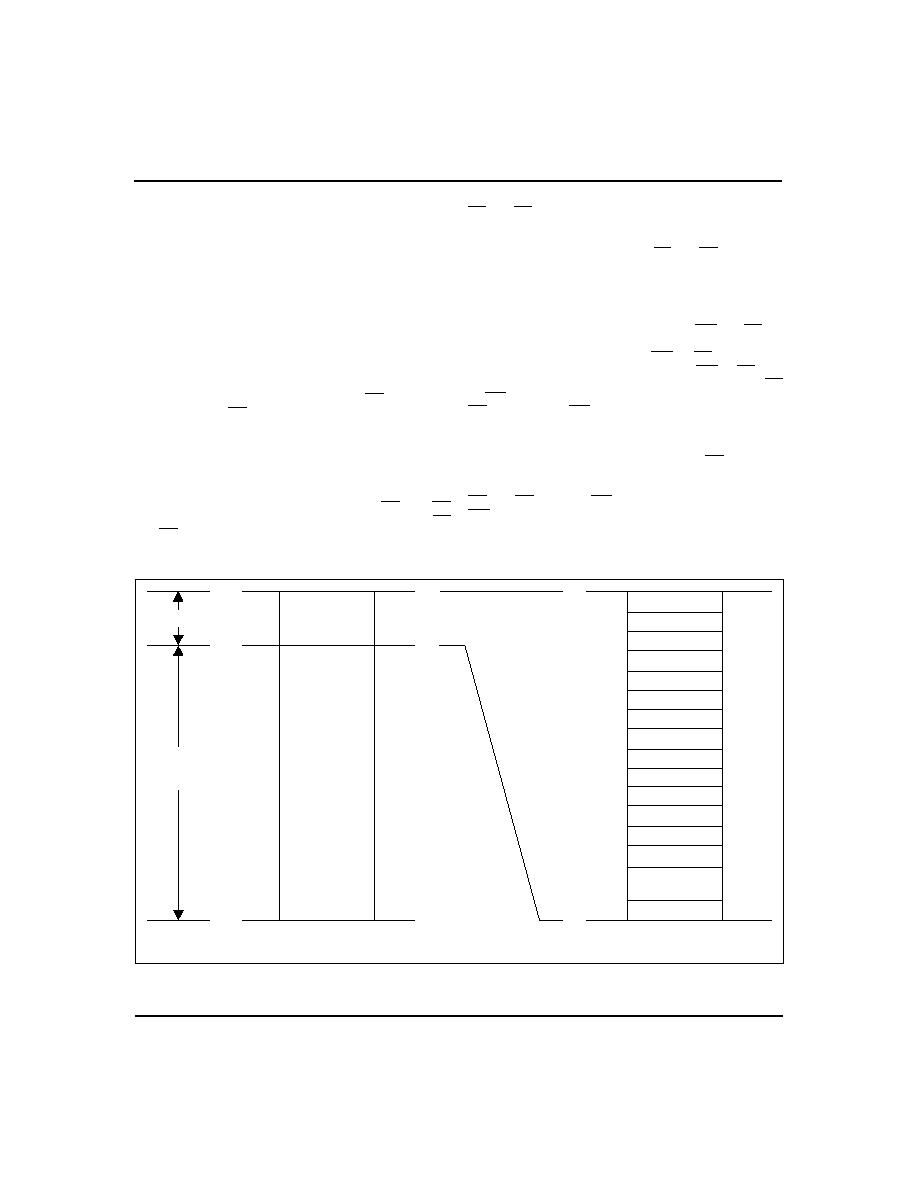
Address Map
The bq4822Y provides 16 bytes of clock and control
status registers and 8,176 bytes of storage RAM.
Figure 2 illustrates the address map for the bq4822Y.
Table 1 is a map of the bq4822Y registers, and Table 2
describes the register bits.
Memory Interface
Read Mode
The bq4822Y is in read mode whenever OE (output en-
able) is low and CE (chip enable) is low. The device ar-
chitecture allows ripple-through access of data from
eight of 65,536 locations in the static storage array.
Thus, the unique address specified by the 13 address in-
puts defines which one of the 8,192 bytes of data is to be
accessed. Valid data is available at the data I/O pins
within t
AA
(address access time) after the last address
input signal is stable, providing that the CE and OE
(output enable) access times are also satisfied. If the CE
and OE access times are not met, valid data is available
after the latter of chip enable access time (t
ACE
) or out-
put enable access time (t
OE
).
CE and OE control the state of the eight three--state data
I/O signals. If the outputs are activated before t
AA
, the data
lines are driven to an indeterminate state until t
AA
. If the
address inputs are changed while CE and OE remain low,
output data remains valid for t
OH
(output data hold time),
but goes indeterminate until the next address access.
Write Mode
The bq4822Y is in write mode whenever WE and CE are
active.
The start of a write is referenced from the
latter--occurring falling edge of WE or CE. A write is
terminated by the earlier rising edge of WE or CE. The
addresses must be held valid throughout the cycle. CE
or WE must return high for a minimum of t
WR2
from
CE or t
WR1
from WE prior to the initiation of another
read or write cycle.
Data-in must be valid t
DW
prior to the end of write and
remain valid for t
DH1
or t
DH2
afterward. OE should be
kept high during write cycles to avoid bus contention; al-
though, if the output bus has been activated by a low on
CE and OE, a low on WE disables the outputs t
WZ
after
WE falls.
3
FG482201.eps
Clock and
Control Status
Registers
1FFF
1FF0
1FEF
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
Year
Month
Date
Days
Hours
Minutes
Seconds
Control
Watchdog
Interrupts
Alarm Date
Alarm Hours
Alarm Minutes
Alarm Seconds
Tenths/
Hundredths
Flags
1FFF
1FFE
1FFD
1FFC
1FFB
1FFA
1FF9
1FF8
1FF7
1FF6
1FF5
1FF4
1FF3
1FF2
1FF1
1FF0
Storage
RAM
16 Bytes
8,176
Bytes
0000
Figure 2. Address Map
May 1997
bq4822Y
Data-Retention Mode
With valid V
CC
applied, the bq4822Y operates as a
conventional static RAM. Should the supply voltage
decay, the RAM automatically power-fail deselects,
write-protecting itself t
WPT
after V
CC
falls below V
PFD
.
All outputs become high impedance, and all inputs are
treated as "don't care."
If power-fail detection occurs during a valid access, the
memory cycle continues to completion. If the memory
cycle fails to terminate within time t
W P T
, write-
protection takes place. When V
CC
drops below V
SO
, the
control circuit switches power to the internal energy
source, which preserves data.
The internal coin cell maintains data in the bq4822Y af-
ter the initial application of V
CC
for an accumulated pe-
riod of at least 10 years when V
CC
is less than V
SO
. As
system power returns and Vcc rises above V
SO
, the bat-
tery is disconnected, and the power supply is switched to
external V
CC
. Write-protection continues for t
CER
after
V
CC
reaches V
PFD
to allow for processor stabilization.
After t
CER
, normal RAM operation can resume.
Clock Interface
Reading the Clock
The interface to the clock and control registers of the
bq4822Y is the same as that for the general-purpose
storage memory. Once every second, the user-accessible
clock/calendar locations are updated simultaneously
from the internal real time counters. To prevent read-
ing data in transition, updates to the bq4822Y clock reg-
isters should be halted. Updating is halted by setting
the read bit D6 of the control register to 1. As long as
the read bit is 1, updates to user-accessible clock loca-
tions are inhibited. Once the frozen clock information is
retrieved by reading the appropriate clock memory loca-
tions, the read bit should be reset to 0 in order to allow
updates to occur from the internal counters. Because the
internal counters are not halted by setting the read bit,
reading the clock locations has no effect on clock accu-
racy. Once the read bit is reset to 0, within one second
the internal registers update the user-accessible regis-
ters with the correct time. A halt command issued dur-
ing a clock update allows the update to occur before
freezing the data.
4
May 1997
Address
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
Range (h)
Register
1FFF
10 Years
Year
00≠99
Year
1FFE
X
X
X
10 Month
Month
01≠12
Month
1FFD
X
X
10 Date
Date
01≠31
Date
1FFC
X
FTE
X
X
X
Day
01≠07
Days
1FFB
X
X
10 Hours
Hours
00≠23
Hours
1FFA
X
10 Minutes
Minutes
00≠59
Minutes
1FF9
OSC
10 Seconds
Seconds
00≠59
Seconds
1FF8
W
R
S
Calibration
00≠31
Control
1FF7
WDS
BM4
BM3
BM2
BM1
BM0
WD1
WD0
Watchdog
1FF6
AIE
PWRIE
ABE
PIE
RS3
RS2
RS1
RS0
Interrupts
1FF5
ALM3
X
10-date alarm
Alarm date
01≠31
Alarm date
1FF4
ALM2
X
10-hour alarm
Alarm hours
00≠23
Alarm hours
1FF3
ALM1
Alarm 10 minutes
Alarm minutes
00≠59
Alarm minutes
1FF2
ALM0
Alarm 10 seconds
Alarm seconds
00≠59
Alarm seconds
1FF1
0.1 seconds
0.01 seconds
00≠99
0.1/0.01 seconds
1FF0
WDF
AF
PWRF
BLF
PF
X
X
X
Flags
Notes:
X = Unused bits; can be written and read.
Clock/Calendar data in 24-hour BCD format.
BLF = 1 for low battery.
OSC = 1 stops the clock oscillator.
Interrupt enables are cleared on power-up.
Table 1. bq4822Y Clock and Control Register Map
bq4822Y
Setting the Clock
Bit D7 of the control register is the write bit. Like the
read bit, the write bit when set to a 1 halts updates to
the clock/calendar memory locations. Once frozen, the
locations can be written with the desired information in
24-hour BCD format. Resetting the write bit to 0 causes
the written values to be transferred to the internal clock
counters and allows updates to the user-accessible regis-
ters to resume within one second.
Stopping and Starting the Clock Oscillator
The OSC bit in the seconds register turns the clock on or
off. If the bq4822Y is to spend a significant period of
time in storage, the clock oscillator can be turned off to
preserve battery capacity. OSC set to 1 stops the clock
oscillator. When OSC is reset to 0, the clock oscillator is
turned on and clock updates to user-accessible memory
locations occur within one second.
The OSC bit is set to 1 when shipped from the Bench-
marq factory.
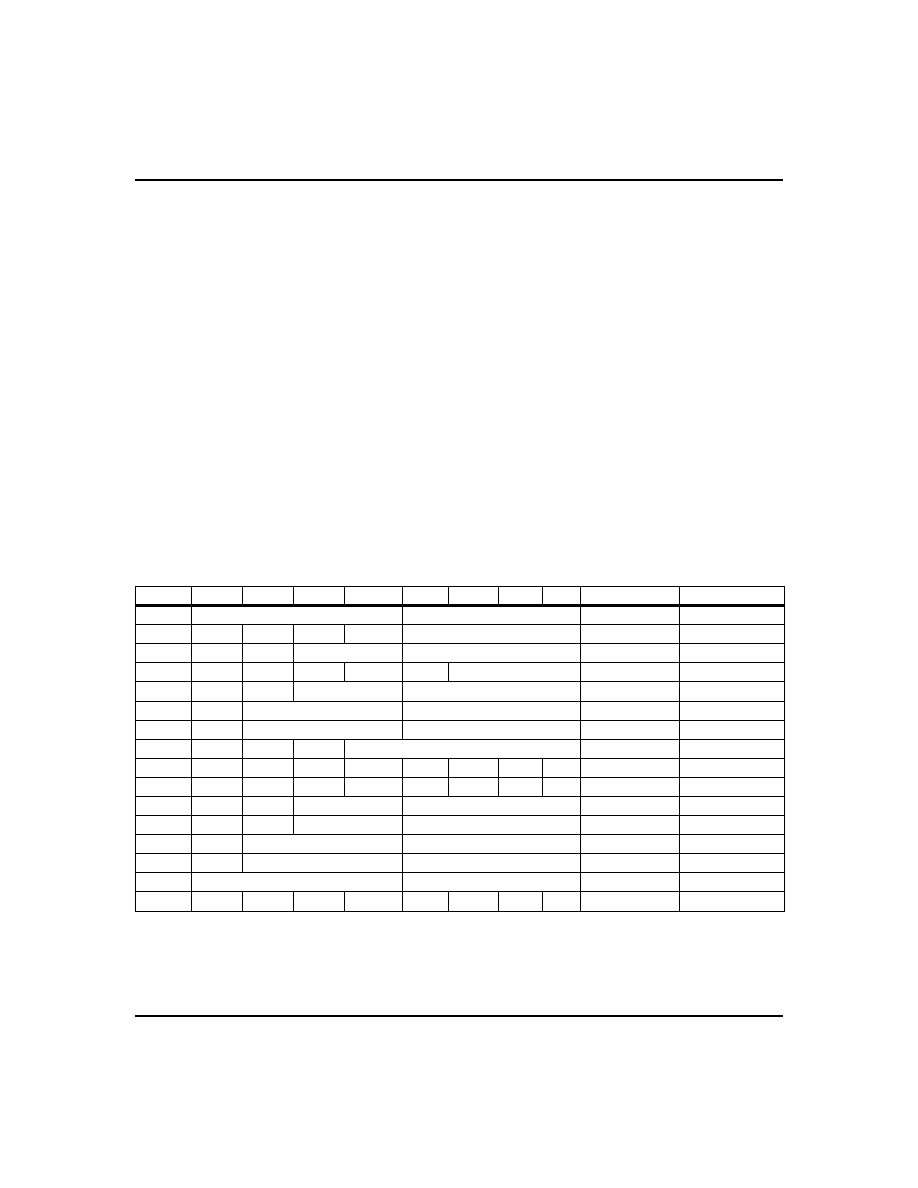
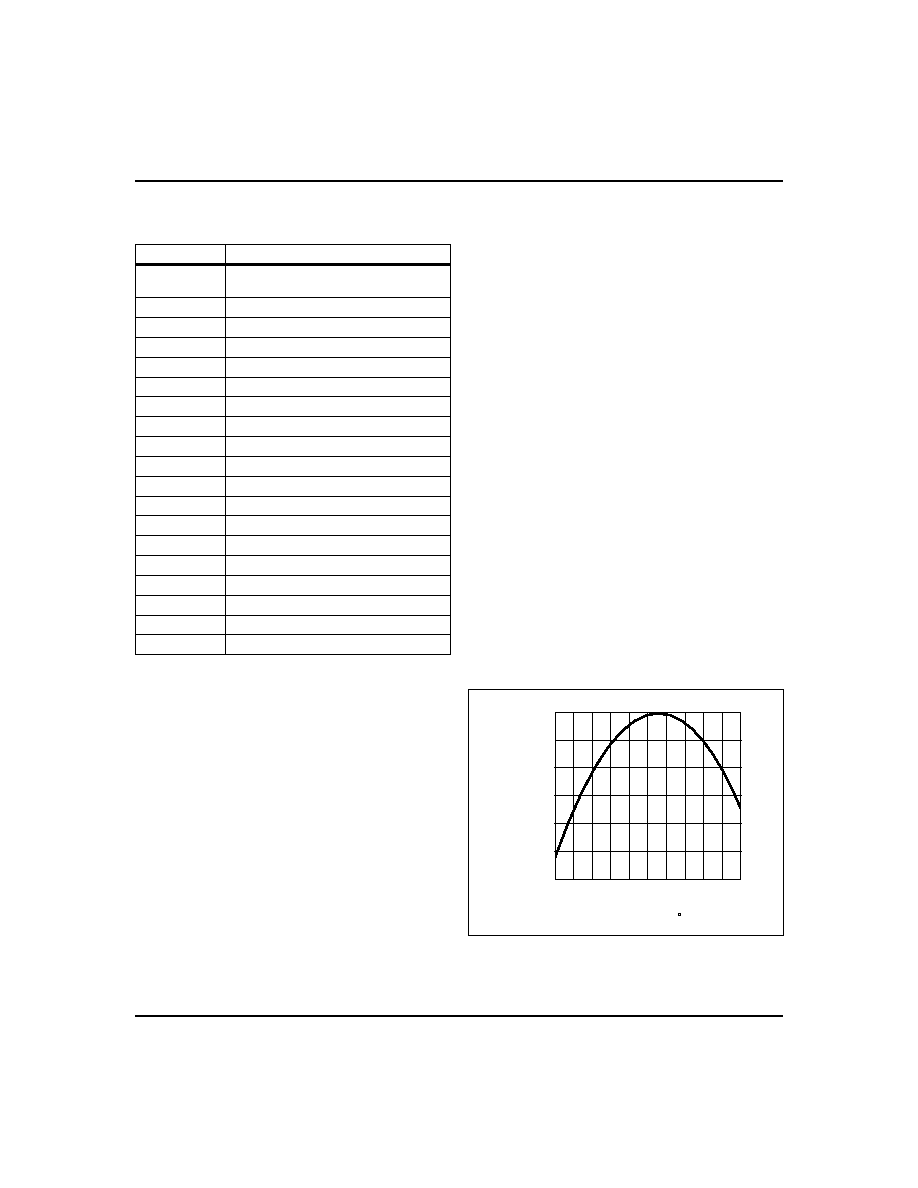
Calibrating the Clock
The bq4822Y real-time clock is driven by a quartz con-
trolled oscillator with a nominal frequency of 32,768 Hz.
The quartz crystal is contained within the bq4822Y
package along with the battery. The clock accuracy of
the bq4822Y module is tested to be within 20ppm or
about 1 minute per month at 25∞C. The oscillation rates
of crystals change with temperature as Figure 3 shows.
To compensate for the frequency shift, the bq4822Y of-
fers onboard software clock calibration. The user can
adjust the calibration based on the typical operating
temperature of individual applications.
The software calibration bits are located in the control
register. Bits D0≠D4 control the magnitude of correc-
tion, and bit D5 the direction (positive or negative) of
correction. Assuming that the oscillator is running at
exactly 32,786 Hz, each calibration step of D0≠D4 ad-
justs the clock rate by +4.068 ppm (+10.7 seconds per
month) or -2.034 ppm (-5.35 seconds per month) depend-
ing on the value of the sign bit D5. When the sign bit is
1, positive adjustment occurs; a 0 activates negative ad-
justment. The total range of clock calibration is +5.5 or
-2.75 minutes per month.
Two methods can be used to ascertain how much cali-
bration a given bq4822Y may require in a system. The
first involves simply setting the clock, letting it run for a
month, and then comparing the time to an accurate
known reference like WWV radio broadcasts. Based on
the variation to the standard, the end user can adjust
the clock to match the system's environment even after
the product is packaged in a non-serviceable enclosure.
The only requirement is a utility that allows the end
user to access the calibration bits in the control register.
5
May 1997
Bits
Description
ABE
Alarm interrupt enable in
battery-backup mode
AF
Alarm interrupt flag
AIE
Alarm interrupt enable
ALM0≠ALM3
Alarm repeat rate
BLF
Battery-low flag
BM0≠BM4
Watchdog multiplier
FTE
Frequency test mode enable
OSC
Oscillator stop
PF
Periodic interrupt flag
PIE
Periodic interrupt enable
PWRF
Power-fail interrupt flag
PWRIE
Power-fail interrupt enable
R
Read clock enable
RS0≠RS3
Periodic interrupt rate
S
Calibration sign
W
Write clock enable
WD0≠WD1
Watchdog resolution
WDF
Watchdog flag
WDS
Watchdog steering
Table 2. Clock and Control Register Bits
-120
-100
-80
-60
-40
-20
0
-30 -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70
Frequency Error
GR482201
Temperature ( C)
Figure 3. Frequency Error
bq4822Y




